Yotpo Reviews is a review platform that helps business:
- Collect and analyze customer reviews from many sources such as Shopify, BigCommerce, WooCommerce, and other eCommerce websites by installing Yotpo widget.
- Collect and analyze reviews from SNS (Simple Notification Service) such as Facebook, Instagram, Google Shopping Reviews, and so on.
- Automatically send review request to customer based on specific conditions.
With this integration, you can ingest the collated customer reviews from Yotpo into Treasure Data™ platform.
- Basic Knowledge of Treasure Data™.
- Basic knowledge of the Yotpo platform
- Get the Yotpo App Key and App Secret Key, see https://support.yotpo.com/en/article/finding-your-yotpo-app-key-and-secret-key
If your security policy requires IP whitelisting, you must add Treasure Data's IP addresses to your allowlist to ensure a successful connection.
Please find the complete list of static IP addresses, organized by region, at the following document
Your first task is to create a new authentication with a set of credentials.
Select Integrations Hub.
Select Catalog.
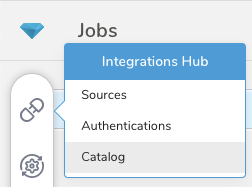
- Search for your Integration in the Catalog; hover your mouse over the icon and select Create Authentication.

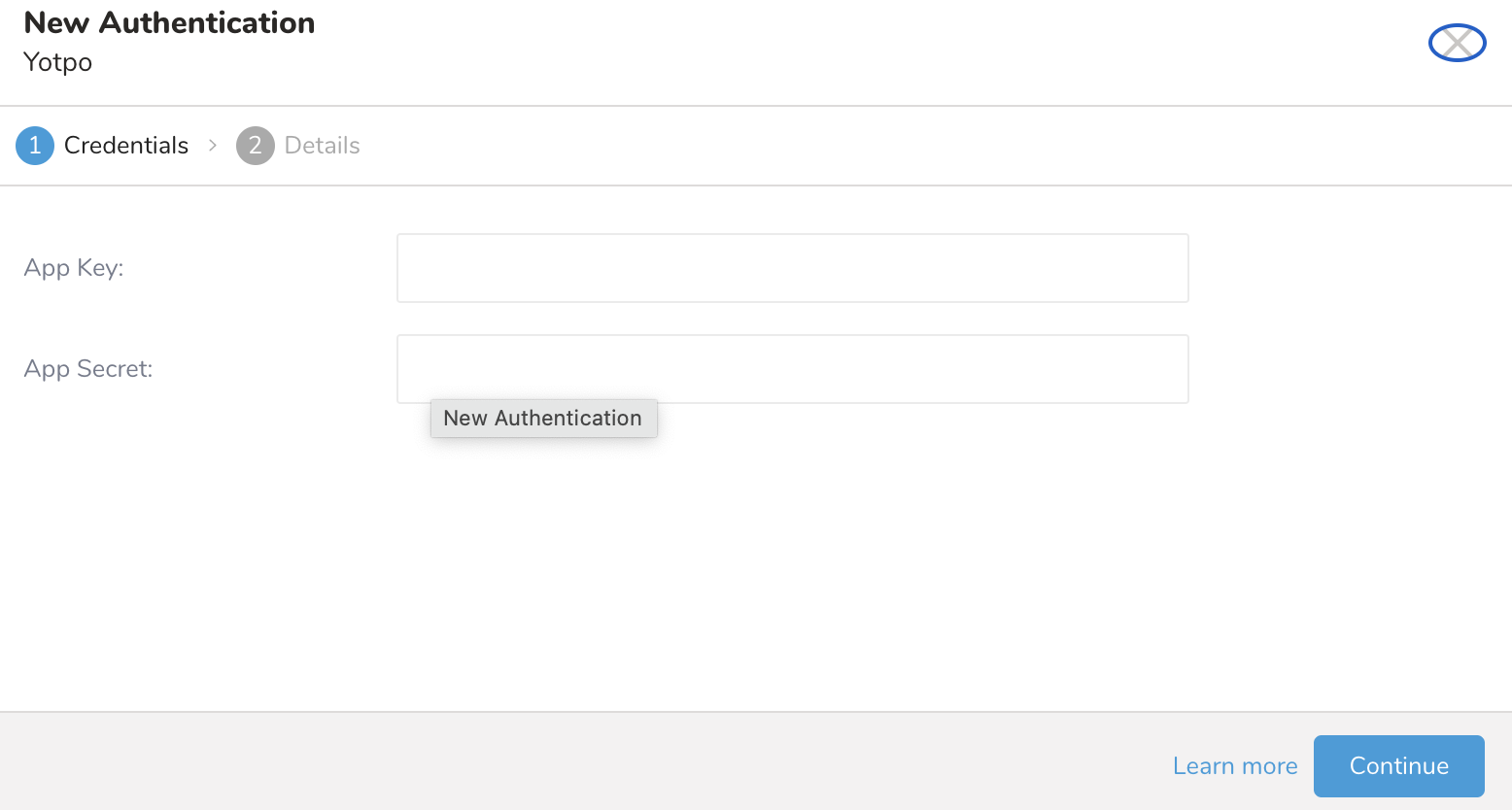
- Ensure that the Credentials tab is selected and then enter credential information for the integration.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| App Key | Your app key |
