The Yahoo! integration exports customer segments for advertising purposes.
- You can upload user id through Partnermatch API
- You can upload User and Audience Attribute to Yahoo!
Consumers expect a seamless online experience, whether they’re shopping, banking, reading the news, gaming, or watching videos, no matter where they are or what device they’re using. Yahoo! content delivery network (CDN) is trusted by some of the world's largest brands for online banking, e-commerce, and media distribution because it offers high quality, performance, reliability, and scale that improve the customer experience and increase loyalty.
Yahoo! helps you:
- Captivate audiences at scale.
- Serve the right ad at the right time.
- Unify Disney and ABC digital broadband messaging.
This topic contains:
- Match your customer base with the fan base of Yahoo! to deliver the best personalized experience.
- Synchronize the segments created on TD with Yahoo!, including custom attributes to provide better categorization and build performant campaigns.
- Upload or remove audiences to or from Yahoo! segment for Yahoo! DMP ads targeting.
- Basic Knowledge of Treasure Data.
- Basic knowledge of Yahoo! DataX API
- MDM ID provided by Yahoo! support
The DataX API performs in an asynchronous manner. All operations from the connector take effect ranging from 30 minutes to more than a day. If you need to download the job result, contact TD support.
Yahoo! and Provider limitations:
- 100 API calls per hour
- 5GB zipped file upload limitation
TD does not support watching the status of the upload segments. You can watch the status by reviewing the TD log.
Contact Yahoo! Support for your MDM ID.
In Treasure Data, you must create and configure the data connection prior to running your query. As part of the data connection, you provide authentication to access the integration.
- Open TD Console.
- Navigate to Integrations Hub > Catalog.
- Search for and select Yahoo!.

- Select Create Authentication.
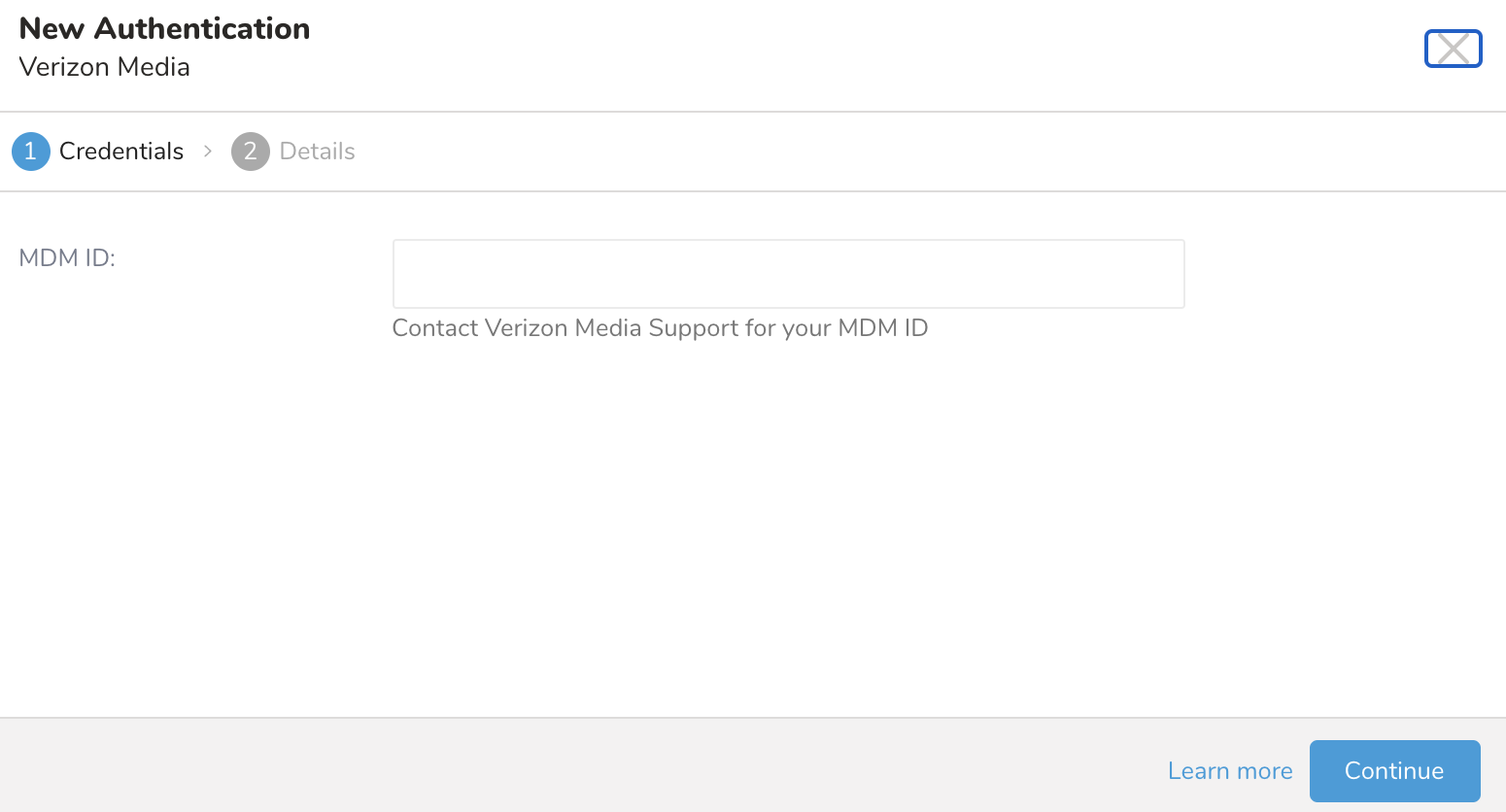
- Type your MDM ID. For example, OH224.
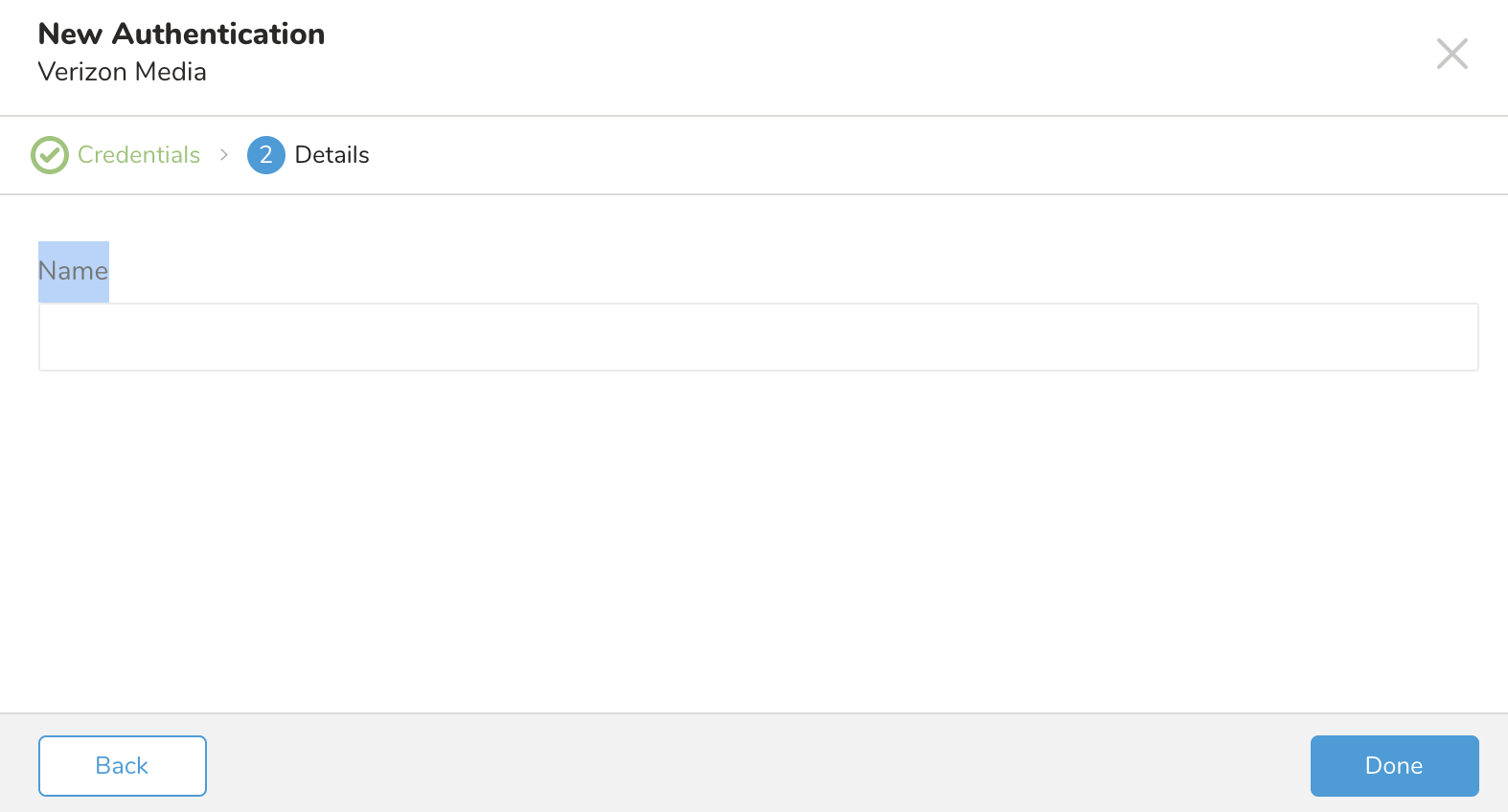
- Type a name for your connection.
