This feature is in BETA version. For more information, contact your Customer Success Representative.
SendGrid is a cloud-based SMTP provider that allows users to send emails without maintaining email servers. This integration enables TD users to collect response events and performance metrics for campaigns created on SendGrid. It also allows for the collection of other marketing data, such as contacts, single sends, and messages.
- Knowledge of Treasure Data
- Knowledge of SendGrid
API key from SendGrid. See API Key.
If your security policy requires IP whitelisting, you must add Treasure Data's IP addresses to your allowlist to ensure a successful connection.
Please find the complete list of static IP addresses, organized by region, at the following document
Follow the steps to create a new authentication to SendGrid.
Open Catalog from Integrations Hub.
Search for SendGrid in the Catalog.
Create Authentication. Enter the API Key and save your authentication.
Follow the steps to import contacts from SendGrid.
- Open TD Console.
- Navigate to Integrations Hub > Authentications.
- Locate your new authentication and select New Source.
Define the following configuration parameters to set up the contacts import job.
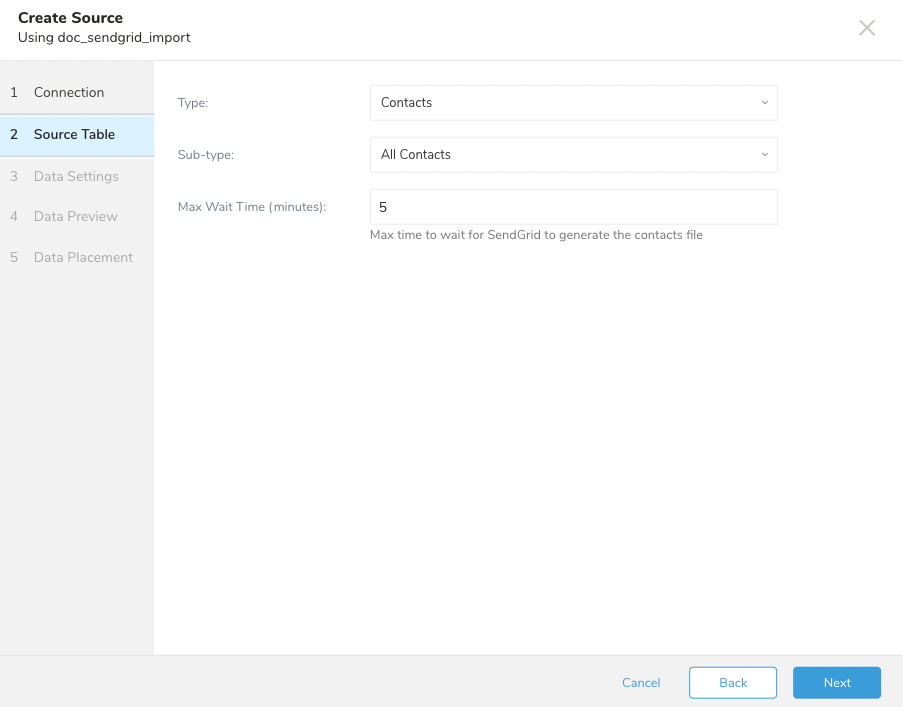
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Type of data to import. Select Contacts. |
| Sub-type | Sub-type of data to import. Users can select: - All Contacts to import all contacts. - Lists to only get contacts in Lists. - Segments to get contacts in Segments. |
| List Name | Only for Lists. Input the names of the lists to filter. |
| Segment Name | Only for Segments. Input the name of the segments to filter. |
| Max Wait Time | The maximum waiting time for SendGrid to generate the data file is in minutes. |
Select Next.
The integration displays fields in the standard contact schema defined by SendGrid.
Select Next.
SendGrid handles the process of preparing and generating contact files. To avoid a time-out, the integration only shows dummy data.
Data preview is optional, and you can safely click Next to go to the next page of the dialog if you would like.
- Display a preview of your data before running the import by selecting Generate Preview.
The data shown in the data preview is approximated from your source. It is not the actual data that is imported.
Verify that the data looks approximately like you expect it to.
