The integration for Teradata enables the import of data from your Teradata Server into Treasure Data.
- Basic knowledge of Treasure Data
- Basic knowledge of Teradata SQL
- A Teradata instance running
- Go to Integrations Hub > Catalog.
- Search and select Teradata.

A dialog will open.
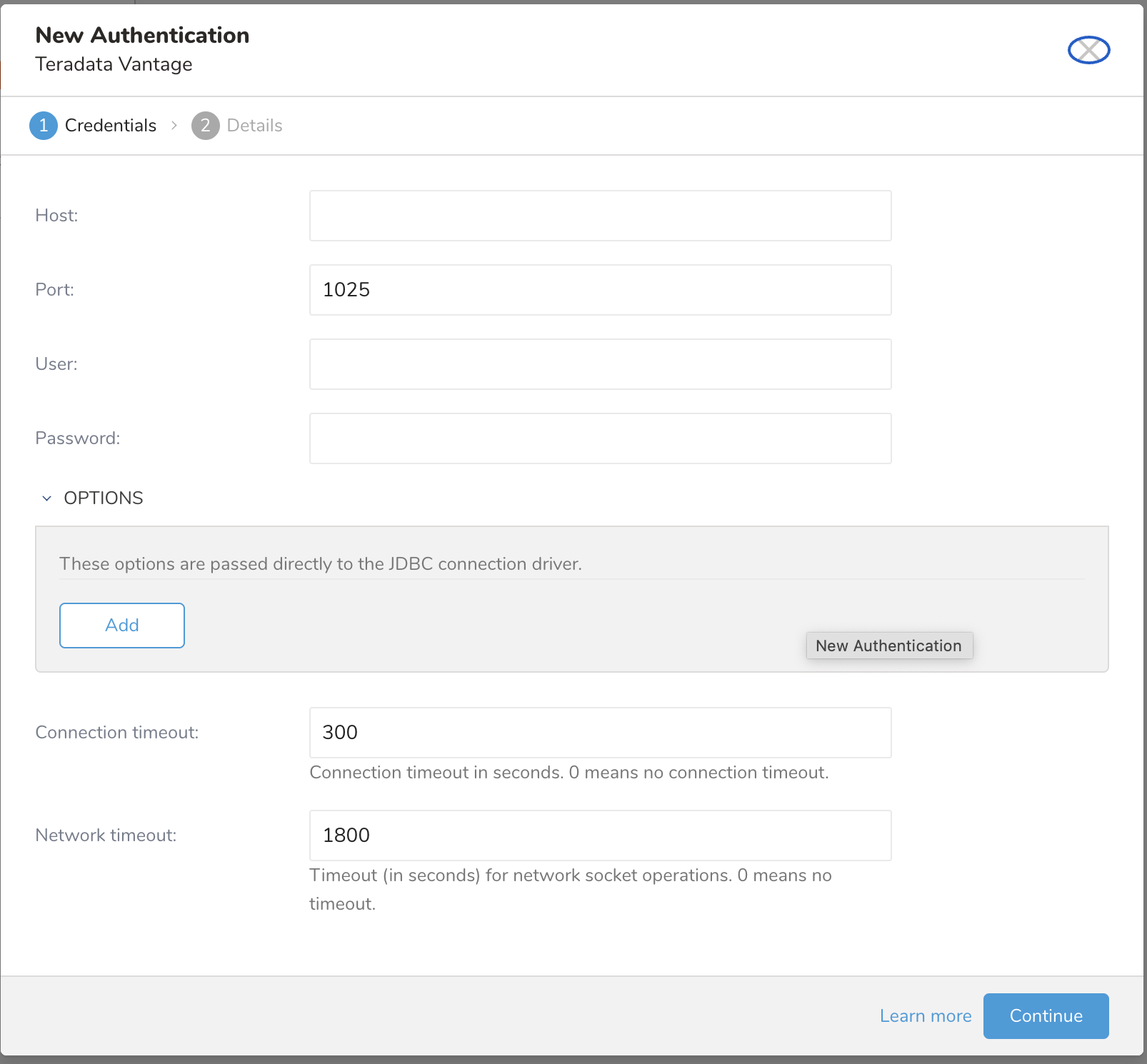
Provide your configuration.