- Select Done.
| Parameter | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mode | Values are:
| Choose the upload mode - Partner Match: upload user id and email through Partner Match API - Audience: upload audience records - Taxonomy: create or modify the taxonomy hierarchy - Opt-out: remove audiences from the entire taxonomy hierarchy |
| Taxonomy Mode | Values are:
| Choose mode for Taxonomy upload:
|
| URN Type | Values differ depending on the mode you have selected. Example types are:
| Values differ depending on the mode you have selected. Uniform Resource Name (URN) identifies a resource or unit of information independent of its location. URNs are globally unique, persistent, and accessible over the network. Yahoo! syntax for an urn: "urn":{string}, "seg":[{"id":{string},"ts":{number},"exp":{number}}] For example, {"urn" : "99ff2333f3fe7659c38b3674bc927f32", "seg" : [{"id":"OH224"}]} |
| Target Segment ID | if Audience mode is selected. | ID of the target Segment. This combines with optional fields in the query result: seg_exp, seg_ts |
| GDPR | if Audience mode is selected. | General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) |
| Dry Run | if Taxonomy is selected | Enable to verify if the synchronization is expected without updating the current Taxonomy. |
| Column name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| String | Yes | This column accepts plain text emails or SHA256 Hashed emails. Plain text email will be hashed before sending to the Yahoo! server | |
| PXID | String | Yes | |
| Phone | String | No | this column accepts plain text or SHA256 Hashed phone. Plain textphone will be hashed before sending to Yahoo! server. |
Query example
select 'abc@tese.com' as email, 'abc' as pxid
UNION ALL SELECT 'abc123@tese.com' as email, 'a12bc' as pxid
UNION ALL SELECT 'abcadcc@tese.com' as email, 'ab1231c' as pxid
select 'abc@tese.com' as email, 'abc' as pxid, '+112345678' as phone
UNION ALL SELECT 'abc123@tese.com' as email, 'a12bc' as pxid, '+134567182' as phone
UNION ALL SELECT 'abcadcc@tese.com' as email, 'ab1231c' as pxid, '+1456104632' as phone| Column name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| urn | String | Yes | Values match your selected URN Type. Plain text email will be hashed before sending |
| <attribute_id> | Any type | Any attribute id defined in your Taxonomy. E.g. Age, Country, G123... You can have multiple attribute ID selected in your query | |
| seg_ts | Long | Timestamp associated with the urn | |
| seg_exp | Long | Expiration time associated with the urn | |
| att_ts | Long | Timestamp associated with the attribute | |
| att_exp | Long | Expiration time associated with the attribute |
Query example
SELECT urn, CT01, GEN, seg_ts, seg_exp, att_ts, att_exp
FROM audiences| Column name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| parent_id | String | Yes | Null value indicates Root taxonomy |
| id | String | Yes | Required value and must be unique across the entire company. |
| name | String | Yes | A human friendly equivalent of "id" |
| type | String | Yes | Current supported types are: SEGMENT, ATTRIBUTE |
| description | String | ||
| att_type | String | Attribute type. Current possible values are: ENUM, DATETIME, ZIPCODE, NUMBER, STRING. For more detail, refer to this external reference: https://developer.yahooinc.com/datax/guide/taxonomy/taxonomy-rep/. | |
| att_values | String | Attribute values. Mandatory for ENUM and NUMBER types. Examples: - For enums: [ “Loyal”, “Occasional”, “Rare” ] - For numbers: [ “1 | |
| gdpr_mode | String |
| Column name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| urn | String | Yes | Values match your selected URN Type. Plain text email will be hashed before sending |
Taxonomy helps Yahoo import the hierarchical (or flat) organization of its partners’ data and its associated metadata. Uploading taxonomy is a prerequisite for uploading user/audience data.
