Using this integration, you can use TD query jobs to
- Add contacts to your Eloqua contact lists
- Add accounts to the Eloqua account groups
- Add data to Eloqua custom data objects (CDO)
- Add contacts to the shared list on Eloqua and add the shared list to the segment.
- Basic knowledge of Treasure Data, including the TD Toolbelt
- An Eloqua account with API access enabled
Go to https://login.eloqua.com.
Log in to the Oracle Eloqua Console using the same Company Name, Username, and Password you used when specifying the CSF authentication keys in Oracle JDeveloper and Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control.
3. After logging in, select **Audience >**Custom Objects.
- Make note of the custom object name and the field names.
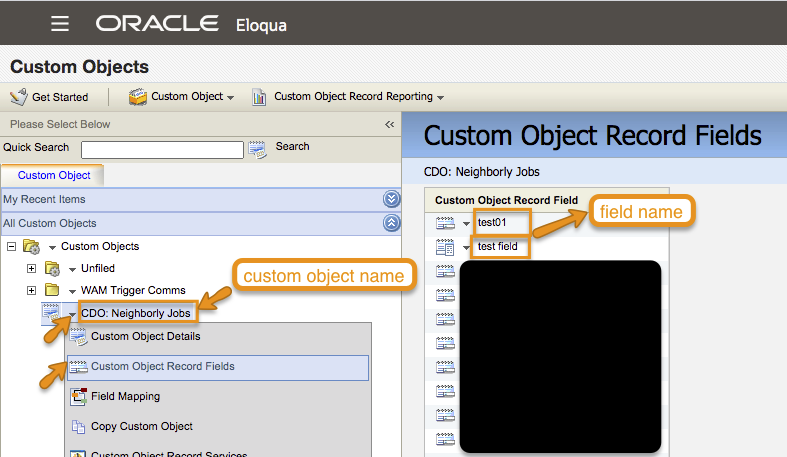
Optionally, you can navigate to Custom Object Record Reporting and select the desired report:
- Custom Object Data —Use this report to view all the custom object records within the individual custom object. You can print and export the report to Excel and copy, delete, or move the custom object records.
- Custom Object and Contact Data — Use this report to view all the custom object records within the individual custom object with the contact information they are mapped to. The report can be viewed in a specified time frame. The default is the past month, but you can change the time range (e.g., Start Date or End Date) or time span (e.g., Last week or Last month). You can print and export the report to Excel.
You must create and configure the data connection in Treasure Data before running your query. As part of the data connection, you provide authentication to access the integration.
Open TD Console.
Navigate toIntegrations Hub > Catalog.
Search for Eloqua in the Catalog; hover over the icon and select Create Authentication.
4. Type the credentials to authenticate:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Authentication Method | Basic (Default) |
| Site Name | URL for the Oracle Eloqua site |
| Username | The username of your Oracle Eloqua account |
| Password | The password for your account |
Select Continue.
Enter a name for your authentication, and select Done.
The following constraints apply to your queries:
- Your query requires each resource type to have specific columns with exact column names (case sensitive) and data types.
- Your query must define the column mapping.
- Custom object or account fields are case-insensitive.
- If the custom object or account field contains a space, you must replace it with an underscore.
- If your query contains any field name that does not exist in the custom object or account field name, an error is returned, and the job fails.
- Complete the instructions in Creating a Destination Integration.
- Navigate to Data Workbench > Queries.
- Select a query for which you would like to export data.
- Run the query to validate the result set.
- Select Export Results.
- Select an existing integration authentication.