Parameters Description Host The host information of the teradata database, eg. an IP address. Port The connection port on the instance,Teradata default is 1025. Username Username to connect to the teradata database. Password Password to connect to the teradata database. OPTIONS JDBC Connection options Any special JDBC connections required by Teradata database. Please don't add these jdbc options because it will be ignore: - DBS_PORT (use port config) - DATABASE (use database config) - USER (use user config) - PASSWORD (use password config) - LOGMECH (currently support TD2 only) connection timeout Timeout (in seconds) for socket connection (default is 300). Network timeout Timeout (in seconds) for network socket operations (default is 1800). 0 means no timeout. Type a name for your connection and select Done .
If you want to load data from a SQL Query, confirm that your query is valid SELECT statement. Multiple statement is not supported.
After creating the connection, you are automatically taken to the Authentications tab. Look for the connection you created and select Source.
Select source type of import, either loading a whole table/view (table/view loading) or loading a SQL result (query loading).
If you want to load a whole table/view, select "Table/View", then provide the "Table/View name" that you want to load.
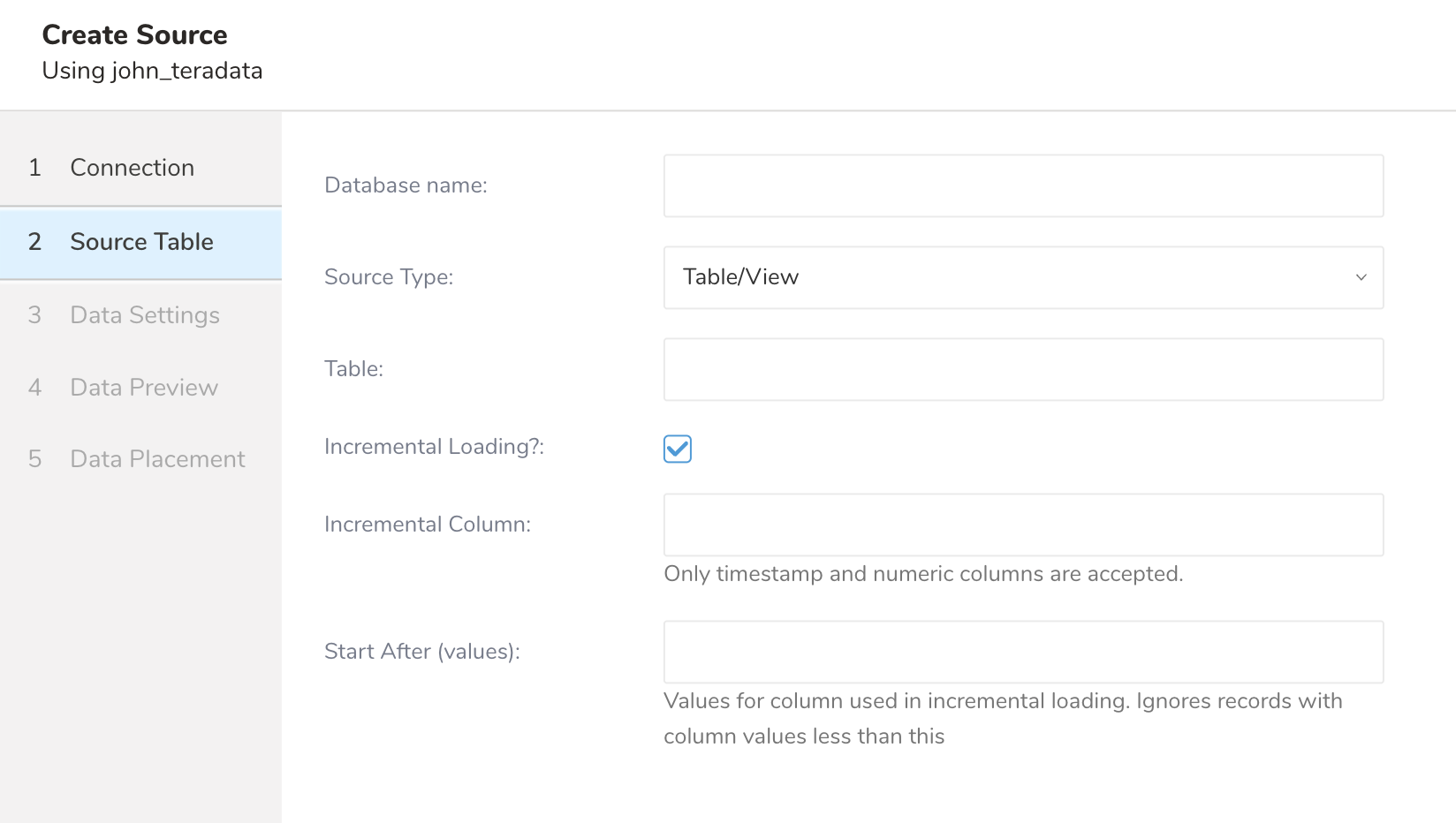
If you want to load a SQL result, select "Query statement", then input an SQL query into the "SQL statement".