- TD Root: All accounts will be created under single root name "Private" (default ID: TD0001). All client sub trees must be appended under this root.
- Each account (represent by MDM ID) will have only one tree (Account tree) with single root E.g Account A.
- The ID of each tree node is unique across all accounts.
- Each node type only accept SEGMENT or ATTRIBUTE
Example of an Treasure Data Taxonomy tree with client subtrees:
+ Private (TD0001)
├-- Account A
| ├── seg1 name(seg1)
| │ ├── seg1.1 name(seg1.1)
| │ └── seg1.2 name(seg1.2)
| └── root attribute name 100(root attribute 100)
| └── att1 name(att1)
├-- Account B
├--- Seg ABThe connector supports 4 modes for Taxonomy tree structure upload:
- Whole Structure
- Append Node
- Replace Node
- Delete Node
Whole Structure: This is default mode for Taxonomy. Upload whole tree structure and keep new nodes only. The old nodes from current account tree will be deleted and replaced with new nodes from new tree. Validation:
- The Account Root node have ID = null (in database parent_id = null), the ID column is required.
- Orphan nodes which have no parent are not allowed.
- Only leaf nodes can be deleted each run.
- If the account Node doesn’t exist, it will append to the TD Root or Private (TD0001).
Only one root (with parent_id = null) is allowed.Append Node
Append single node or a sub tree into an existing parentId node. If the company tree not created then new tree will be create with input root and it will be appended under TD Root.
Validation:
- If account tree doesn't exist then new account tree is created with one input root and it will be appended to Private (default ID: TD0001).
- If account tree doesn't exist then maximum 1 root node is allowed in query result.
- If account tree exists then root node is not allowed. in the query result.
- Parent Id of each node must be existed when company root is not null.
- Append node must not be in used if company tree not null.
E.g:
Current account tree
root segment name 200 (root segment 200)
├── SEG Child 6 (seg6)
├── SEG Child 2 (seg2)
├── SEG Child 5 (seg5)
│ ├── SEG Child 5.1 (seg5.1)
│ └── SEG Child 5.2 (seg5.2)
├── SEG Child 4(seg4)
│ ├── SEG Child 4.3 (seg4.3)
│ └── SEG Child 4.1 (seg4.1)
└── SEG Child 3 (seg3)
├── SEG Child 3.1 (seg3.1)
└── SEG Child 3.2 (seg3.2)Input data
SELECT parent_id, id, name, type
FROM
(
VALUES
('TD0008','seg8.1','SEG 8.1','SEGMENT')
) tbl (parent_id,id,name,type);The expected tree will be look like below:
root segment name 200 (root segment 200)
├── SEG Child 6 (seg6)
│ ├── SEG Child 6.1 (seg6.1)
│ └── SEG Child 6.2 (seg6.2)
├── SEG Child 2 (seg2)
├── SEG Child 5 (seg5)
│ ├── SEG Child 5.1 (seg5.1)
│ └── SEG Child 5.2 (seg5.2)
├── SEG Child 4 (seg4)
│ ├── SEG Child 4.3 (seg4.3)
│ └── SEG Child 4.1 (seg4.1)
├── SEG Child 3 (seg3)
│ ├── SEG Child 3.1 (seg3.1)
│ └── SEG Child 3.2 (seg3.2)
├── SEG 8 (seg8)
│ └── SEG Child 8.1 (seg8.1)
└── SEG 7 (seg7)Replace NodeReplace existing taxonomy node and its sub-tree with a new taxonomy data. Do not allow to replace Company roots or TD root. Only sub trees of company root are allowed to replace.
Validation:
- Account tree must exist to do this operation.
- Input subtree roots must not be empty.
- Replacing account root is not allowed.