| App Secret | Your app secret key |
- Enter a name for your authentication, and select Done.
Open TD Console.
Navigate to Integrations Hub > Authentications.
Locate your new authentication and select New Source.
Complete the following table for the source.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Transfer Name | You can define the name of your transfer. |
| Authentication | The authentication name that is used for a transfer. |
Type a source name in the Data Transfer Name field.
Select Next.
The Create Source page displays with the Source Table tab selected.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
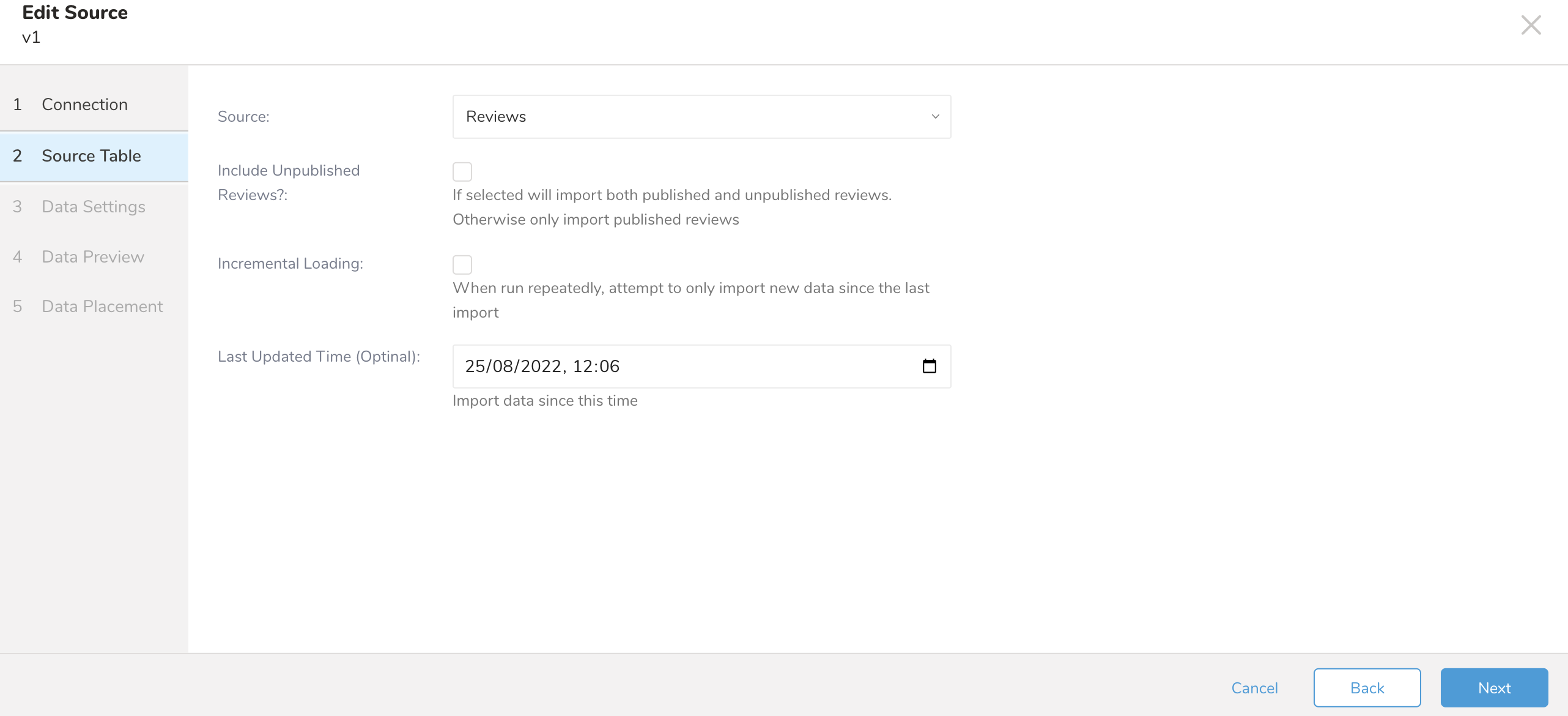
| Source | Data type to import: - Reviews |
| Include Unpublished Reviews | If selected, imports both published and unpublished reviews. Otherwise, only imports published reviews. |
| Incremental Loading | When run repeatedly, attempt to only import new data since the last import. |
| Last Updated Time | Import data since this time. For CLI configuration, we need a timestamp in RFC3339 UTC "Zulu" format, accurate to nanoseconds, for example: "2022-08-22T15:01:23Z". |
Click Next.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
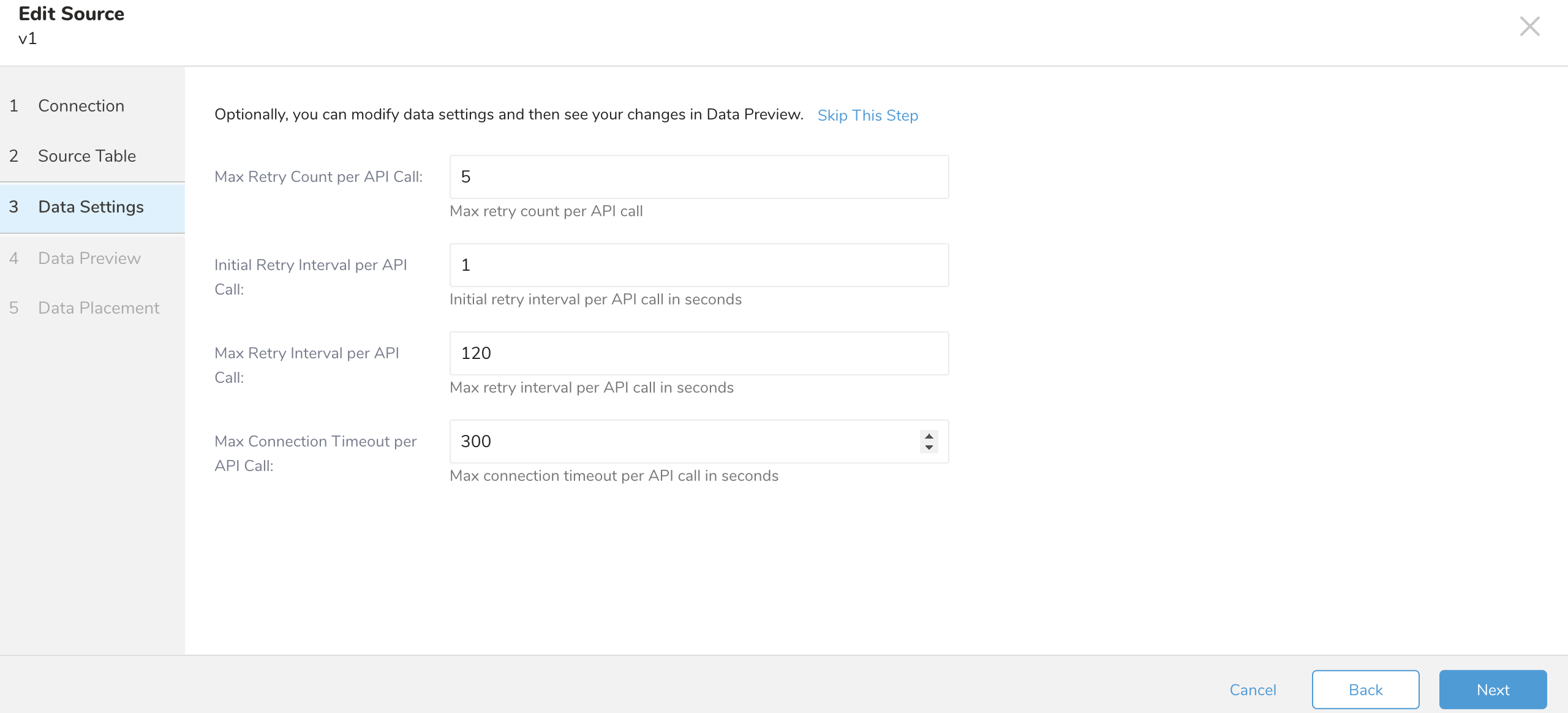
| Max Retry Count per API Call | Default 5, min 0 ,max 10 |
| Initial Retry Interval per API Call | In seconds, Default 1, min 1 ,max 300 |
