This feature is in BETA version. For more information, contact your Customer Success Representative.
The Shopify Import Connector V2 is a new version of the Shopify connector specifically designed to work with Shopify’s GraphQL Admin API. This version has been developed in response to Shopify’s deprecation of several REST API endpoints (including /productsand /variants) which are being replaced by their GraphQL counterparts. Consequently, to ensure continued functionality and future compatibility, we have developed this V2 connector to handle data imports for resources affected by the API deprecation.
The V2 connector specifically handles the following import operations that were previously managed by REST APIs:
- Product Data Import
- Basic product information
- Product variants
- Product status and visibility settings
- Product options and variants configuration
- Product Variant Data Import
- Variant-specific attributes
- SKU information
- Pricing details
- Inventory tracking information
- Metafields Import
- Product metafields
- Product variant metafields
Continue using the V1 version of the connector for:
- Inventory levels import
- Inventory items import
- Location data import
- Collection metafields import
- Product image metafields import
- Any other resource types not listed in V2 scope
However, use the V2 Connector for:
- Importing product data
- Importing product variant data
- Importing product metafields
- Importing product variant metafields
- Basic Knowledge of Treasure Data
- Basic knowledge of Shopify
- Metafield Import Restrictions
- Maximum 250 metafields per product
- Maximum 250 metafields per product variant
- Product Variants imports no longer supports incremental loading by the created_at timestamp. It now only supports loading by the updated_at timestamp.
If your security policy requires IP whitelisting, you must add Treasure Data's IP addresses to your allowlist to ensure a successful connection.
Please find the complete list of static IP addresses, organized by region, at the following document
Your first step is to create a new authentication with a set of credentials.
- Select Integrations Hub.
- Select Catalog.
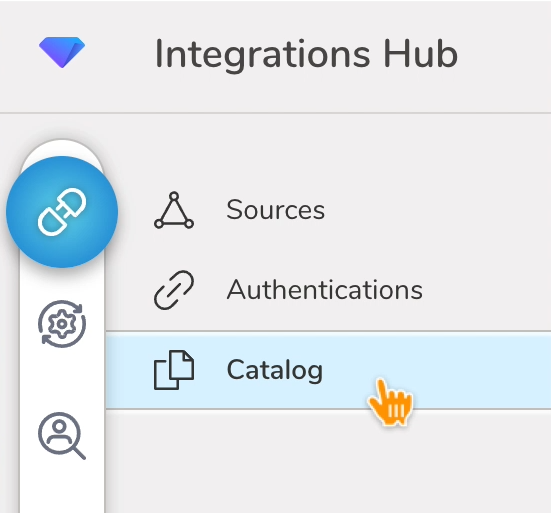 3. Search for your Shopify in the Catalog; hover your mouse over the icon and select Create Authentication.
3. Search for your Shopify in the Catalog; hover your mouse over the icon and select Create Authentication.


- Ensure that the Credentials tab is selected and then enter credential information for the integration.
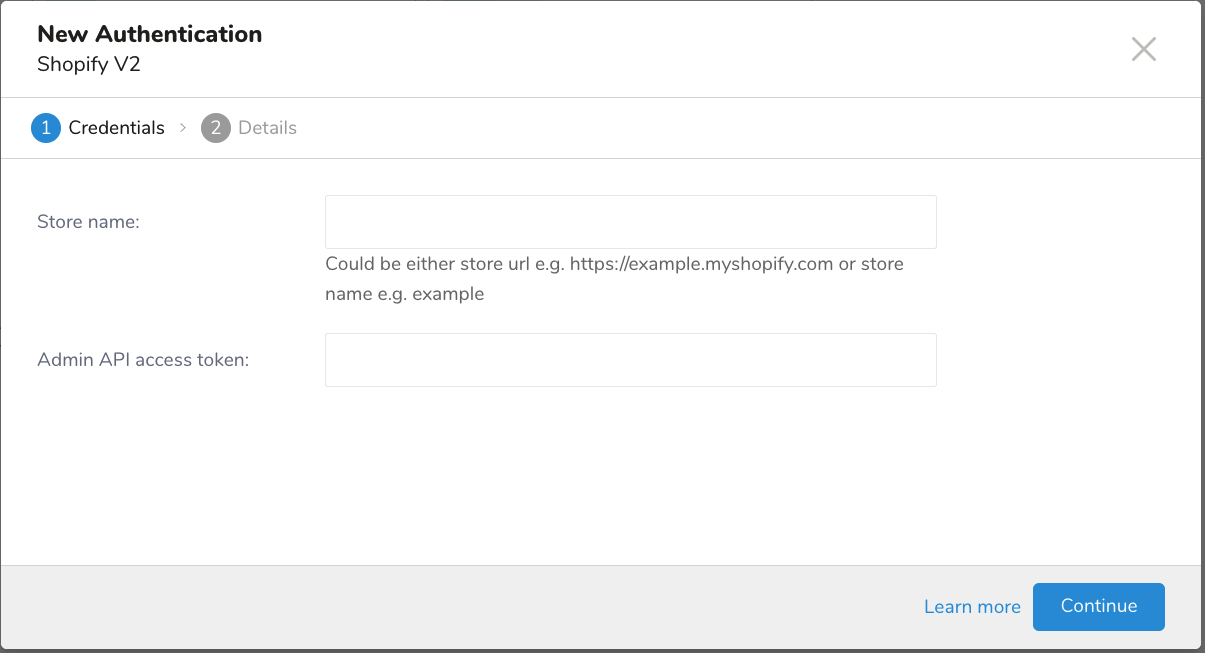