- Replacing TD root (Private) is not allowed.
- Input tree root node must be under account tree.
E.g
We have an account tree as below
Sample TD Segment(TD0002)
├── Child 1(TD0003)
│ └── Child 1.1(TD0007)
│ └── Child 1.1.1(TD0008)
│ └── SEG 8.1(seg8.1)
└── Child 2(TD0004)
├── Child 2.1(TD005)
│ └── Child 2.1.1(TD005_1)
└── Child 2.2(TD0006)
└── Child 2.2.2(TD0006_1)We expect to build this hierarchy from the SQL data
SELECT parent_id, id, name, type
FROM
(
VALUES
('','TD0007','Child 1.1','SEGMENT'),
('TD0007','TD0008','Child 1.1.1','SEGMENT'),
('TD0007','TD0009','Child 1.1.2','SEGMENT'),
('TD0007','TD0010','Child 1.1.3','SEGMENT')
) tbl (parent_id,id,name,type);Then the expected tree will become like this
Sample TD Segment(TD0002)
├── Child 1(TD0003)
│ └── Child 1.1(TD0007)
│ ├── Child 1.1.2(TD0009)
│ ├── Child 1.1.1(TD0008)
│ └── Child 1.1.3(TD0010)
└── Child 2(TD0004)
├── Child 2.1(TD005)
│ └── Child 2.1.1(TD005_1)
└── Child 2.2(TD0006)
└── Child 2.2.2(TD0006_1)Replace NodeDelete existing taxonomy node along with its sub-tree.
Validation:
- Do not allow to delete any tree roots (Account Root or TD Root).
Node must not be null & exists in account tree.Company tree must exist to do this operation.
E.g:
We have an account tree as below
Sample TD Segment(TD0002)
├── Child 1(TD0003)
│ └── Child 1.1(TD0007)
│ └── Child 1.1.1(TD0008)
└── Child 2(TD0004)
├── Child 2.1(TD005)
│ └── Child 2.1.1(TD005_1)
└── Child 2.2(TD0006)
└── Child 2.2.2(TD0006_1)We expect to build this hierarchy from the SQL data
SELECT parent_id,id,name,type
FROM
(
VALUES
('','TD005_1','Child 2.1.1','SEGMENT')
)tbl (parent_id,id,name,type);Then the expected tree will become like this
Sample TD Segment(TD0002)
├── Child 1(TD0003)
│ └── Child 1.1(TD0007)
│ └── Child 1.1.1(TD0008)
└── Child 2(TD0004)
├── Child 2.1(TD005)
└── Child 2.2(TD0006)
└── Child 2.2.2(TD0006_1)You can use Scheduled Jobs with Result Export to periodically write the output result to a target destination that you specify.
Treasure Data's scheduler feature supports periodic query execution to achieve high availability.
When two specifications provide conflicting schedule specifications, the specification requesting to execute more often is followed while the other schedule specification is ignored.
For example, if the cron schedule is '0 0 1 * 1', then the 'day of month' specification and 'day of week' are discordant because the former specification requires it to run every first day of each month at midnight (00:00), while the latter specification requires it to run every Monday at midnight (00:00). The latter specification is followed.
Navigate to Data Workbench > Queries
Create a new query or select an existing query.
Next to Schedule, select None.

In the drop-down, select one of the following schedule options:
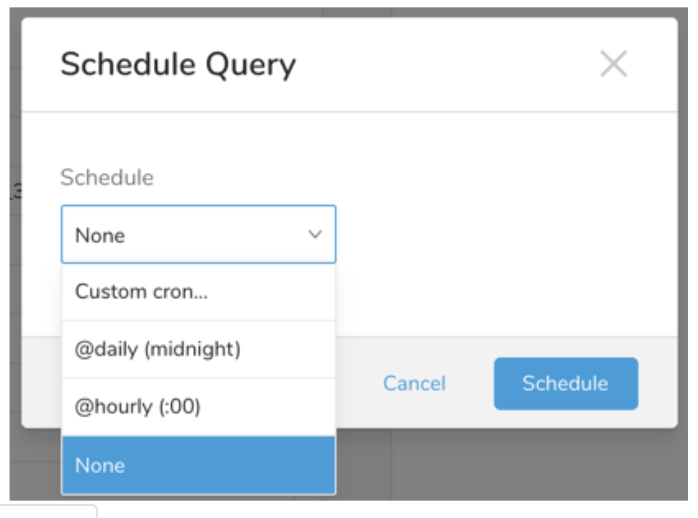
Drop-down Value Description Custom cron... Review Custom cron... details. @daily (midnight) Run once a day at midnight (00:00 am) in the specified time zone. @hourly (:00) Run every hour at 00 minutes. None No schedule.
