First, let's define an AI Agent. Its technical definition is "a software program that uses artificial intelligence to interact with its environment and perform tasks." However, it's more important to understand what it can do. AI agents collect data, learn from experiences, and make decisions to achieve goals.
This topic includes:
- Define Agent Details
- Create System Prompts
- Add Tools
- Specify the Tool
- Specify a Target
- Add Outputs
- Add Prompt variables
For best practices on writing effective system prompts, see Best Practices for Agent System Prompts.
- Open TD Console.
- Navigate to AI Agent Foundry.
- Select a project.
- Select Agents Tab and then select Create agent.
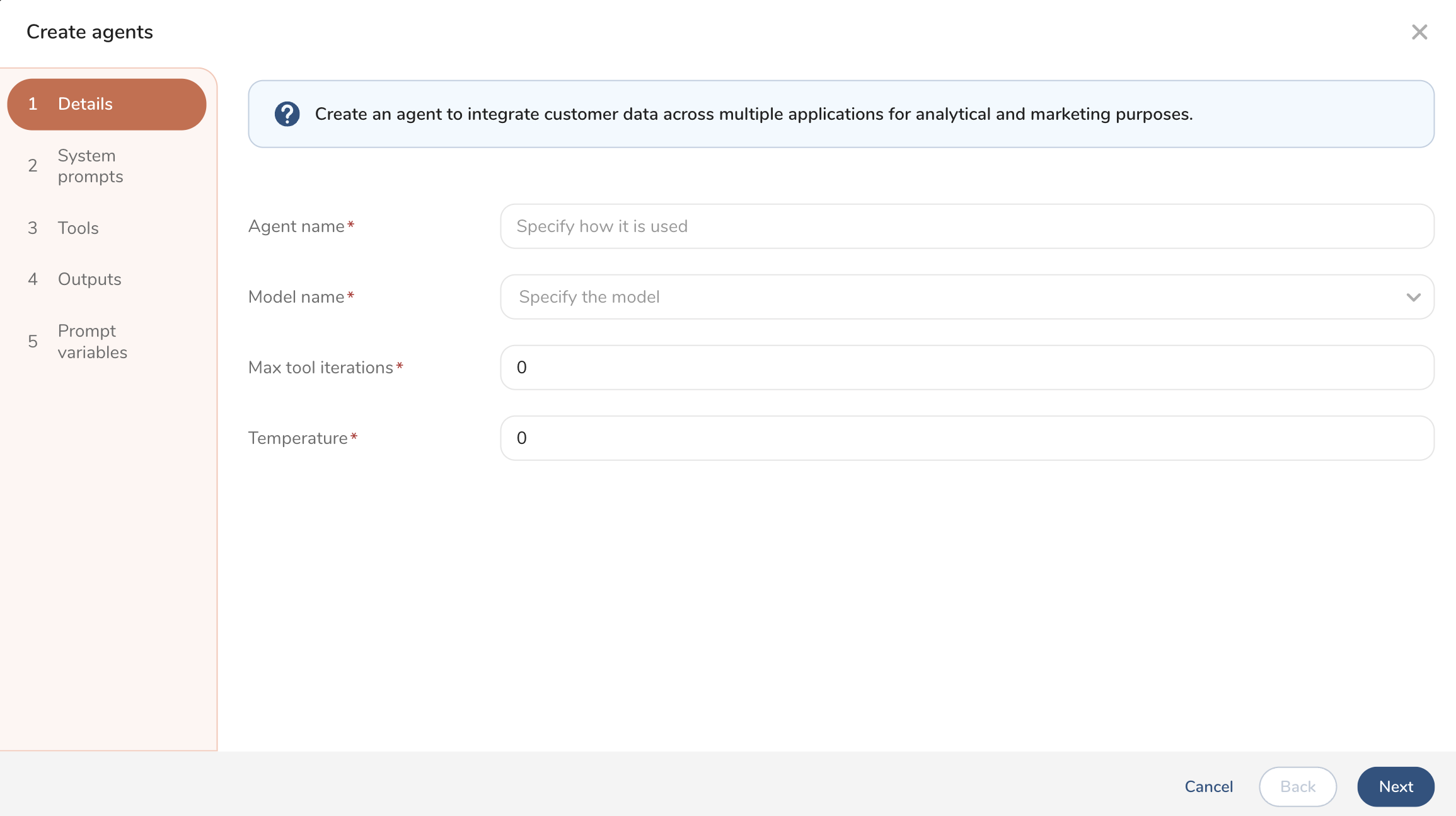
- Complete the form to define agent details.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Agent name | Create a name that helps users understand what the agent is used for. For example, you might want to create an agent to write an email message and name it Email Creator. |
| Model name | Select a model from the drop-down list. |
| Identifying a model for your agent provides additional information to the agent's user. For example, some LLM models perform better at high-reasoning tasks, while others are better at fast-response tasks. | |
| Max tool iterations | Tool iterations repeatedly refine and improve a tool by going through development cycles. You can choose the maximum number of tool iterations allowed per agent. The default is 0.Learn more about adding tools. |
| Temperature | The temperature parameter controls the randomness of an LLM's output. Lower values (e.g., 0.1) make responses more deterministic, while higher values (e.g., 0.8) increase creativity and variation. Specify a number between 0 to 1. |
- Select Next.