New Authentication Fields
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Store name | The store identifier for your Shopify store. This can be entered in two formats: - Full store URL: for example https://mountbaker.myshopify.com - Store name only: for example: mountbakerIf you’re using just the store name, it should be the unique identifier of your store without the .myshopify.com domain. |
| Admin API access token | The access token used to authenticate with Shopify’s Admin API. This token can be generated from your Shopify admin panel under Apps > Develop apps > Create an app > Configure Admin API scopes. The token needs the appropriate permissions to perform operations like managing metafields. |
- Select Continue.
- Enter a name for your authentication, and then select Done.
After the authentication becomes available on the console, configure your import job.
- Open TD Console.
- Navigate to Integrations Hub > Authentications.
- Locate your Shopify authentication and select New Source.
- Type a source name in the Data Transfer Name field.
- Select Next.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Transfer Name | Enter a name for your transfer. |
| Authentication | This field contains the name of the authentication that will be used to connect with Shopify. |
- Configure the fields for the source table.
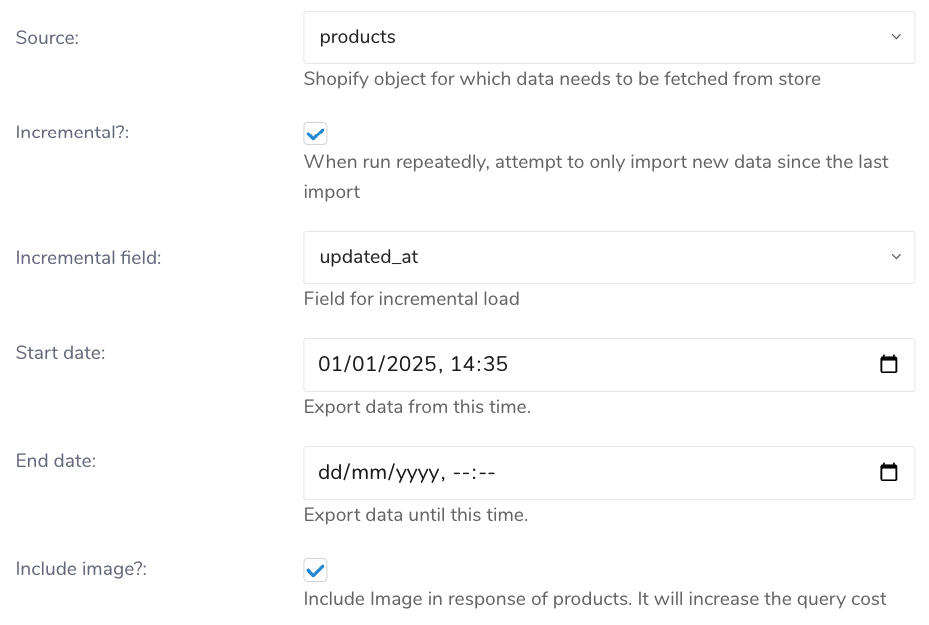
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Source | A drop-down menu that contains the following Shopify objects:
Select Shopify object that that contains the data you want to import from your Shopify store. |
| Incremental? | When enabled, the connector will only import new or updated data since the last import run, making subsequent imports more efficient. |
| Incremental field | Choose which timestamp to use for incremental loading:
|
| Start date | The beginning timestamp from which to export data (Format: dd/mm/yyyy, hh:mm) |
| End date | The ending timestamp where you want to finish exporting data (Format: dd/mm/yyyy, hh:mm). If left empty, the end date will be the current time. |
| Include image? | When enabled, product image data will be included in the response. Note that this will increase the query cost. |
| Resource | Select product to specify the resource type for the metafields. |
| Objects | Choose the object type for metafields:
|
Product ID | This field is required. Enter a comma-separated list of product IDs you want to get metafields for. If product variant is selected, the field name changes to Variant ID. |
- Select Next.