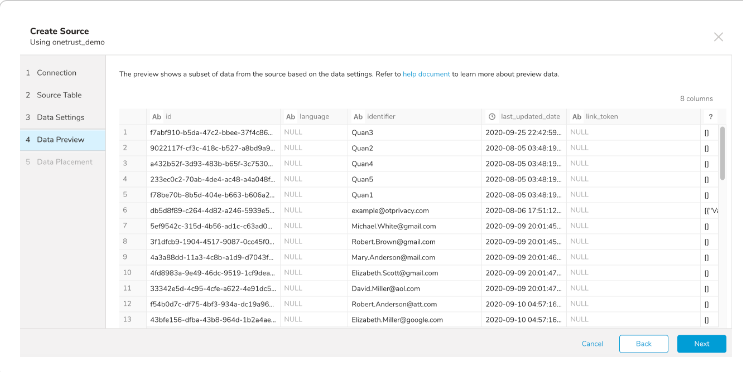
Select Next.
For data placement, select the target database and table where you want your data placed and indicate how often the import should run.
Select Next. Under Storage, you will create a new or select an existing database and create a new or select an existing table for where you want to place the imported data.
Select a Database > Select an existing or Create New Database.
Optionally, type a database name.
Select a Table> Select an existing or Create New Table.
Optionally, type a table name.
Choose the method for importing the data.
- Append (default)-Data import results are appended to the table. If the table does not exist, it will be created.
- Always Replace-Replaces the entire content of an existing table with the result output of the query. If the table does not exist, a new table is created.
- Replace on New Data-Only replace the entire content of an existing table with the result output when there is new data.
Select the Timestamp-based Partition Key column. If you want to set a different partition key seed than the default key, you can specify the long or timestamp column as the partitioning time. As a default time column, it uses upload_time with the add_time filter.
Select the Timezone for your data storage.
Under Schedule, you can choose when and how often you want to run this query.
- Select Off.
- Select Scheduling Timezone.
- Select Create & Run Now.
- Select On.
- Select the Schedule. The UI provides these four options: @hourly, @daily and @monthly or custom cron.
- You can also select Delay Transfer and add a delay of execution time.
- Select Scheduling Timezone.
- Select Create & Run Now.
After your transfer has run, you can see the results of your transfer in Data Workbench > Databases.
Follow sample configuration to retrieve statistics from SendGrid