- Define any additional Export Results details. In your export integration content, review the integration parameters. For example, your Export Results screen might be different, or you might not have additional details to fill out:
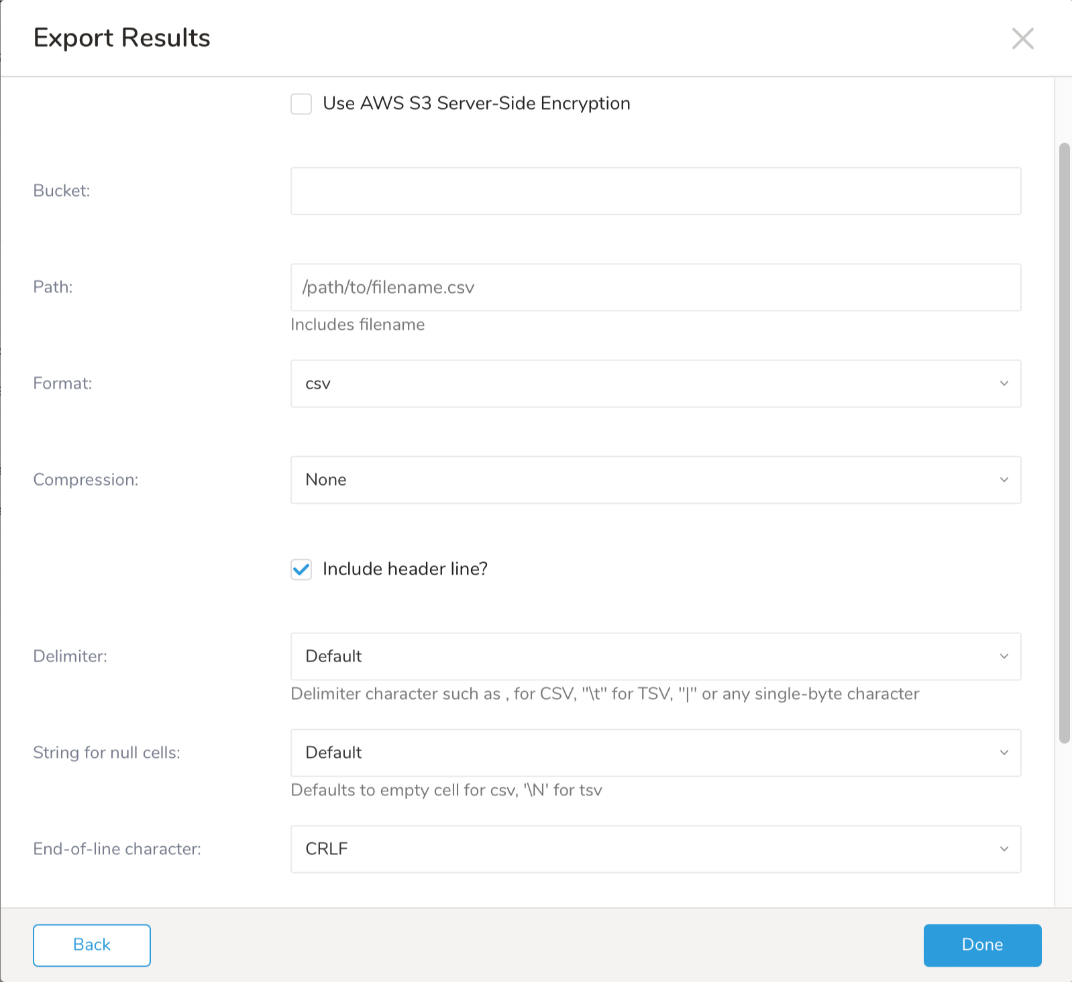
- Select Done.
- Run your query.
- Validate that your data moved to the destination you specified.
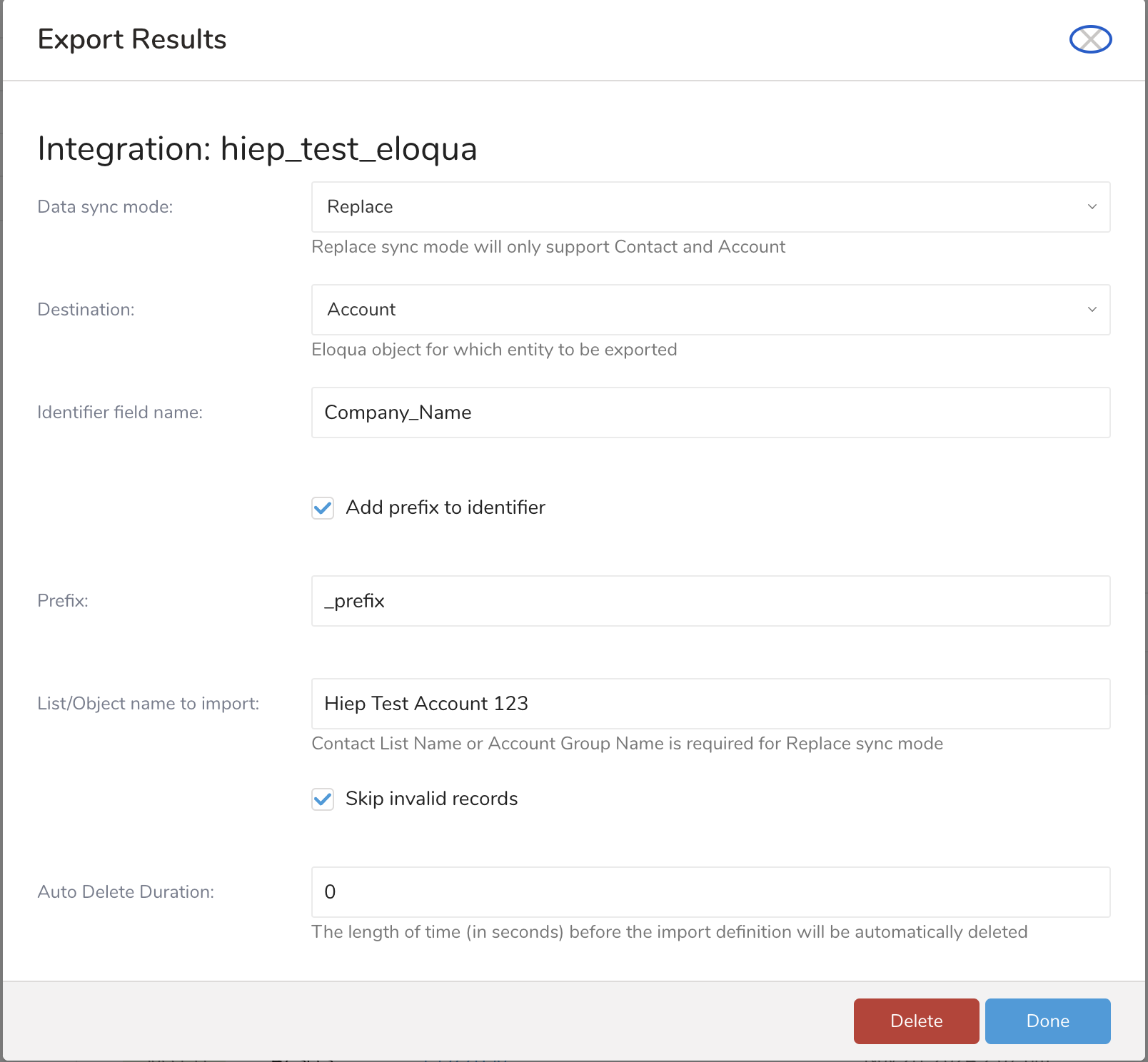
| Parameters | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Data sync mode | Append or Replace | The Eloqua action to export data (Append or Replace) |
| Destination | Contact | The Eloqua object to export data (contact list or custom object or account) |
| Custom Object Data | The Eloqua object to export data (contact list or custom object or account) | |
| Account | The Eloqua object to export data (contact list or custom object or account) | |
| Contact Shared List | The Eloqua object to export data (contact shared list) | |
| Add a prefix to the identifier | Check if you want to modify the identifier value by adding a prefix value to the identifier column. This option is supported for an identifier column with a data type of string type. | |
| Prefix | string value | This option is supported for an identifier column with a data type of string. The prefix value will be added to identify the column value. |
| List/Object name to import | Custom object names can be case-insensitive. Group account name that can be case-insensitive (optional) | The contact list name or object name for the exported data. The custom object name that you want to export data into. Group account name for the exported data. The shared list name is for exported data. It is required with the contact shared list. |
| Shared List Identifier Field Name | Shared List Identifier Field Name | The field name is used to identify the contact entity. If you chose a Contact's email address, you must have the c_emailaddress field in your query with the Contact's external ID as the c_externalid field and the Contact's ID as the c_id field. |