- Configure the data settings.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Retry Limit | The number of retries before the import fails. |
| Initial retry time wait in millis | The initial time in milliseconds to wait before retrying. |
| Max retry wait in millis | The maximum time in milliseconds to wait before retrying. |
- Select Next.
You can see a preview of your data before running the import by selecting Generate Preview. Data preview is optional and you can safely skip to the next page of the dialog if you choose to.
- Select Next. The Data Preview page opens.
- If you want to preview your data, select Generate Preview.
- Verify the data.
For data placement, select the target database and table where you want your data placed and indicate how often the import should run.
Select Next. Under Storage, you will create a new or select an existing database and create a new or select an existing table for where you want to place the imported data.
Select a Database > Select an existing or Create New Database.
Optionally, type a database name.
Select a Table> Select an existing or Create New Table.
Optionally, type a table name.
Choose the method for importing the data.
- Append (default)-Data import results are appended to the table. If the table does not exist, it will be created.
- Always Replace-Replaces the entire content of an existing table with the result output of the query. If the table does not exist, a new table is created.
- Replace on New Data-Only replace the entire content of an existing table with the result output when there is new data.
Select the Timestamp-based Partition Key column. If you want to set a different partition key seed than the default key, you can specify the long or timestamp column as the partitioning time. As a default time column, it uses upload_time with the add_time filter.
Select the Timezone for your data storage.
Under Schedule, you can choose when and how often you want to run this query.
- Select Off.
- Select Scheduling Timezone.
- Select Create & Run Now.
- Select On.
- Select the Schedule. The UI provides these four options: @hourly, @daily and @monthly or custom cron.
- You can also select Delay Transfer and add a delay of execution time.
- Select Scheduling Timezone.
- Select Create & Run Now.
After your transfer has run, you can see the results of your transfer in Data Workbench > Databases.
You can import data from Shopify reports via workflow using td_load>: src_id. If you have already created a source, you can run it; if you don't want to create a source, you can import it using a .yml file.
- Select Integrations Hub > Sources.
- On the Filters pane on the far right of the screen, use the Integration Type drop-down menu to select Shopify V2.
- In the Sources pane, identify the row that contains the source you want to use, and then use the more drop-down menu ( ••• icon) for that row to select Copy Unique ID.
- Define a workflow task, and for td_load>: use the ID you copied in step 3.
+load:
td_load>: unique_id_of_your_source
database: ${td.dest_db}
table: ${td.dest_table}- Run the workflow.
- Identify your .yml file.
If you need to create the .yml file, refer to the instructions found in Create Seed Config File (seed.yml). 2. Define a workflow task, and for td_load>: specify your .yml file.
+load:
td_load>: config/daily_load.yml
database: ${td.dest_db}
table: ${td.dest_table}- Run the workflow.
Visit Treasure Boxes for a sample workflow code.
Before setting up the integration, install the latest version of the TD Toolbelt.
in:
type: shopify_v2
admin_api_access_token: xxxxxxxx
target: products
store_name: xxxxxxx
from_date: '2024-12-31T17:00:00.000Z'
incremental_field: created_at
out:
mode: replaceThis example gets a list of Shopify Product objects. The from_date specifies the date to start getting data from. In this case, the import will start pulling data from December 31, 2024 at 17:00.