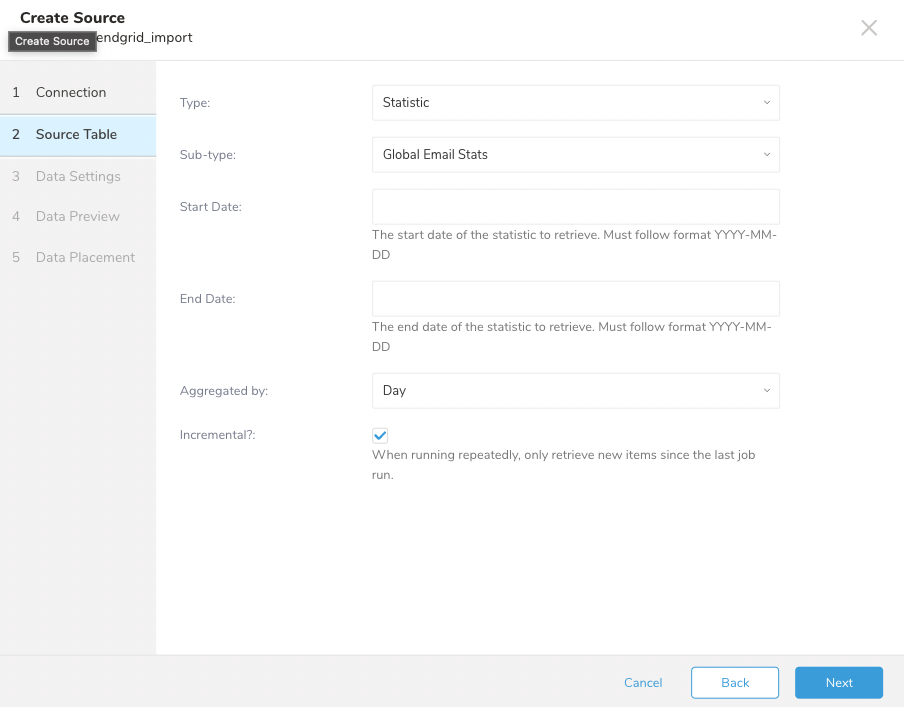
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Type of data to import. Select Statistic. |
| Sub-type | Sub-type of data to import. Users can select: Global Email Statsto import statistics from all emails sent out. SingleSend Statsto import statistics by single sends. Automation Stats to import statistics by automation. |
| Start Date - End Date | Only available for Global Email Stats. Filter by date. The Start Date is required. |
| Aggregated by | Only available for Global Email Stats. Define how the data is aggregated (Day, Week, Month, None). |
| Incremental | Only available for Global Email Stats. For repetitive runs, only search for data in the next time frame. |
Follow the sample configuration to get suppression events from SendGrid. The integration supports:
- Bounces
- Unsubscribes
- Blocks
- Spam Reports
- Invalid
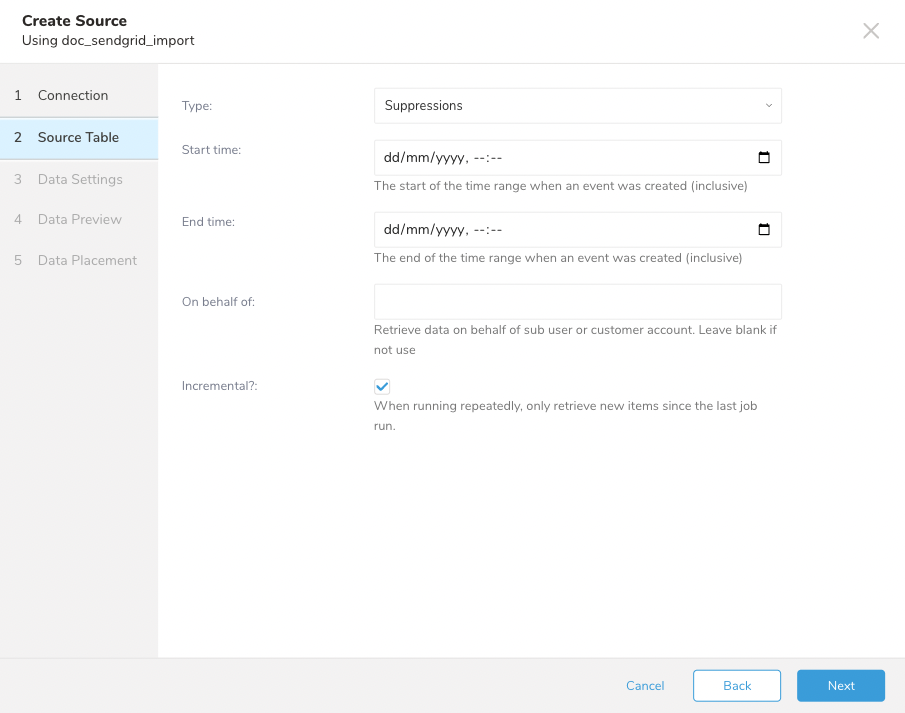
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Type of data to import. Select Suppressions. |
| Start Time - End Time | Define the search period. The Start Time is required when incremental is on. |
| On behalf of | (Optional) Use to retrieve data from a sub-user or customer account. |
| Incremental | For repetitive runs, only search for data in the next time frame. |
As the data definition from SendGrid differs from the suppression type, the following is the data schema when ingested into TD.
type;created;email;reason;status;ipblock;1714970265;testemail4@email.com;blockreason;blockstatus;nullinvalid;1714970265;testemail5@email.com;dummyreason;null;nullbounce;1714970265;testemail@email.com;550 Inconsistent;550;nullspam_report;1714970265;testemail2@email.com;null;null;192.168.1.1unsubscribe;1714970265;testemail3@email.com;null;null;nullFollow the steps to import Sing Sends data from SendGrid.