System Prompt is an instractuion for LLM model how it hehaves, writing in natural language. Instracting with structured format is more appropriate. Defining role, tasks, and the details will make agent more behave expectedly.
For detailed guidance on writing effective system prompts, including templates, best practices, and practical examples, see Best Practices for Agent System Prompts.
- Select System prompts.

- Add your prompt to the text box.
- Select Next.
A tool represents the agent's functions, such as searching and querying data in the knowledge base and utilizing other agents.
- Select Tools and then select + Add tool.
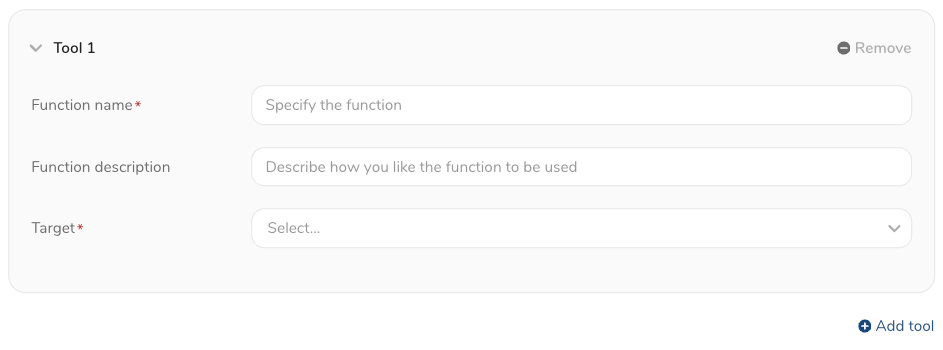
- Enter a function name and description:
- Function Name : Enter a unique name for the function—for example, list_columns.
- Function Description : (Optional) Enter a function description—for example, list the available tables and columns. LLM sees the description. LLM can choose approproate tool if the detailed description is defined.
Choose one of the following: Knowledge Base or Agent.
Select Knowledage Base as target if you want to access data.
- Select Knowledge Base as a Target.
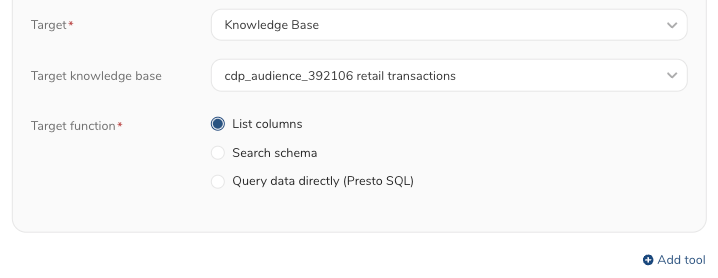
- From the drop-down list, select a knowledge base name.
- Select a function for the target:
- List columns : List the tables' schema in the tgarget knowledge base.
- Search schema : Search columns with a search term.
- Query data directly (Presto SQL) : Query data with an SQL statement.