Parameters Reference
| Name | Description | Value | Default Value | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| type | The source of the import. | "shopify_v2" | Yes | |
| admin_api_access_token | The access token used to authenticate with Shopify’s Admin API. This token can be generated from your Shopify admin panel under Apps > Develop apps > Create an app > Configure Admin API scopes. The token needs the appropriate permissions to perform operations like managing metafields. | String | Yes | |
| target | The source you want to collect the data from | String. Valid targets can be - products - product_variants - meta_fields | Yes | |
| store_name | The store identifier for your Shopify store. This can be entered in two formats: - Full store URL: for example https://mountbaker.myshopify.com - Store name only: for example: mountbaker If you’re using just the store name, it should be the unique identifier of your store without the .myshopify.com domain. | String. | Yes | |
| incremental | List of metrics your report should be grouped by. Allowable values depend on report type. | Boolean. | False | No |
| incremental_field | Timestamp to use for incremental loading. | String. | created_at | No |
| start_date | The beginning timestamp from which to export data | String. Format: yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SS'Z' | No | |
| end_date | The ending timestamp where you want to finish exporting data | String. Format: yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SS'Z' | No | |
| metafield_resource | The meta field target | String. The value will be "product". | Yes (if the target is meta_fields | |
| metafield_object | The metafield object | String. The value can be either - product - product_variant | Yes (if the target is meta_fields) | |
| product_ids | Comma separated list of product IDs you want to get metafields from | String. For example, "gid://shopify/Product/8472042950, gid://shopify/Product/8472044230" | Yes (if the metafield_object is product) | |
| product_variant_ids | Comma separated list of product variant IDs you want to get metafields from | String. For example, "gid://shopify/ProductVariant/28753686918, gid://shopify/ProductVariant/28753705670" | Yes (if the metafeld_object is product_variant) |
To preview the data, use the td connector:preview command.
td connector:preview load.ymlIt might take a couple of hours, depending on the size of the data. Be sure to specify the Treasure Data database and table where the data should be stored. Treasure Data also recommends specifying the --time-column option because Treasure Data’s storage is partitioned by time (see data partitioning). If this option is not provided, the data connector chooses the first long or timestamp column as the partitioning time. The type of the column specified by --time-column must be either of long and timestamp type.
If your data doesn’t have a time column, you can add a time column by using the add_time filter option. For more details see the documentation for the add_time Filter Function.
$ td connector:issue load.yml --database td_sample_db --table td_sample_table --time-column created_atThe connector:issue command assumes that you have already created a database(td_sample_db) and a table(td_sample_table). If the database or the table does not exist in TD, this command fails. Create the database and table manually or use --auto-create-table option with td connector:issue command to auto-create the database and table.
$ td connector:issue load.yml --database td_sample_db --table td_sample_table--time-column created_at --auto-create-tableThe data connector does not sort records on the server side. To use time-based partitioning effectively, sort records in files beforehand.
If you have a field called time, you don’t have to specify the --time-column option.
$ td connector:issue load.yml --database td_sample_db --table td_sample_tableSpecify the file import mode in the out: section of the load.yml file. The out: section controls how data is imported into a Treasure Data table. For example, you may choose to append data or replace data in an existing table.
| Mode | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Append | Records are appended to the target table. | in: ... out: mode: append |
| Always Replace | Replaces data in the target table. Any manual schema changes made to the target table remain intact. | in: ... out: mode: replace |
| Replace on new data | Replaces data in the target table only when there is new data to import. | in: ... out: mode: replace_on_new_data |
You can schedule periodic data connector execution for incremental file import. The Treasure Data scheduler is optimized to ensure high availability.
For the scheduled import, you can import all files that match the specified prefix and one of these conditions:
- If use_modified_time is disabled, the last path is saved for the next execution. On the second and subsequent runs, the integration only imports files that come after the last path in alphabetical order.
- Otherwise, the time that the job is executed is saved for the next execution. On the second and subsequent runs, the connector only imports files that were modified after that execution time in alphabetical order.
A new schedule can be created using the td connector:create command.
$ td connector:create daily_import "10 0 * * *" td_sample_db td_sample_table load.ymlTreasure Data also recommends specifying the --time-column option because Treasure Data’s storage is partitioned by time (see data partitioning).
$ td connector:create daily_import "10 0 * * *" td_sample_db td_sample_table load.yml --time-column created_atThe cron parameter also accepts three special options: @hourly, @daily, and @monthly.
By default, the schedule is set up in the UTC timezone. You can set the schedule in a timezone using -t or --timezone option. The --timezone option supports only extended timezone formats like Asia/Tokyo, America/Los_Angeles, etc. Timezone abbreviations like PST, CST are not supported and might lead to unexpected schedules.