Before creating transfer, confirm that your query is valid SELECT query and single statement. If you fetch data from Query and Incremental then the query statement must exclude ORDER BY clause
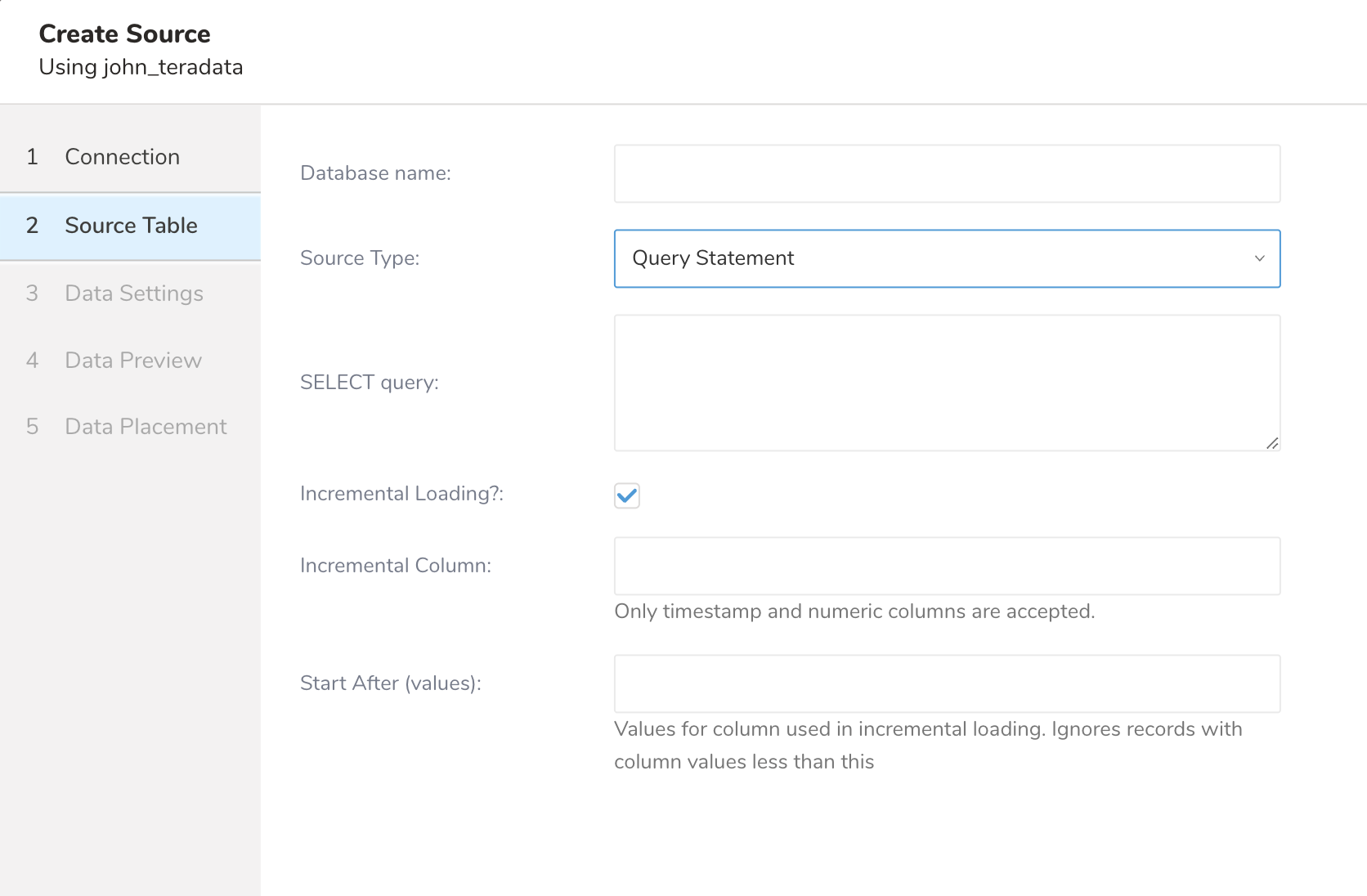
Incremental loading can load only new records after last execution by using increasing, unique column(s), such as an auto-increment ID column or timestamp column.
