In Audience Studio, marketers can manually create segments using attribute-based rules to determine which customers are in which segment. This is useful for the scenario when a marketer exactly knows how to split the parent segment into different groups for specific targeted campaigns.
In some cases, marketers may benefit from the automated creation of segments. This clustering notebook uses k-means clustering to group customers based on their attributes and form customer segments. The notebook makes multiple attempts at clustering between the minimum and maximum number of clusters and then finds the ideal number of clusters to maximize the mean Silhouette coefficient. Alternatively, you can provide a specific number of segments to override the automatic calculation.
While this solution notebook is primarily intended for customer segmentation, it performs general k-means clustering and can be applied to any kind of segmentation from customer segmentation to item segmentation.
This notebook automatically segments based on the input_table using k-means clustering. The cluster_id is to be assigned to each row in the input_table, and the augmented table can be exported to the Treasure Data table using the output_table option.
An optimal number of clusters is automatically derived by the system between min_clusters and max_clusters, and the default values can be overwritten. If the desired number of clusters is known in advance, you can explicitly set the number of clusters by the num_clusters option.
While any kind of table can be used for the input_table , it's generally recommended to exclude meaningless columns such as rowid and/or userid for better clustering by the ignore_columns option (this notebook automatically ignores columns having a single value).
This notebook performs basic EDA (Exploratory Data Analysis) and XAI (eXplainable AI) using feature GINI importance and Shapley values on the clustering labels using the RandomForest classifier.
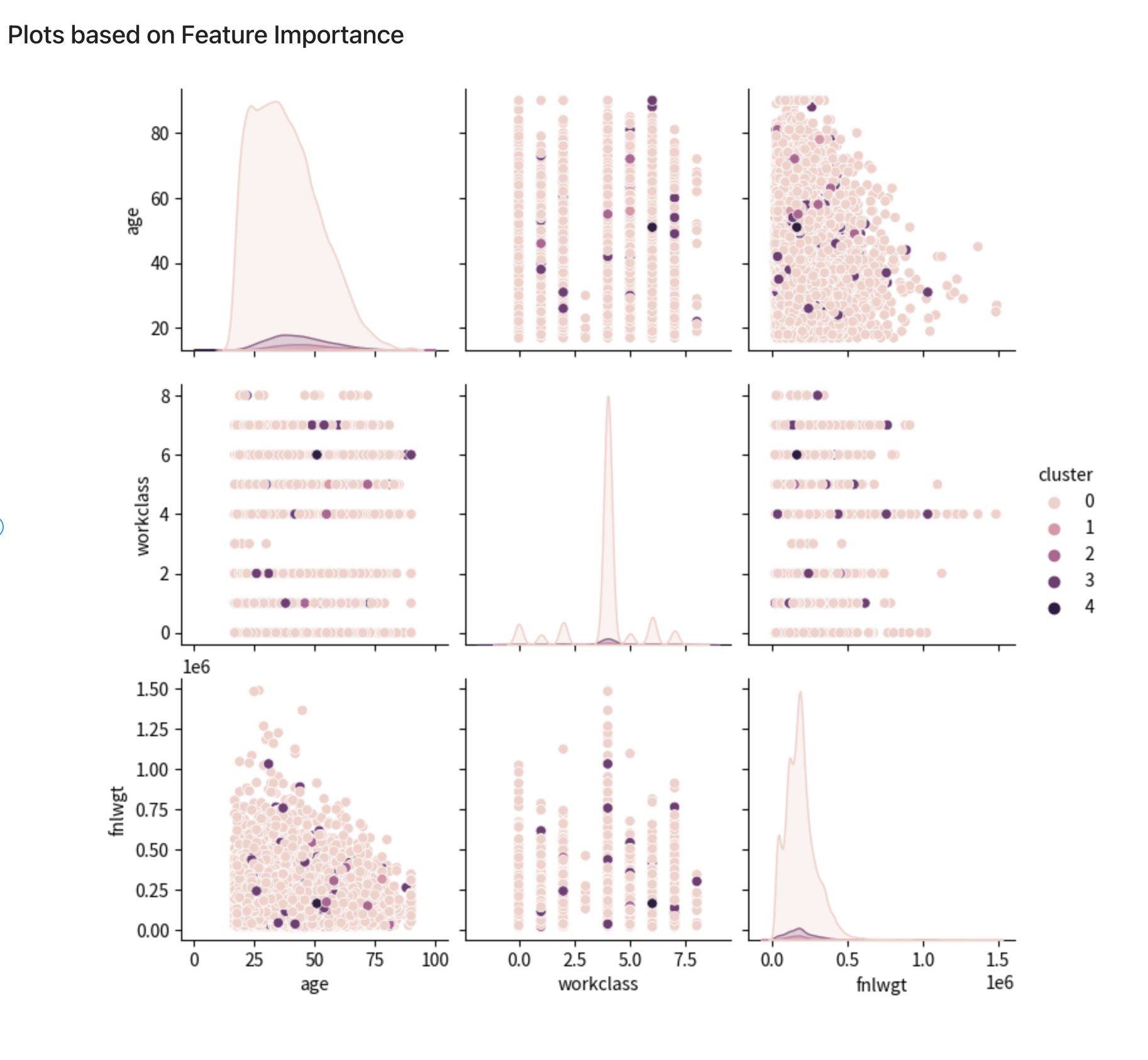
The following plot graph shows the top three features for each cluster.
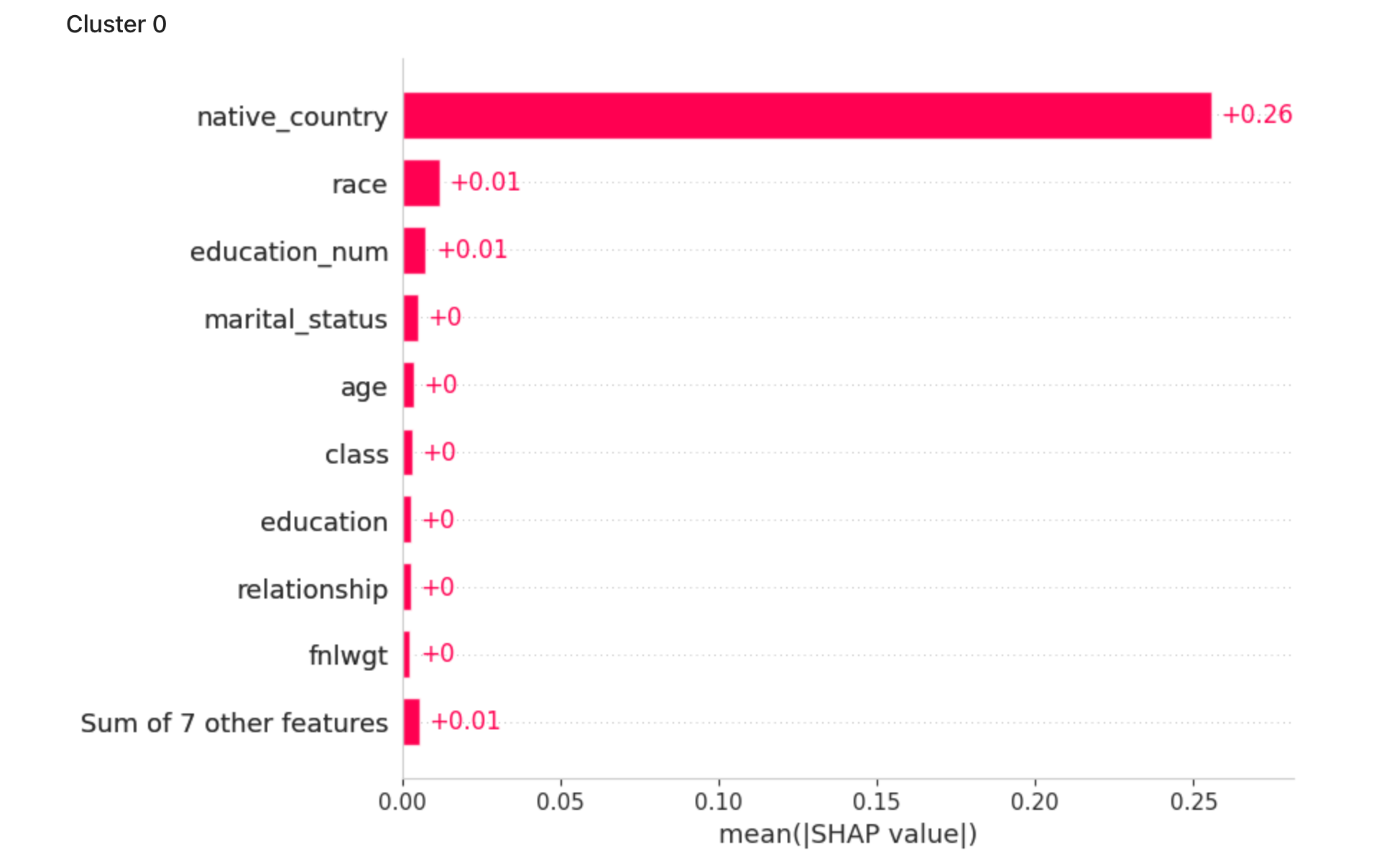
The following plot shows mean SHAP values for each cluster. This graph illustrates which attributes contribute the most to the cluster assignment.
Find a sample workflow here in Treasure Boxes.
+clustering_gluon:
ipynb>:
notebook: clustering
input_table: ml_datasets.gluon_train
output_table: ml_test.gluon_train_clustered_${session_id}| Parameter Name | Parameter on Console | Description | Required | Default Value | example value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| input_table | specify a TD table used for clustering as dbname.table_name | yes | string (dbname.table_name) | ||
| ml_dataset.gluon_train | |||||
| output_table | specify a TD table to export clustering results as dbname.table_name | no | string (dbname.table_name) | ||
| ml_output.cluster | |||||
| model_name | optionally specify a model name to save. No need to set in general. | no | string | ||
| gluon_model | |||||
| force_refit | force fitting even with an existing trained model. Note that setting force_refit to false is an experimental option. | no | boolean | true | true |
| output_mode | output mode for exporting output_table. Usually, there is no need to specify. | no | string (overwrite/replace or append) | overwrite | overwrite |
| min_clusters | specify a minimum number of clusters | no | integer | 2 | 5 |
| max_clusters | specify a maximum number of clusters | no | integer | 9 | 25 |