| Max Retry Interval per API Call | In seconds, Default 120, min 1 ,max 300 |
| Max Connection Timeout per API Call | In seconds, Default 300, min 30 ,max 300 |
Click Next.
You can see a preview of your data before running the import by selecting Generate Preview. Data preview is optional and you can safely skip to the next page of the dialog if you choose to.
- Select Next. The Data Preview page opens.
- If you want to preview your data, select Generate Preview.
- Verify the data.
For data placement, select the target database and table where you want your data placed and indicate how often the import should run.
Select Next. Under Storage, you will create a new or select an existing database and create a new or select an existing table for where you want to place the imported data.
Select a Database > Select an existing or Create New Database.
Optionally, type a database name.
Select a Table> Select an existing or Create New Table.
Optionally, type a table name.
Choose the method for importing the data.
- Append (default)-Data import results are appended to the table. If the table does not exist, it will be created.
- Always Replace-Replaces the entire content of an existing table with the result output of the query. If the table does not exist, a new table is created.
- Replace on New Data-Only replace the entire content of an existing table with the result output when there is new data.
Select the Timestamp-based Partition Key column. If you want to set a different partition key seed than the default key, you can specify the long or timestamp column as the partitioning time. As a default time column, it uses upload_time with the add_time filter.
Select the Timezone for your data storage.
Under Schedule, you can choose when and how often you want to run this query.
- Select Off.
- Select Scheduling Timezone.
- Select Create & Run Now.
- Select On.
- Select the Schedule. The UI provides these four options: @hourly, @daily and @monthly or custom cron.
- You can also select Delay Transfer and add a delay of execution time.
- Select Scheduling Timezone.
- Select Create & Run Now.
After your transfer has run, you can see the results of your transfer in Data Workbench > Databases.
You can import data from Yotpo by using td_load>: operator of workflow. If you have already created a SOURCE, you can run it; if you don't want to create a SOURCE, you can import it using a yml file.
Identify your source.
To obtain a unique ID, open the Source list and then filter by product.
Open the menu and click "Copy Unique ID".
- Define a workflow task using td_load> operator.
+load:
td_load>: unique_id_of_your_source
database: ${td.dest_db}
table: ${td.dest_table}- Run a workflow.
Identify your yml file. If you need to create the yml file, review Amazon S3 Import Integration Using CLI for reference.
Define a workflow task using td_load> operator.