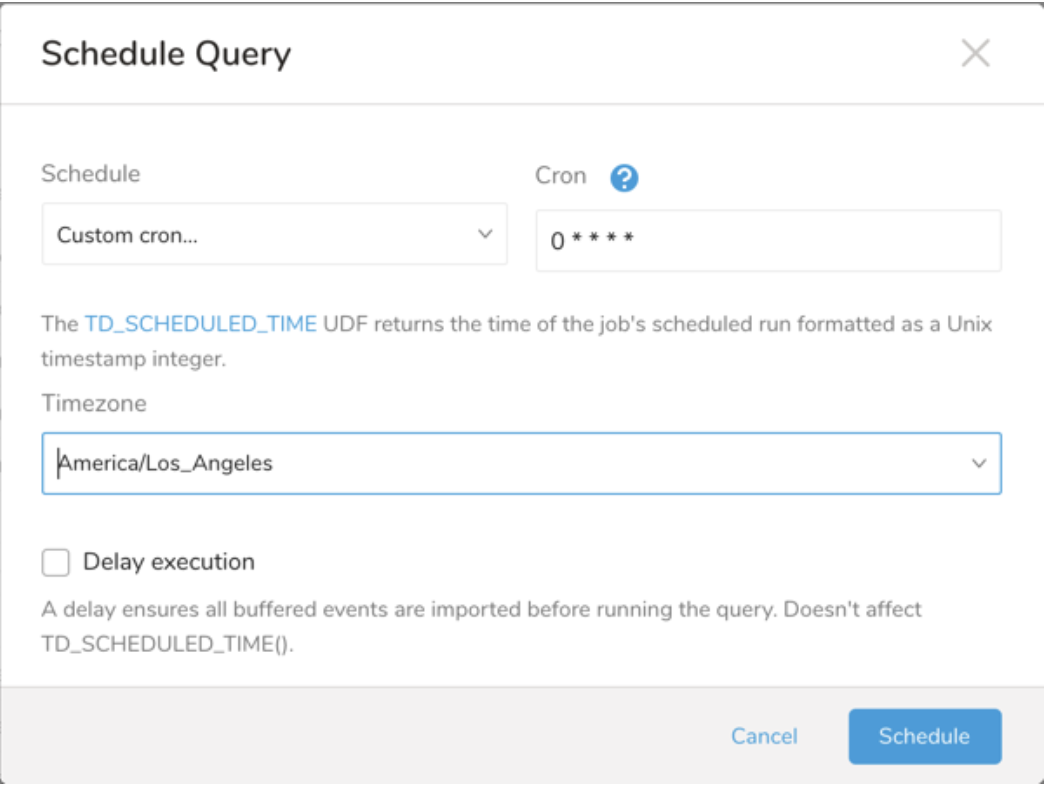
| Cron Value | Description |
|---|---|
0 * * * * | Run once an hour. |
0 0 * * * | Run once a day at midnight. |
0 0 1 * * | Run once a month at midnight on the morning of the first day of the month. |
| "" | Create a job that has no scheduled run time. |
* * * * *
- - - - -
| | | | |
| | | | +----- day of week (0 - 6) (Sunday=0)
| | | +---------- month (1 - 12)
| | +--------------- day of month (1 - 31)
| +-------------------- hour (0 - 23)
+------------------------- min (0 - 59)The following named entries can be used:
- Day of Week: sun, mon, tue, wed, thu, fri, sat.
- Month: jan, feb, mar, apr, may, jun, jul, aug, sep, oct, nov, dec.