The supported target function is only read if the Text type Knowledge Base is selected
The supported target function is only read if the Text type Knowledge Base is selected
You will see Project Runtime text Resource KB when Use runtime text resource is enabled. Find more details on Create a Self-Defined Project
The supported target functions are;
- List segment folders : Listing up folders that exist in the parent segment
- List by folder : Listing up instances that exist in a particular folder. This requires folder id
- List attributes : Retrieve the attributed defintions configured on the parent segment config
- List behaviors : Retrieve the behavior defintions configured on the parent segment config
- Get segment : Retrieve the metadata of a particular segment. This requires segment id
- Get journey : Retrieve the metadata of a particular journey. This requires journey id
- Get audience : Retrieve the metadata of the parent segment config. This requires journey id
- Get query : Retrieve the count SQL of a particular segment. This requires segment id
- Query data directly : Issue a SQL to the parent segment data
- Query segment analytics : Issue a SQL to analyze on a particular segment. This requires segment id
If the function require a particular instance id, agent must retrive its id. Usually agent can retrieve such id by calling "List segment folders" and/or "List by folder" function.
Parent Segment Knowledge Base is automatically created in the managed project that is created by and associated with a particular parent segment. Find more Create a Managed project
Choose Agent as Target to defer a specific task to the existing agent.
- Select Agent as a Target.
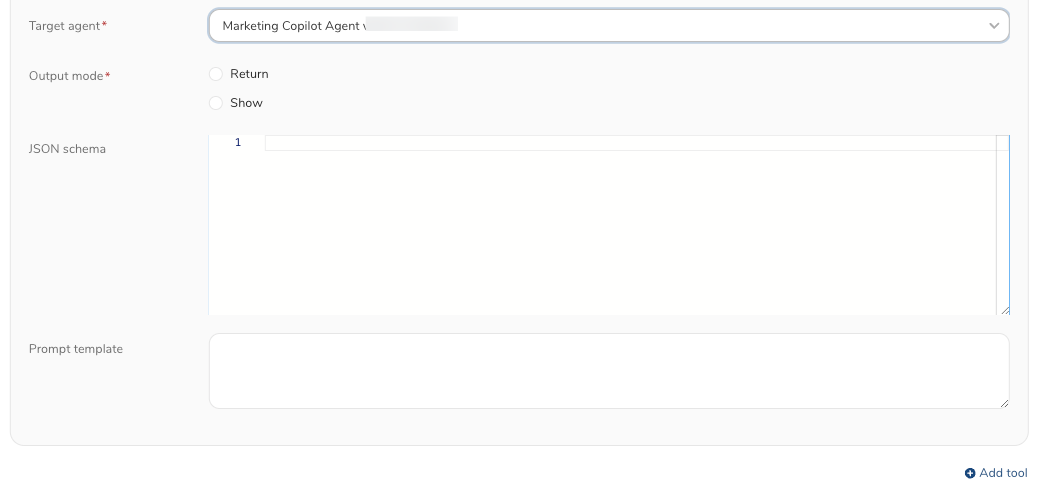
- Target agent: An agent to call. Select an agent from the list.
- Output mode:
- Return : The target agent passes an output to caller agent, caller agent output the generated content based on the output result it got
- Show : The target agent's output is rendered directly.
- JSON schema: Argument structure definition when the tool is called.
- Prompt template: A user prompt that is used when the target agent is called. This can utilize paramter with "{{parameter_name}}" format. parameter_name must be defined in the JSON schema
Use the Image generator tool to generate an Image.