| Identifier Field Name | For destination Contact
| The field name is used to identify the contact entity. If you chose a Contact's email address, you must have the c_emailaddress field in your query with the Contact's external ID as the c_externalid field and the Contact's ID as the c_id field. |
For destination Custom Object Data or Account It is one of the field names from your custom object or account data query. For example, if your query is: SELECT col_a, col_b, col_c FROM your_table;then the value should be col_a or col_b or col_c. | The field name is used to identify the custom object or account row. | |
| Update Rule |
| The rule is used when doing updates on existing data. For more information about this parameter, see the Oracle Eloqua Developer Help Center. |
| Skip invalid records | If checked, Eloqua will return success even if it encounters data row errors. Otherwise, the job will fail if there are invalid records. | |
| Map custom object to contact | If you checked, the job tries to map a custom object to a contact. | |
| Perform case-sensitive search when mapping custom object to contact | Perform a case-sensitive search when mapping a custom object to a contact. | |
| CDO source field | Column name of the field | Input the column name of the field to be mapped, as used in the export schema. Required when Map custom object to contact is enabled. |
| Contact map field | Column name of the field | Input the contact field for mapping. Required when Map custom object to contact is enabled. |
| Auto Delete Duration | integer | The length of time (in seconds) before the import definition will be automatically deleted, 0 or greater than 3600 |
Your query requires each resource type to have specific columns and exact names (case sensitive) and data types.