A single space is required between each field. The values for each field can be composed of:
| Field Value | Example | Example Description |
|---|---|---|
| A single value, within the limits displayed above for each field. | ||
A wildcard '*' to indicate no restriction based on the field. | '0 0 1 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) on the first day of each month. |
A range '2-5', indicating the range of accepted values for the field. | '0 0 1-10 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) on the first 10 days of each month. |
A list of comma-separated values '2,3,4,5', indicating the list of accepted values for the field. | 0 0 1,11,21 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) every 1st, 11th, and 21st day of each month. |
A periodicity indicator '*/5' to express how often based on the field's valid range of values a schedule is allowed to run. | '30 */2 1 * *' | Configures the schedule to run on the 1st of every month, every 2 hours starting at 00:30. '0 0 */5 * *' configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) every 5 days starting on the 5th of each month. |
A comma-separated list of any of the above except the '*' wildcard is also supported '2,*/5,8-10'. | '0 0 5,*/10,25 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) every 5th, 10th, 20th, and 25th day of each month. |
- (Optional) You can delay the start time of a query by enabling the Delay execution.
Save the query with a name and run, or just run the query. Upon successful completion of the query, the query result is automatically exported to the specified destination.
Scheduled jobs that continuously fail due to configuration errors may be disabled on the system side after several notifications.
(Optional) You can delay the start time of a query by enabling the Delay execution.
You can also send segment data to the target platform by creating an activation in the Audience Studio.
- Navigate to Audience Studio.
- Select a parent segment.
- Open the target segment, right-mouse click, and then select Create Activation.
- In the Details panel, enter an Activation name and configure the activation according to the previous section on Configuration Parameters.
- Customize the activation output in the Output Mapping panel.
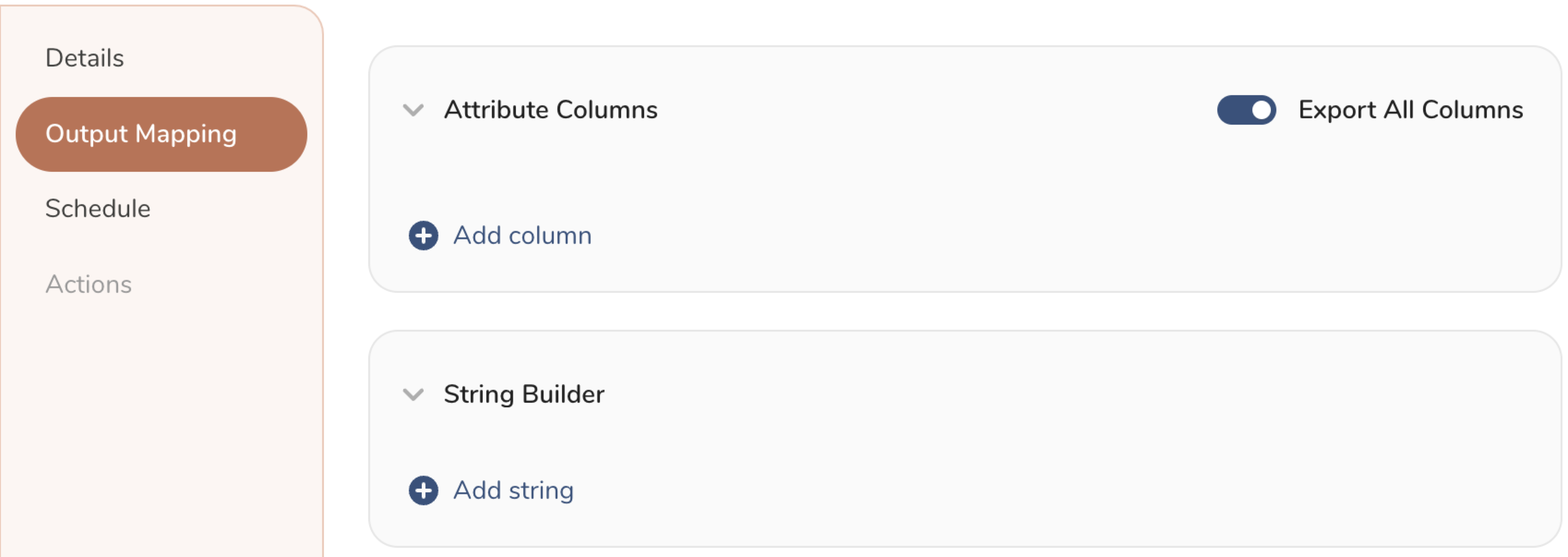
- Attribute Columns
- Select Export All Columns to export all columns without making any changes.