- Select Image generator as a Target
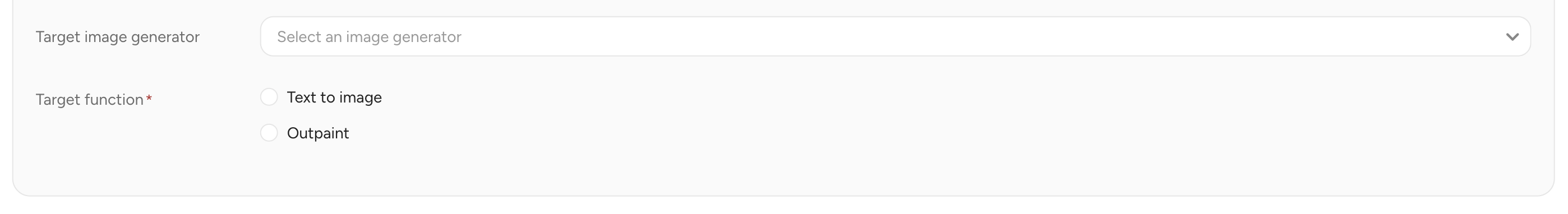
- Target image Generator : An image generator to use. Select an image generator from existing image generater instances
- Target function :
- Text to Image : Create an image from text prompt, appropriate for 0 to1 case
- Outpaint : Edit the surroundings of the specified area
- Inpaint : Edit the inside or the specific area
- Image Variation : Create image variation(s) from the given image
- Remove Background : Remove the surroundings of the specified area
Use the Workflow Executor tool to execute a TD workflow. Workflow is executed by workflow_id. To execute proper workflow, you may have to search workflow by name, retrieve its id then execute it. Search workflow target function help agent to find a workflow.
Workflow can be executed with a certain parameter, you can define the schema of the parameter in the system prompt and let agent generate it when agent calls Execute workflow tool.
- Select Workflow Executor
- Target function :
- Execute workflow : execute workflow with workflow id
- Search workflow : Search a particular workflow to execute
Following is the example of using Workflow execution tool. The wf_test workflow will be called with the parameter when you execute this agent.
Output is used when the agent needs to generate content that meets the Json schema requirement. This is useful when the agent is called via tool from other agent. The caller agent can get the structured output from the callee agent via tool with "return" mode, if the callee agent define output function and call it.
Other typical use case is to draw a chat using Ploty.js library. Chat interface will draw the chart using Plotly.js library when the agent calls output function if it named :plotly:.