- Custom objects or account fields, such as col_a, col_b, and col_c, can be case-insensitive.
- If the Eloqua server's custom object or account field name contains a space, replace it with an underscore in your query.
- If your query contains any field name that does not exist in the custom object or account field name, an error is returned, and the job fails.
custom object query
SELECT col_a, col_b, col_bFROM your_table;For example, to export a contact, you could use queries similar to these:
SELECT c_emailaddress, c_firstname, c_lastnameFROM contact;
SELECT identifier_type, identifierFROM table my_tableYou can use Scheduled Jobs with Result Export to periodically write the output result to a target destination that you specify.
Treasure Data's scheduler feature supports periodic query execution to achieve high availability.
When two specifications provide conflicting schedule specifications, the specification requesting to execute more often is followed while the other schedule specification is ignored.
For example, if the cron schedule is '0 0 1 * 1', then the 'day of month' specification and 'day of week' are discordant because the former specification requires it to run every first day of each month at midnight (00:00), while the latter specification requires it to run every Monday at midnight (00:00). The latter specification is followed.
Navigate to Data Workbench > Queries
Create a new query or select an existing query.
Next to Schedule, select None.

In the drop-down, select one of the following schedule options:
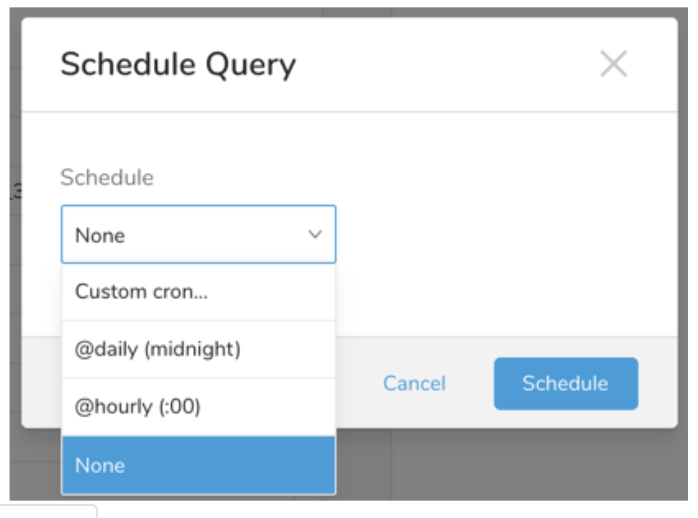
Drop-down Value Description Custom cron... Review Custom cron... details. @daily (midnight) Run once a day at midnight (00:00 am) in the specified time zone. @hourly (:00) Run every hour at 00 minutes. None No schedule.