Follow the steps to import Message Data from SendGrid.
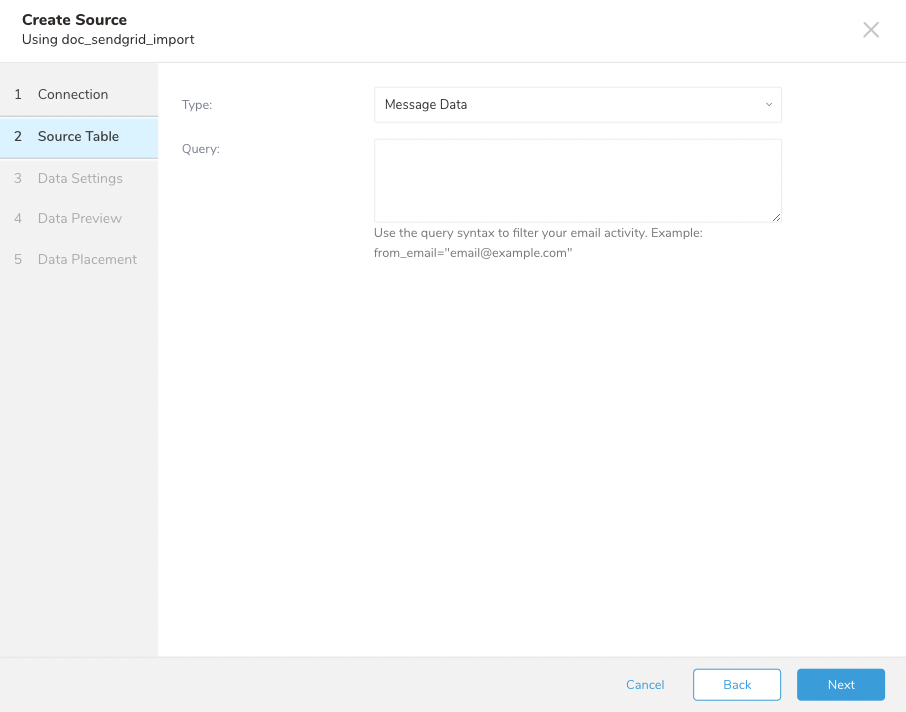
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Type of data to import. Select Message Data. |
| Query | Filter by query. See query syntax |
You can import data from SendGrid using td_load>: operator of workflow. If you have already created a SOURCE, you can run it; if you don't want to create one, you can import it using a yml file.
- Identify your source.
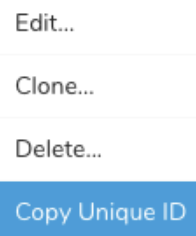
- To obtain a unique ID, open the Source list and filter by SendGrid.
- Open the menu and select Copy Unique ID.
- Define a workflow task using the td_load > operator.
+load:
td_load>: unique_id_of_your_source
database: ${td.dest_db}
table: ${td.dest_table}- Run a workflow.
- Identify your yml file. If you need to create the yml file, review Amazon S3 Import Integration Using CLI for reference.
- Define a workflow task using the td_load > operator.
+load:
td_load>: config/daily_load.yml
database: ${td.dest_db}
table: ${td.dest_table}- Run a workflow.