- Select + Add Columns to add specific columns for the export. The Output Column Name pre-populates with the same Source column name. You can update the Output Column Name. Continue to select + Add Columnsto add new columns for your activation output.
- String Builder
- + Add string to create strings for export. Select from the following values:
- String: Choose any value; use text to create a custom value.
- Timestamp: The date and time of the export.
- Segment Id: The segment ID number.
- Segment Name: The segment name.
- Audience Id: The parent segment number.
- + Add string to create strings for export. Select from the following values:
- Set a Schedule.
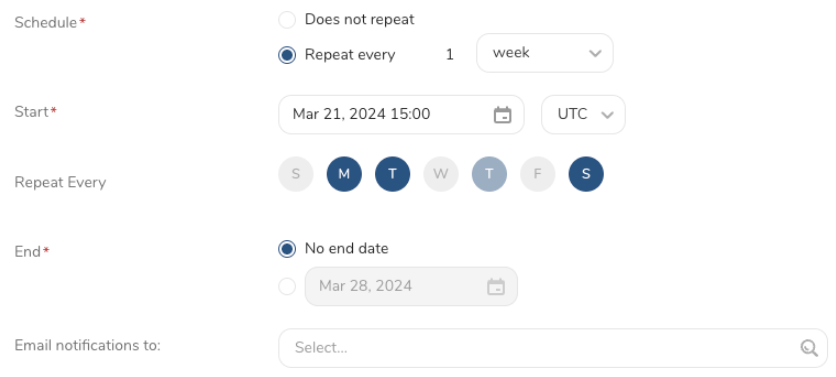
- Select the values to define your schedule and optionally include email notifications.
- Select Create.
If you need to create an activation for a batch journey, review Creating a Batch Journey Activation.
Within Treasure Workflow, you can specify the use of this data connector to export data.
Learn more at Using Workflows to Export Data with the TD Toolbelt.
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| type | String | Yes | verizon_media |
| mdm_id | String | Yes | Your company MDM ID |
| upload_mode | String | Yes | PARTNER_MATCH, TAXONOMY, AUDIENCE_UPLOAD, OPT_OUT |
| taxonomy_mode | String | Apply for Taxonomy upload only | |
| urn_type | String | Yes | Apply for Audience upload only |
| partner_match_urn_type | String | Yes | Apply for Partner Match mode only |
| opt_out_urn_type | String | Yes | Apply for Opt-out mode only |
| target_segment_id | String | Upload audiences to this segment | |
| gdpr | Boolean | Default true | |
| taxonomy_dry_run | Boolean | Verify the Taxonomy upload job run only (without changing actual data). Default false |
_export:
td:
database: td.database
+verizon_media_export_task:
td>: export_verizon_media.sql
database: ${td.database}
result_connection: verizon_media
result_settings:
type: verizon_media
upload_mode: audience
urn_type: EmailYou can also use the CLI provided by TD Toolbelt to export query results to Yahoo!.
Using the td query command, you would specify the LINE conversion server URL with the --result RESULT_URL option. See td query for more information.
The format of the option is JSON and the general structure is as follows.
{
"type": "verizon_media",
"mdm_id": "100",
"upload_mode": "taxonomy",
"taxonomy_mode": "append_node"
}Parameters
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| type | String | Yes | verizon_media |
| mdm_id | String | Yes | Your company MDM ID |
| upload_mode | String | Yes | PARTNER_MATCH, TAXONOMY, AUDIENCE_UPLOAD, OPT_OUT |
| taxonomy_mode | String | Apply for Taxonomy upload only. Values: - whole_structure - append_node, - replace_node - delete_node | |
| urn_type | String | Yes | Apply for Audience upload only |
| partner_match_urn_type | String | Yes | Apply for Partner Match mode only |
| opt_out_urn_type | String | Yes | Apply for Opt-out mode only |
| target_segment_id | String | Upload audiences to this segment | |
| gdpr | Boolean | Default true | |
| taxonomy_dry_run | Boolean | Verify the Taxonomy upload job run only (without changing actual data). Default false |
td query \
--result '{
"type": "verizon_media",
"upload_mode": "taxonomy",
"taxonomy_mode": "append_node",
"mdm_id": "100"
}' \
-d sample_datasets \
"SELECT * FROM verizon_media_tbl" \
-T presto