Note that agent calls output function using Function Name. Output name is a identifier for the system. :plotly: is a special output name that is recognized by the System.
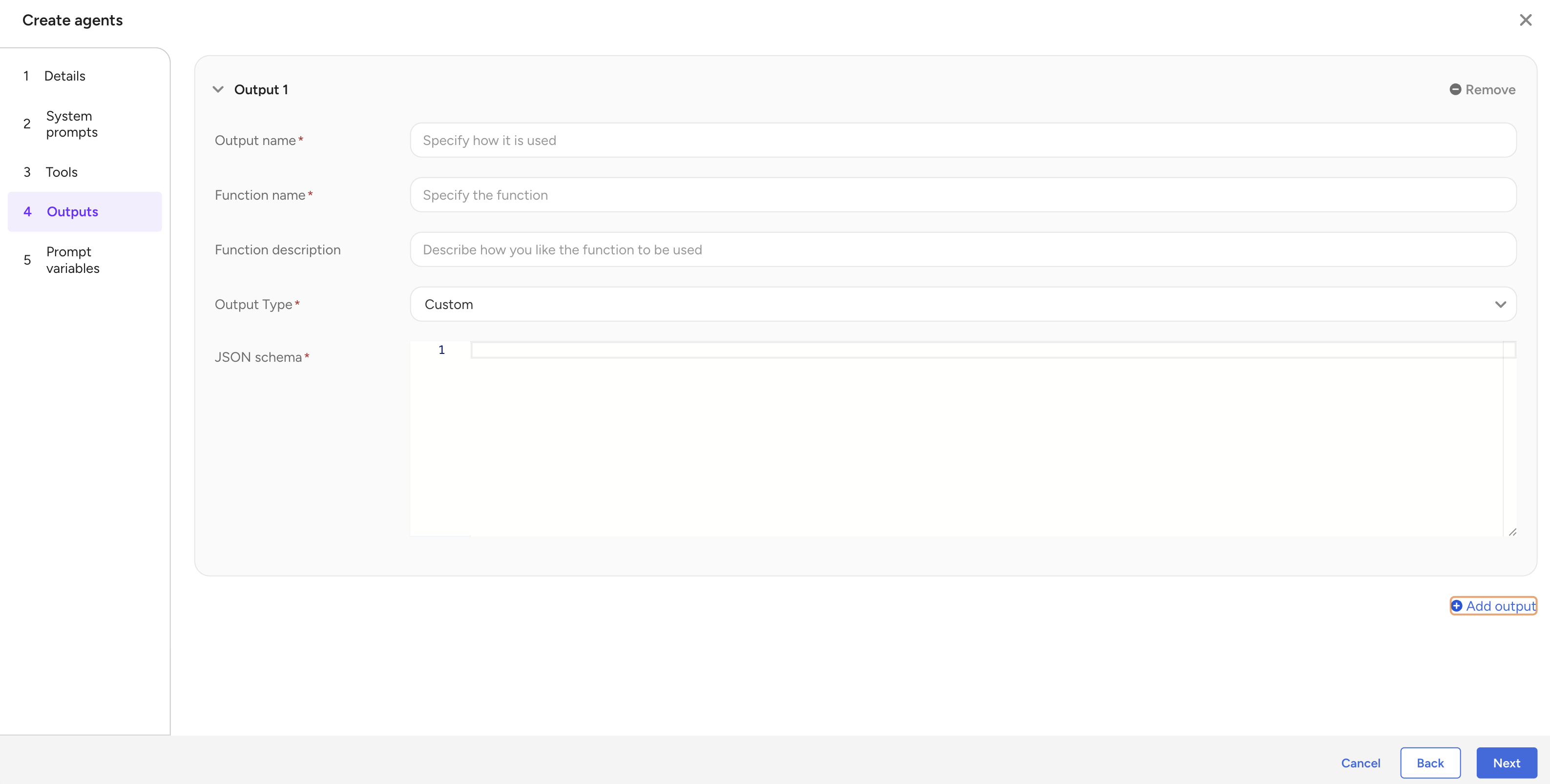
To create a custom Output
- Select Outputs and then select Add output.

- Complete the form.

| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Output Name | Enter a unique name. AI Agent Foundry uses this name for recognition. _:plotly:_ is a special name used for rendering a Plotly chart. |
| Function Name | Enter a name for the function. The agent refers to this name. |
| Function Description | (Optional) Enter a function description. |
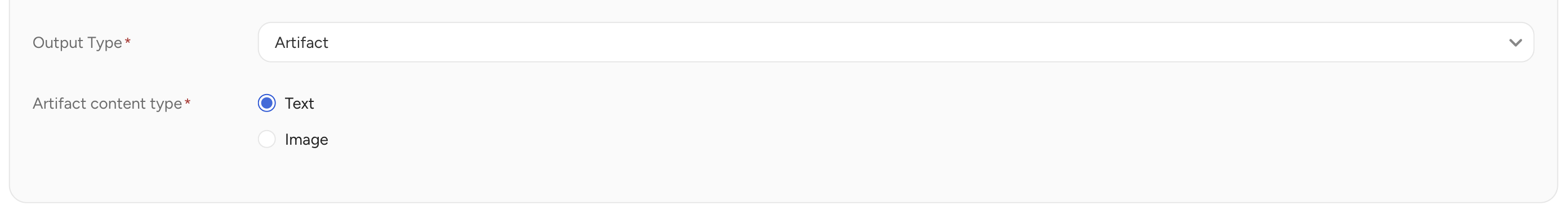
| Output Type | Choose Custom or Artifact.
|
| JSON Schema (for Custom) | Provide the JSON schema for the output data structure. The agent creates output following this definition. |
| Artifact | Persist the output as an individual object from chat conversations. The form-type interface supports only artifact outputs.
|

- Select + Add output to add another output or select Save to save the Agent.
Define :plotly: as below. When Agent calls newPlot function, plotly chart would be rendered as the output.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Output Name | :plotly: |
| Function Name | newPlot |
| Function Description | Render a chart using Plotly.js. |
| JSON Schema | Example JSON schema of the output data structure: |
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"data": {
"type": "array",
"description": "Plotly.js data JSON objects",
"items": {
"type": "object"
}
},
"layout": {
"type": "object",
"description": "Plotly.js layout JSON object"
}
},
"required": [
"data"
]
}Trasure Data supports prompt variables where is a concept of embedding a necessary data into the system prompt at the runtime.
Select Prompt variables and then select Add prompt vriable.