| Name | Description | Value | Default Value | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| type | Integration type | sendgrid | sendgrid | Yes |
| api_key | API key for the connection | N/A | N/A | Yes |
| data_type | The data type for fetching | statistic suppressions contacts message_data single_sends | statistic | Yes |
| sub_type_statistic | Subtype for statistic | global_email_stats single_send_stats automation_stats | global_email_stats | No |
| sub_type_contacts | Subtype for contacts | all_contacts lists segments | all_contacts | No |
| start_date | Start date for all_contacts | String | Required only when incremental_statistics is true | |
| end_date | End date for all_contacts | String | No | |
| aggregated_by | Aggregated by for all_contacts | day week month year | day | No |
| incremental_statistics | Incremental mode for all_contacts | true false | true | No |
| start_time | Start time for data_type suppressions | String | No | |
| end_time | End time for data_type suppressions | String | No | |
| incremental_suppressions | Incremental mode for suppressions | true false | true | No |
| on_behalf_of | Use to retrieve data from sub user or customer account. | String | No | |
| sub_type_contacts | Subtype for contacts | all_contacts lists segments | all_contacts | No |
| list_name | Name of lists of contacts | List of strings separated by comma | Required if sub_type_contacts is lists | |
| segment_name | Name of segments for contacts | List of strings separated by comma | Required if sub_type_contacts is segments | |
| max_wait_time | Max waiting time for contact to export in minutes | Integer | 5 | No |
| query | Query for message_data | String | No | |
| maximum_retries | Maximum retry times | Integer | 5 | No |
| initial_retry_interval_millis | Initial retry waiting time in milliseconds | Integer | 500 | No |
| maximum_retry_interval_millis | Maximum retry waiting time in milliseconds | Integer | 30000 | No |
| columns | Columns definition | Json | Yes |
Visit Treasure Boxes for a sample workflow code.
Before setting up the integration, install the most current TD Toolbelt.
in:
type: sendgrid
api_key: XXXXXXXXXX
data_type: contacts
sub_type_statistic: global_emal_stats
sub_type_contacts: list
start_time: '2023-01-19-T00:51:29.937Z'
end_time: '2023-01-19-T00:51:29.937Z'
start_date: '2023-01-01'
end_date: '2023-01-01'
aggregated_by: day
query: to_email="dumy@gmail.com"
list_name: 'abc,def'
segment_name: 'abc,def'
incremental_statistic: true
incremental_suppressions: true
max_wait_time: 5
on_behalf_of: xxx
initial_retry_interval_millis: 500
maximum_retries: 5
maximum_retry_interval_millis: 30000
out:
mode: append| Name | Description | Value | Default Value | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| type | Integration type | sendgrid | sendgrid | Yes |
| api_key | API key for connection | N/A | N/A | Yes |
| data_type | Data type for fetching | statistic suppressions contacts message_data single_sends | statistic | Yes |
| sub_type_statistic | Subtype for statistic | global_email_stats single_send_stats automation_stats | global_email_stats | No |
| sub_type_contacts | Subtype for contacts | all_contacts lists segments | all_contacts | No |
| start_date | Start date for all_contacts | String | Required only when incremental_statistics is true | |
| end_date | End date for all_contacts | String | No | |
| aggregated_by | Aggregated by for all_contacts | day week month year | day | No |
| incremental_statistics | Incremental mode for all_contacts | true false | true | No |
| start_time | Start time for data_type suppressions | String | No | |
| end_time | End time for data_type suppressions | String | No | |
| incremental_suppressions | Incremental mode for suppressions | true false | true | No |
| on_behalf_of | Use to retrieve data from a sub-user or customer accounts. | String | No | |
| sub_type_contacts | Subtype for contacts | all_contacts lists segments | all_contacts | No |
| list_name | Name of lists of contacts | List of strings separated by comma | Required if sub_type_contacts is lists | |
| segment_name | Name of segments for contacts | List of strings separated by comma | Required if sub_type_contacts is segments | |
| max_wait_time | Max waiting time for contact to export in minutes | Integer | 5 | No |
| query | Query for message_data | String | No | |
| maximum_retries | Maximum retry times | Integer | 5 | No |
| initial_retry_interval_millis | Initial retry waiting time in milliseconds | Integer | 500 | No |
| maximum_retry_interval_millis | Maximum retry waiting time in milliseconds | Integer | 30000 | No |
The data integration imports all files that match the specified prefix.
- Example
path_prefix: path/to/sample_ –> path/to/sample_201501.csv.gz, path/to/sample_201502.csv.gz, …, path/to/sample_201505.csv.gz
Use connector:guess. This command automatically reads the source files and uses logic to guess the file format and its field/columns.