| num_clusters | specify a fixed number of clusters | no | integer | None | 3 |
| ignore_columns | columns to ignore for building a prediction model | no | string (comma separated) | time | time, rowid |
| dimension_reduction_threshold | threshold used for dimension reduction. | no | integer | 50 | 30 |
| export_feature_importance | export feature importance as a TD table if specified. | no | string ([dbname.]table_name) | None | ml_test.feature_importance |
| export_shap_values | export SHAP values for each cluster as a TD table | no | string ([dbname.]table_name) | None | ml_test.shap_values |
| hide_table_contents | suppress showing table contents | no | boolean | false | false |
| audience_name | Audience name to merge an attribute table | no | string | None | my_master_segment_name |
| foreign_key | foreign key column name of a master segment used for Audience integration. | no | string | None | td_canonical_id |
| rowid_column | rowid (primary key) column in the input_table. Required and used as an attribute table join key for Audience integration. | no | string | None | userid |
Audience integration
To add an attribute table to a CDP master segment, set all three options: audience_name , foreign_key , and rowid_column. The rowid_column is the join key in the output_table to be joined within the audience master table. Note CDP segments are automatically generated for each cluster when those options are set. Marketers can modify the cluster rules in the Audience Studio Rule Builder further. For example, using other attributes, you can combine the generated segments with additional rules.
Setting the parameter force_refit to false and using pre-computed models (k-means centroids) is an experimental feature, and it is not recommended to change from the default true option.