+load:
td_load>: config/daily_load.yml
database: ${td.dest_db}
table: ${td.dest_table}- Run a workflow
| Name | Description | Value | Default Value | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| type | Connector import type | string | yotpo | yes |
| data_source | Data type to import | string | reviews | |
| include_unpublished_reviews | If selected, will import both published and unpublished reviews. Otherwise, it imports only published reviews | boolean | false | |
| incremental | When run repeatedly, attempt to only import new data since the last import | boolean | false | |
| last_updated_time | Import data since this time. Example: "2022-08-22T15:01:23Z". | datetime | ||
| retry_limit | Max retry count per API call | integer | 5 | |
| initial_retry_wait | Initial retry interval per API call in seconds | integer | 1 | |
| max_retry_wait | Max retry interval per API call in seconds | integer | 120 | |
| connection_timeout | Max connection timeout per API call in seconds | integer | 300 |
Visit Treasure Boxes for sample workflow code.
Before setting up the connector, install the most current TD Toolbelt.
in:
type: yotpo
app_key: xxxx
app_secret: xxxxxx
data_source: reviews
incremental: true
last_updated_time: '2022-08-23T11:26:32Z'
include_unpublished_reviews: true
retry_limit: 1
initial_retry_wait: 2
max_retry_wait: 123
connection_timeout: 234To preview the data, use the td connector:preview command.
$ td connector:preview load.ymlSubmit the load job.
It might take a couple of hours depending on the size of the data. Be sure to specify the Treasure Data database and table where the data should be stored.
Treasure Data also recommends specifying --time-column option because Treasure Data’s storage is partitioned by time (see data partitioning). If this option is not provided, the data connector chooses the first long or timestamp column as the partitioning time. The type of the column specified by --time-column must be either of long and timestamp type.
If your data doesn’t have a time column, you can add a time column by using add_time filter option. For more details, see add_time filter plugin.
td connector:issue load.yml \
--database td_sample_db --table td_sample_table \
--time-column created_atThe connector:issue command assumes that you have already created a *database(td_sample_db)*and a table(td_sample_table). If the database or the table does not exist in TD, this command fails. Create the database and table manually or use --auto-create-table option with td connector:issue command to auto-create the database and table.
td connector:issue load.yml \
--database td_sample_db \
--table td_sample_table \
--time-column created_at \
--auto-create-tableThe data connector does not sort records on the server side. To use time-based partitioning effectively, sort records in files beforehand.
If you have a field called time, you don’t have to specify the --time-column option.
td connector:issue load.yml \
--database td_sample_db \
--table td_sample_tableYou can specify file import mode in the out section of the load.yml file. The out: section controls how data is imported into a Treasure Data table. For example, you may choose to append data or replace data in an existing table in Treasure Data.
| Mode | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Append | Records are appended to the target table. | in: ... out: mode: append |
| Always Replace | Replaces data in the target table. Any manual schema changes made to the target table remain intact. | in: ... out: mode: replace |
| Replace on new data | Replaces data in the target table only when there is new data to import. | in: ... out: mode: replace_on_new_data |
You can schedule periodic data connector execution for incremental file import. Treasure Data configures our scheduler carefully to ensure high availability.
For the scheduled import, you can import all files that match the specified prefix and one of these fields by condition:
- If use_modified_time is disabled, the last path is saved for the next execution. On the second and subsequent runs, the connector only imports files that come after the last path in alphabetical order.
- Otherwise, the time that the job is executed is saved for the next execution. On the second and subsequent runs, the connector only imports files that were modified after that execution time in alphabetical order.
A new schedule can be created using the td connector:create command.
td connector:create daily_import "10 0 * * *" \
td_sample_db td_sample_table load.ymlTreasure Data also recommends that you specify the --time-column option, because Treasure Data’s storage is partitioned by time (see also data partitioning).
$ td connector:create daily_import "10 0 * * *" \
td_sample_db td_sample_table load.yml \
--time-column created_atThe cron parameter also accepts three special options: @hourly, @daily, and @monthly.
By default, the schedule is set up in the UTC timezone. You can set the schedule in a timezone using -t or --timezone option. --timezone option supports only extended timezone formats like 'Asia/Tokyo', 'America/Los_Angeles', etc. Timezone abbreviations like PST, CST are not supported and might lead to unexpected schedules.