$ td connector:guess seed.yml -o load.ymlYou can open load.yml to review the definitions of file formats, encodings, column names, and types.
in:
type: sendgrid
api_key: XXXXXXXXXX
data_type: contacts
sub_type_statistic: global_emal_stats
sub_type_contacts: list
start_time: '2023-01-19-T00:51:29.937Z'
end_time: '2023-01-19-T00:51:29.937Z'
start_date: '2023-01-01'
end_date: '2023-01-01'
aggregated_by: day
query: to_email="dumy@gmail.com"
list_name: 'abc,def'
segment_name: 'abc,def'
incremental_statistic: true
incremental_suppressions: true
max_wait_time: 5
on_behalf_of: xxx
initial_retry_interval_millis: 500
maximum_retries: 5
maximum_retry_interval_millis: 30000
columns:
- {name: email, type: string}
- {name: first_name, type: string}
- {name: last_name, type: string}
- {name: created_at, type: timestamp, format: '%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S%z'}
- {name: date, type: timestamp, format: '%Y-%m-%d'}
out:
mode: appendTo preview the data, use the td connector:preview command.
$ td connector:preview load.ymlThe guess command requires more than three rows and two columns in the source data file because the command assesses the column definition using sample rows from the source data.
If the system detects your column name or column type unexpectedly, modify the load.yml file and preview again.
- Submit the load job.
It might take a couple of hours, depending on the data size. Be sure to specify the Treasure Data database and table where the data should be stored.
Treasure Data also recommends specifying --time-column option because Treasure Data’s storage is partitioned by time (see data partitioning).
If not provided this option, the data connector chooses the first long or timestamp column as the partitioning time. The type of the column specified by --time-column must be either long or timestamp type.
If your data doesn’t have a time column, you can add one using the add_time filter option. For more details, see the add_time filter plugin.
$ td connector:issue load.yml --database td_sample_db --table td_sample_table --time-column created_atThe connector:issue command assumes that you have already created a *database(td_sample_db)*and a table(td_sample_table). If the database or the table does not exist in TD, this command fails. Create the database and table manually or use --auto-create-table option with td connector:issue command to auto-create the database and table.
$ td connector:issue load.yml --database td_sample_db --table td_sample_table --time-column created_at --auto-create-tableThe data connector does not sort records on the server side. To use time-based partitioning effectively, sort records in files beforehand.
If you have a field called time, you don’t have to specify the --time-column option.
$ td connector:issue load.yml --database td_sample_db --table td_sample_tableYou can specify file import mode in the out section of the load.yml file. The out: section controls how data is imported into a Treasure Data table. For example, you may choose to append data or replace data in an existing table in Treasure Data.
| Mode | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Append | Records are appended to the target table. | in: ... out: mode: append |
| Always Replace | Replaces data in the target table. Any manual schema changes made to the target table remain intact. | in: ... out: mode: replace |
| Replace on new data | Replaces data in the target table only when there is new data to import. | in: ... out: mode: replace_on_new_data |
You can schedule periodic data integration execution for incremental file import. Treasure Data configures our scheduler carefully to ensure high availability.
For the scheduled import, you can import all files that match the specified prefix and one of these fields by condition:
- If use_modified_time is disabled, the last path is saved for the next execution. The integration only imports files after the last path in alphabetical order on the second and subsequent runs.
- Otherwise, the job is execution time is saved for the next execution. On the second and subsequent runs, the integration only imports files modified after that execution time in alphabetical order.
A new schedule can be created using the td connector:create command.
$ td connector:create daily_import "10 0 * * *" td_sample_db td_sample_table load.ymlTreasure Data also recommends that you specify the --time-column option, because Treasure Data’s storage is partitioned by time (see also data partitioning).
$ td connector:create daily_import "10 0 * * *" td_sample_db td_sample_table load.yml --time-column created_atThe cron parameter also accepts three special options: @hourly, @daily, and @monthly.
By default, the schedule is set up in the UTC timezone. You can set the schedule in a timezone using -t or --timezone option. --timezone option supports only extended timezone formats like 'Asia/Tokyo', 'America/Los_Angeles', etc. Timezone abbreviations like PST, CST are unsupported and might lead to unexpected schedules.
SendGrid Export Integration - SendGrid Output
SendGrid API - API Reference