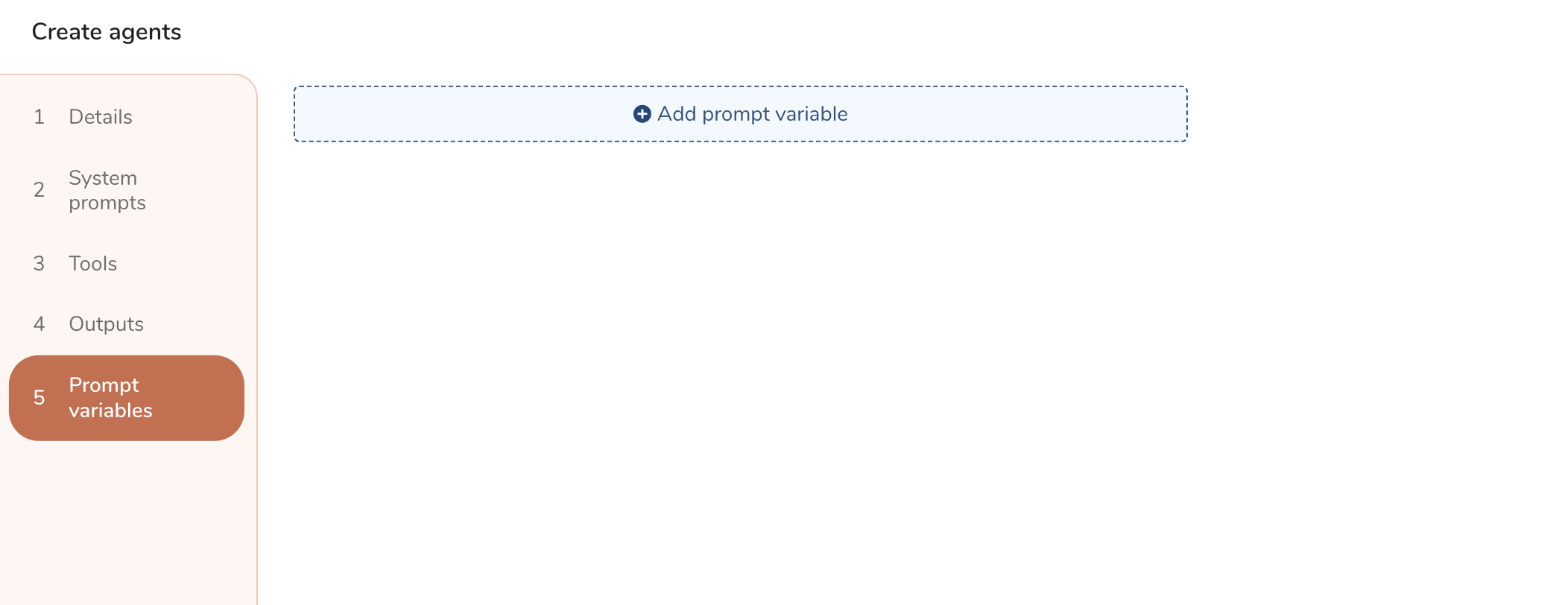
Complte the form.

| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Variable Name | Enter a unique name. This name is referred in the system prompt |
| Target knowledge base | Enter a knowledge base name to use |
| Target function | Only List columns is available |
| List of variables | List for expression to specify the target tables and columns |
The string is a comma-separated list of expressions (expression-1, expression-2, ...)
An expression is either of followings:
Table name: if the expression doesn’t include special characters like . or , it’s a table name. It’s identical to TABLE_NAME..
Pattern with “*”: if the expression includes special characters, it’s a matching rule, where * matches with any strings.
!expression: if the expression starts with !, it negates the following expression, where the expression is either of above.
examples
| Example | Result |
|---|---|
| customers, behavior_pageviews, behavior_clicks | All columns of customers, behavior_pageviews, and behavior_clicks tables.customers., behavior_pageviews., behavior_clicks.* |
| customers., !customers.time, behavior_., products.{id,name}, !.email | All columns except “time” of customers table, all columns of all behavior tables, and id and name columns of products table. But exclude all “email” columns from all tables. |
The next step is defining user prompts.