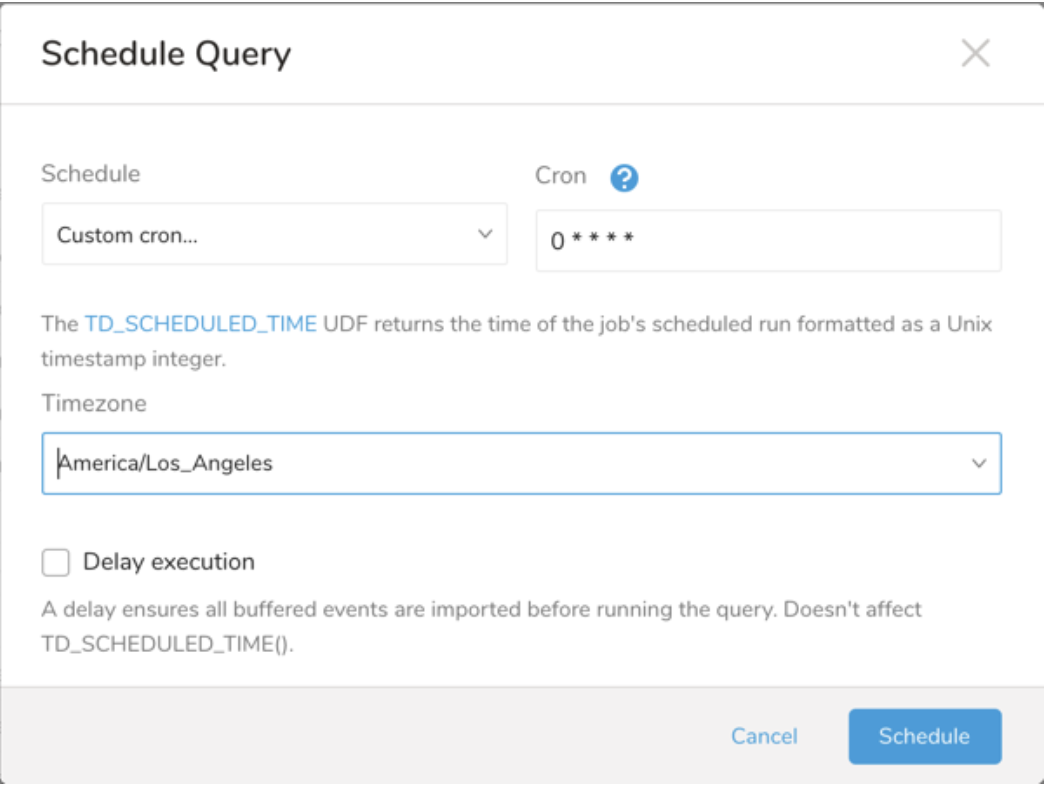
| Cron Value | Description |
|---|---|
0 * * * * | Run once an hour. |
0 0 * * * | Run once a day at midnight. |
0 0 1 * * | Run once a month at midnight on the morning of the first day of the month. |
| "" | Create a job that has no scheduled run time. |
* * * * *
- - - - -
| | | | |
| | | | +----- day of week (0 - 6) (Sunday=0)
| | | +---------- month (1 - 12)
| | +--------------- day of month (1 - 31)
| +-------------------- hour (0 - 23)
+------------------------- min (0 - 59)The following named entries can be used:
- Day of Week: sun, mon, tue, wed, thu, fri, sat.
- Month: jan, feb, mar, apr, may, jun, jul, aug, sep, oct, nov, dec.
A single space is required between each field. The values for each field can be composed of:
| Field Value | Example | Example Description |
|---|---|---|
| A single value, within the limits displayed above for each field. | ||
A wildcard '*' to indicate no restriction based on the field. | '0 0 1 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) on the first day of each month. |
A range '2-5', indicating the range of accepted values for the field. | '0 0 1-10 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) on the first 10 days of each month. |
A list of comma-separated values '2,3,4,5', indicating the list of accepted values for the field. | 0 0 1,11,21 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) every 1st, 11th, and 21st day of each month. |
A periodicity indicator '*/5' to express how often based on the field's valid range of values a schedule is allowed to run. | '30 */2 1 * *' | Configures the schedule to run on the 1st of every month, every 2 hours starting at 00:30. '0 0 */5 * *' configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) every 5 days starting on the 5th of each month. |
A comma-separated list of any of the above except the '*' wildcard is also supported '2,*/5,8-10'. | '0 0 5,*/10,25 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) every 5th, 10th, 20th, and 25th day of each month. |
- (Optional) You can delay the start time of a query by enabling the Delay execution.
Save the query with a name and run, or just run the query. Upon successful completion of the query, the query result is automatically exported to the specified destination.
Scheduled jobs that continuously fail due to configuration errors may be disabled on the system side after several notifications.
(Optional) You can delay the start time of a query by enabling the Delay execution.
You can also send segment data to the target platform by creating an activation in the Audience Studio.
- Navigate to Audience Studio.
- Select a parent segment.
- Open the target segment, right-mouse click, and then select Create Activation.