To enable it, check Incremental Loading, then specify column name to increment into "Incremental Column Name."
Only INTEGER or BIGINT type and TIMESTAMP type are supported as an incremental column.
Input Start After in case you would like to start incremental loading from this value. If incremental column have Timestamp Type then input much be Timestamp string in format yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSSSS and the value will be treat as UTC timezone.
This connector records "last record" which is the latest record ordered by the incremental column. In the next execution, it loads records by running a query built by the following rule using the last record:
With table loading, all fields are selected with the WHERE clause.
SELECT * FROM `${dataset}.${table}` WHERE ${incremental_column} > ${value_of_last_record}With query loading, the raw query is wrapped with the WHERE clause.
SELECT * FROM (${query}) embulk_incremental_ WHERE ${incremental_column} > ${value_of_last_record}- Select Next. The Data Settings page opens.
- Optionally, edit the data settings or skip this page of the dialog.
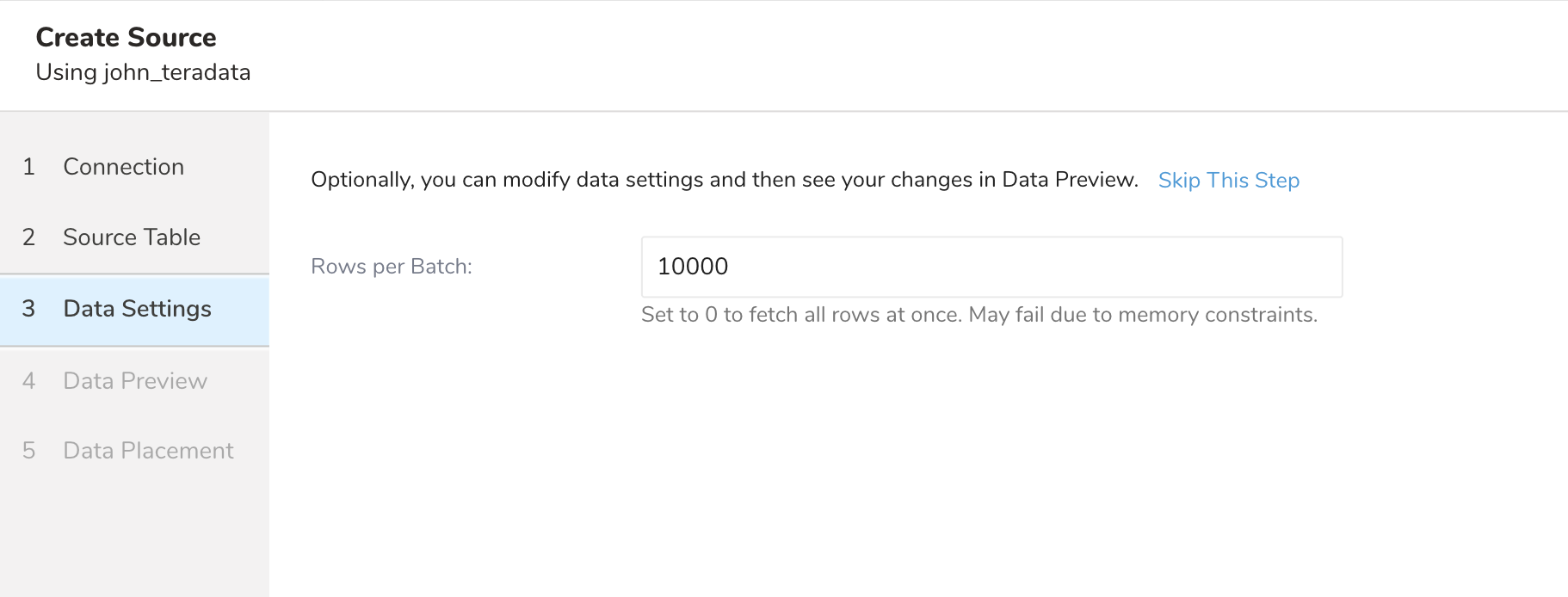
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Rows per batch | Extremely large datasets can lead to memory issues and, subsequently, failed jobs. Use this flag to break down the import job into batches by the number of rows to reduce the chances of memory issues and failed jobs. Set 0 for unlimited. Otherwise the value must be greater than 0 |
After configuring the data source, select Next then Next and click Generate Previewto see a sample result from the source.