- In the Details panel, enter an Activation name and configure the activation according to the previous section on Configuration Parameters.
- Customize the activation output in the Output Mapping panel.
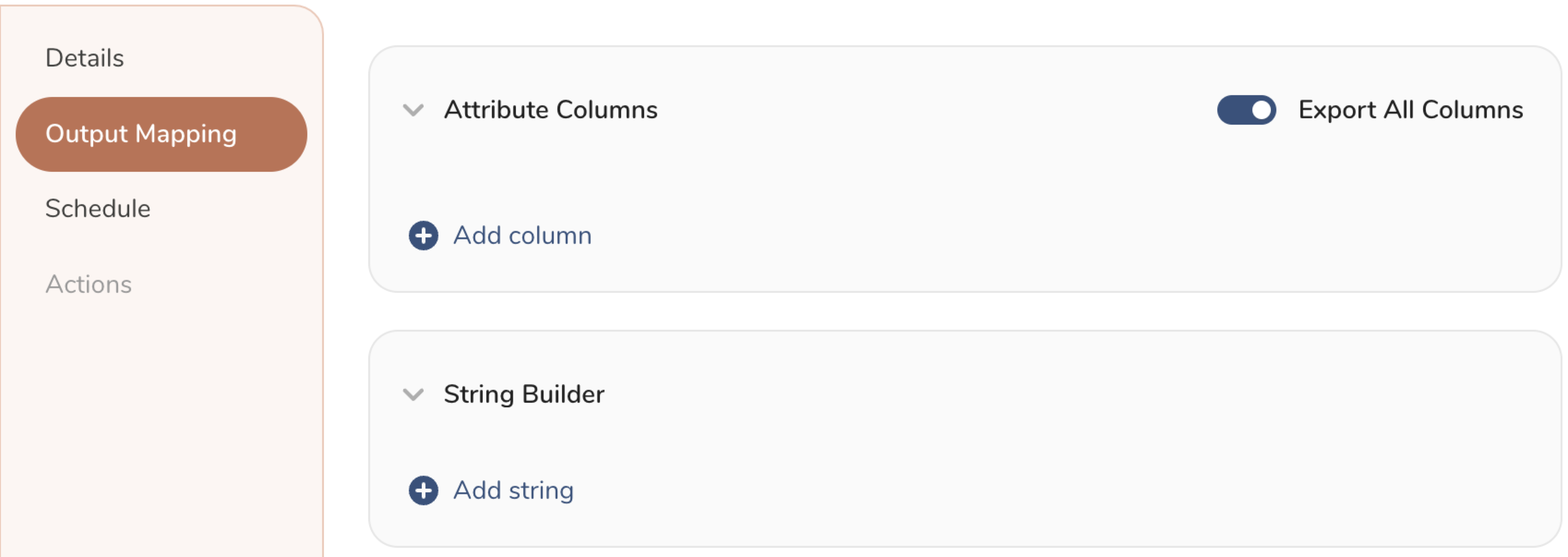
- Attribute Columns
- Select Export All Columns to export all columns without making any changes.
- Select + Add Columns to add specific columns for the export. The Output Column Name pre-populates with the same Source column name. You can update the Output Column Name. Continue to select + Add Columnsto add new columns for your activation output.
- String Builder
- + Add string to create strings for export. Select from the following values:
- String: Choose any value; use text to create a custom value.
- Timestamp: The date and time of the export.
- Segment Id: The segment ID number.
- Segment Name: The segment name.
- Audience Id: The parent segment number.
- + Add string to create strings for export. Select from the following values:
- Set a Schedule.
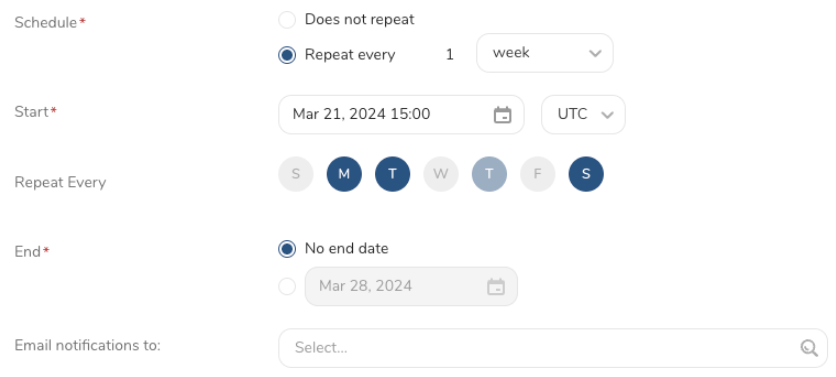
- Select the values to define your schedule and optionally include email notifications.