After you select Next from the preview, you are asked to select the database and table in Treasure Data where you want to transfer the data into. If you want to create a new database, select Create new database and give your database a name. Do the same with Create new table.
Select whether to append records to an existing table or replace your existing table.
If you want to set a different partition key seed than the default key, you can select one from the "Partition key seed".
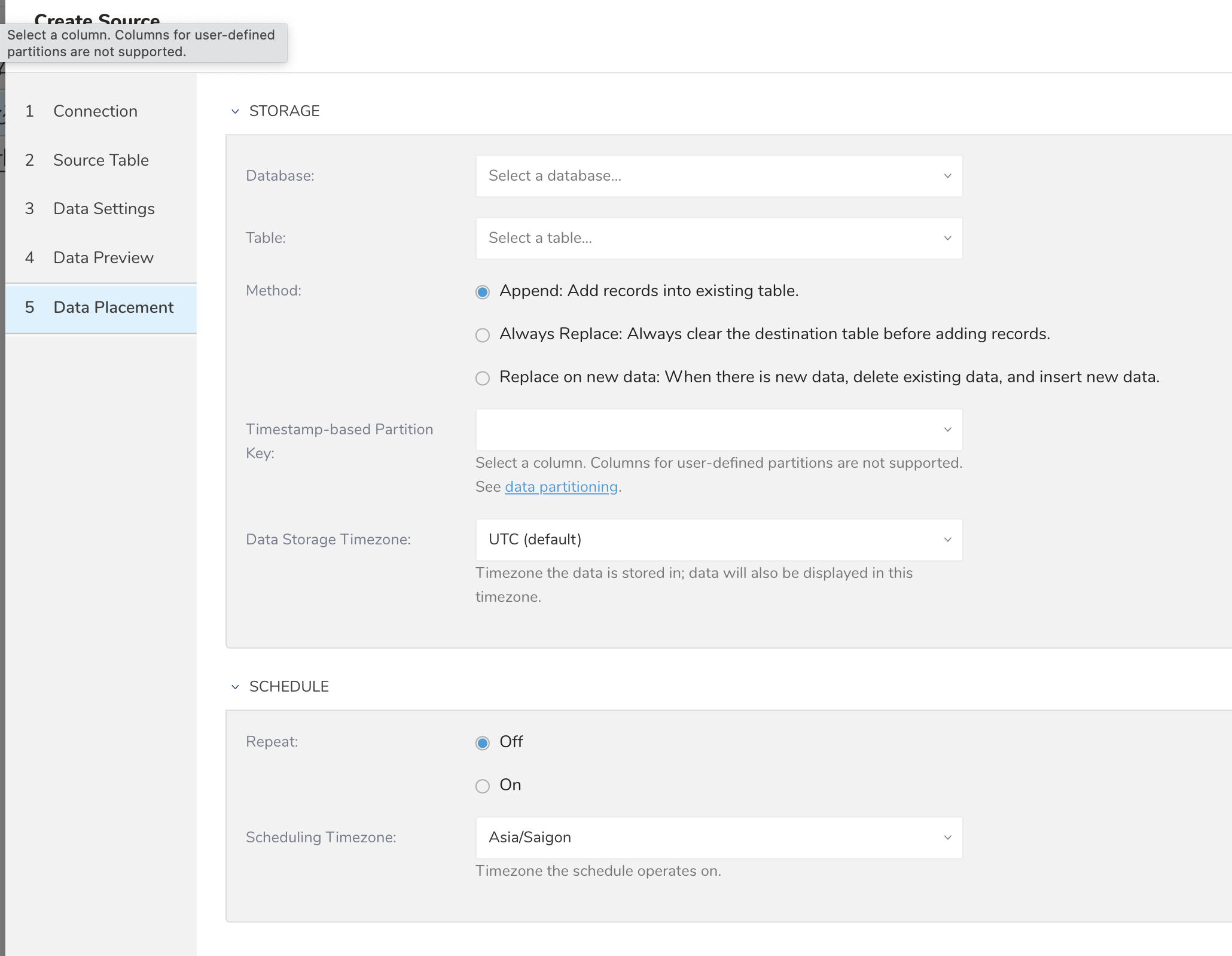
On the SCHEDULE section, you can specify the import job as a one-time transfer, or you can schedule an automated recurring transfer.