- Select Create.
If you need to create an activation for a batch journey, review Creating a Batch Journey Activation.
You can specify using this data connector to export data within Treasure Workflow.
Learn more at Using Workflows to Export Data with the TD Toolbelt.
The identifier_field_name accepts the following values:
- C_EmailAddress
- C_ExternalID
- C_ID
The update_rule accepts the following values:
- always
- ifNewIsNotNull
- ifExistingIsNull
- useFieldRule
_export:
td:
database: eloqua_db
+eloqua_custom_object_export_task:
td>: export_contact.sql
database: ${td.database}
result_connection: new_created_eloqua_auth
result_settings:
type: eloqua
data_sync_mode: append # replace mode is only support account or contact list
target: contact
identifier_field_name: C_EmailAddress
list_name: td_shared_list2
update_rule: always
skip_invalid_records: true
auto_delete_duration: 3600The custom_object_identifier_field is one of the fields named in the export_custom_object.sql query.
The update_rule accepts the following values:
- always
- ifNewIsNotNull
- ifExistingIsNull
- useFieldRule
You can get custom_object_name from the Oracle Eloqua Console.
_export:
td:
database: eloqua_db
+eloqua_custom_object_export_task:
td>: export_custom_object.sql
database: ${td.database}
result_connection: new_created_eloqua_auth
result_settings:
type: eloqua
target: custom_object
custom_object_identifier_field: {xxxxx}
list_name: {custom_object_name}
update_rule: always
skip_invalid_records: true
map_custom_object_to_contact: true,
perform_case_sensitive_search: false,
cdo_source_field: Email_Address,
contact_map_field: C_EmailAddress
auto_delete_duration: 0The account_identifier_field is one of the fields named in the export_account.sql query.
The update_rule accepts the following values:
- always
- ifNewIsNotNull
- ifExistingIsNull
- useFieldRule
You can get the group_account_name from the Oracle Eloqua Console.
_export:
td:
database: eloqua_db
+eloqua_account_export_task:
td>: export_account.sql
database: ${td.database}
result_connection: new_created_eloqua_auth
result_settings:
type: eloqua
data_sync_mode: append/replace
target: account
account_identifier_field: {xxxxx}
list_name: {group_account_name}
custom_identifier: true
prefix_identifier: prefix_value
update_rule: always
skip_invalid_records: true
auto_delete_duration: 0The identifier_field_name accepts the following values:
- C_EmailAddress
- C_ExternalID
- C_ID
The update_rule accepts the following values:
- always
- ifNewIsNotNull
- ifExistingIsNull
- useFieldRule
_export:
td:
database: eloqua_db
+eloqua_custom_object_export_task:
td>: export_contact.sql
database: ${td.database}
result_connection: new_created_eloqua_auth
result_settings:
type: eloqua
data_sync_mode: append
target: contact_shared_list
identifier_field_name: C_EmailAddress
list_name: td_shared_list2 # Required
segment_name: td_segment_name #Required
update_rule: always
skip_invalid_records: true
auto_delete_duration: 3600You can also use CLI(Toolbelt) to export results to Eloqua
You need to specify the information for export to your server as --result option of td query command. About td query command, you can see this article.
Example for Usage
td query -d your_data_base_here \
-w "SELECT c_emailaddress AS C_EmailAddress, c_firstname AS C_First_Name, c_lastname AS C_Last_Name, c_company AS Company from eloqua_contact_output" \
-T presto \
--result '{ "type": "eloqua","auth_method": "basic", "site_name": "your site name", "username": "username","password": "password","data_sync_mode": "replace","target": "contact", "list_name": "your list name","identifier_field_name": "C_EmailAddress"}'- API Overview: https://docs.oracle.com/en/cloud/saas/marketing/eloqua-rest-api/APIRequests.html
- Bulk 2.0: https://docs.oracle.com/en/cloud/saas/marketing/eloqua-rest-api/Getting_Started_Bulk.html