After your transfer runs, you can see the results of your transfer in the Databases tab.
Teradata's data types are automatically converted to a corresponding Treasure Data type, as indicated in the following table. If you include unsupported types in the schema of the table/view or query result, you receive errors.
| Teradata Data Type | TD Data Type |
|---|---|
| BYTEINT | Long |
| SMALLINT | Long |
| INTEGER | Long |
| BIGINT | Long |
| FLOAT | Double |
| DECIMAL | String |
| CHAR | String |
| VARCHAR | String |
| BYTE | Unsupport |
| VARBYTE | Unsupport |
| DATE | String |
| TIME | String |
| TIMESTAMP | Timestamp |
| CLOB | String |
| BLOB | Unsupport |
| Structured UDT | String |
| INTERVAL | String |
| JSON | String |
| XML | String |
| PERIOD | String |
| GEO | String |
Any quotas and limits of Teradata Server.
If you prefer, you can use the connector via TD Toolbelt.
Set up TD Toolbelt on the CLI.
Create configuration YAML file that is referred to as "config.yml" here.
Example: Import from table with incremental, incremental column in biginteger data type and last_record set
in:
type: teradata
host: xxx
options: {"xxx": "xxx"}
connect_timeout:300
socket_timeout:1800
user: xxx
port: 1025
password: xxxx
database: xxxxx
source_type: table_view
table: xxxx
fetch_rows: 10000
incremental: true
incremental_column: big_int_column
last_record: 100Example: Import from Query with incremental, incremental column in timestamp data type and last_record set
in:
type: teradata
host: xxx
options: {"xxx": "xxx"}
connect_timeout:300
socket_timeout:1800
user: xxx
port: 1025
password: xxxx
database: xxxxx
source_type: query
query: |
SELECT * FROM tbl; fetch_rows: 10000 incremental: true incremental_column: created_at last_record: '2025-08-26T12:10:42.010000'| Name | Description | Type | Value | Default Value | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| type | connector type | string | teradata | N/A | Yes |
| host | Teradata server host | string | N/A | N/A | Yes |
| port | Teradata server port | number | N/A | 1025 | |
| options | Teradata JDBC option | string (in hash object format) | N/A | N/A | No |
| connect_timeout | Teradata logon timeout | number | N/A | 300 | No |
| socket_timeout | Network socket operations timeout | number | N/A | 1800 | No |
| database | Teradata database | string | N/A | N/A | Yes |
| source_type | Source import | string | Support values: - table_view - query | table | Yes |
| table | Table Name | string | N/A | N/A | Yes if source_type is table_view |
| query | SQL statement | string | N/A | N/A | Yes if source_type is query |
| incremental | Whether to enable incremental loading | boolean | true/false | false | No |
| incremental_column | Column name for incremental loading Only support for INTEGER, BIGINT ot TIMESTAMP data type | string | N/A | N/A | Yes if incremental is true |
| last_record | Start incremental import from this value. If column incremental have data type timestamp then this value must follow format yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSSSS and will be treat as UTC timezone | string | N/A | N/A | No |
Run td td connector:preview command to validate your configuration file
td connector:preview config.ymlRun td connector:create.
By the following example, a daily import session with Teradata connector is created.
td connector:create daily_teradata_import \
"10 0 * * *" td_sample_db td_sample_table config.ymlConnector sessions need at least one timestamp column in result data to be used as data partition key and the first timestamp column is chosen as the key by default. Use "--time-column" option if you want to explicitly specify a column.
$ td connector:create --time-column created_at \
daily_teradata_import ...If your result data doesn't have any timestamp column, add the "time" column by adding the filter configuration as follows.
in:
type: teradata
...
filters:
- type: add_time
from_value:
mode: upload_time
to_column:
name: time
out:
type: td