This article explains how to write job results to your existing MySQL instance.
For sample workflows of this, view Treasure Boxes.
- Basic knowledge of Treasure Data, including the TD Toolbelt.
- A MySQL instance.
- Treasure Data must have SELECT, INSERT, DELETE, CREATE, DROP, and ALTER privileges.
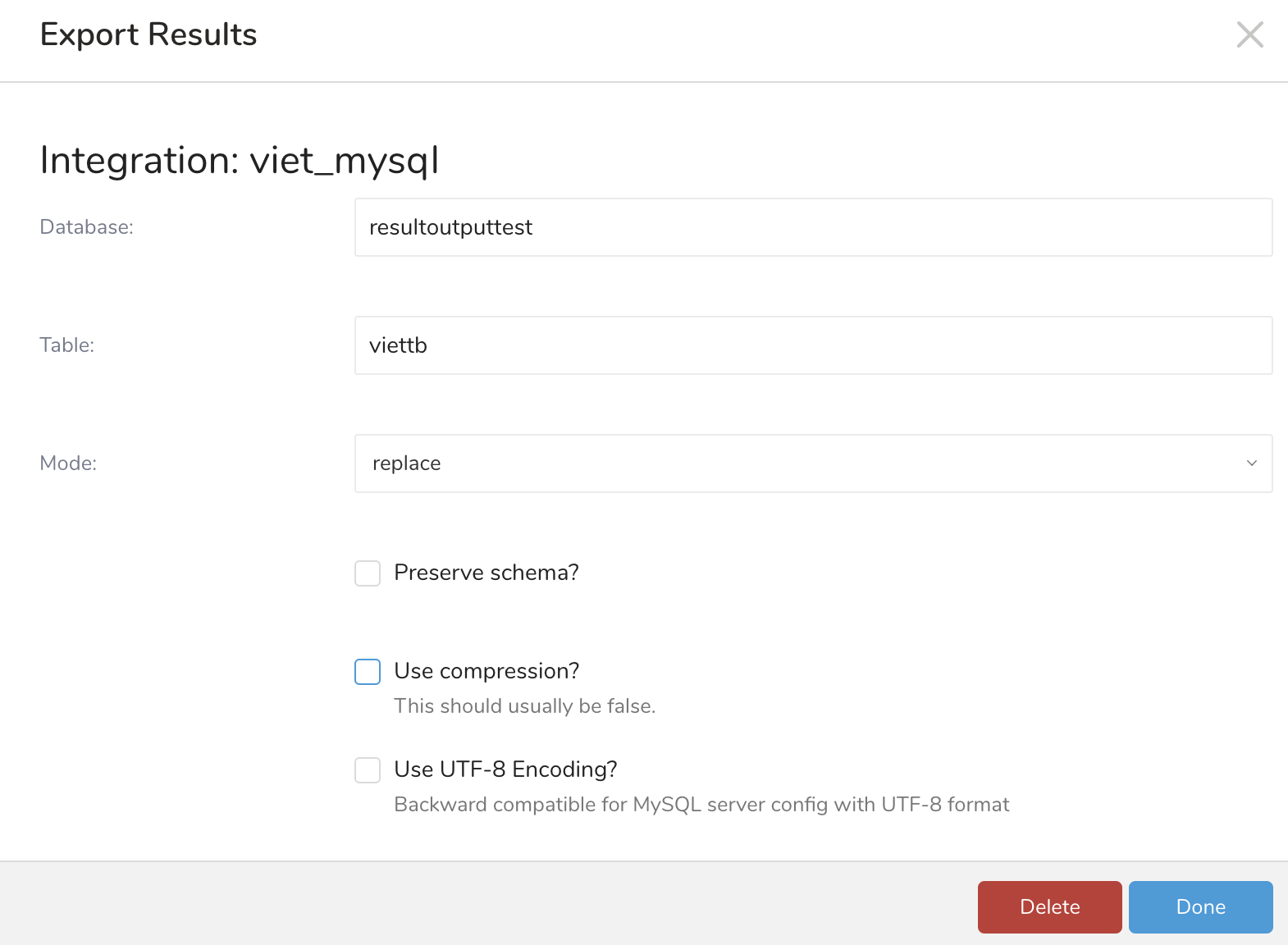
Using replace mode may change the schema of the MySQL table. To avoid schema changes to the target table, select the Preserve schema? option.
Export from Treasure Data uses queries. You create or reuse a query. In the query, you configure the data connection.
- Open TD Console.
- Navigate to Data Workbench > Queries.
- Select New Query in the top right corner to create a new query.
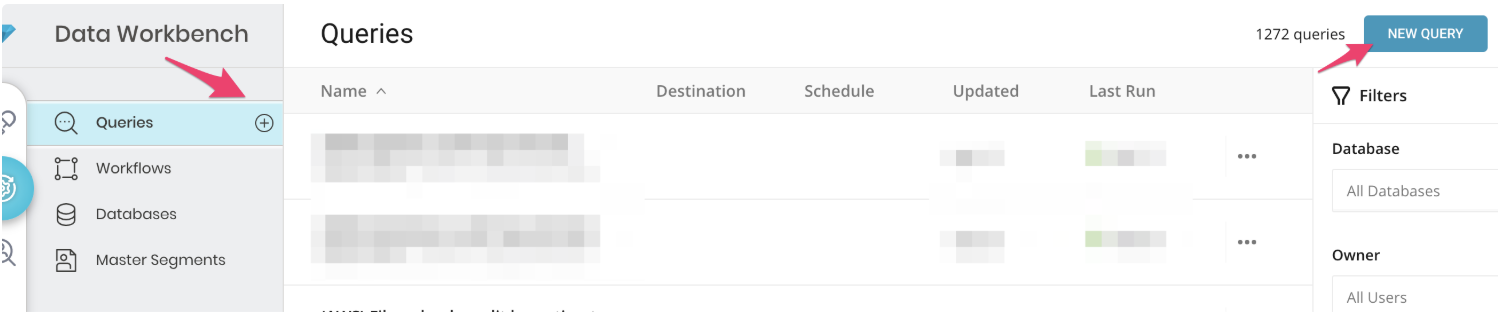
Select the query that you plan to use to export data.
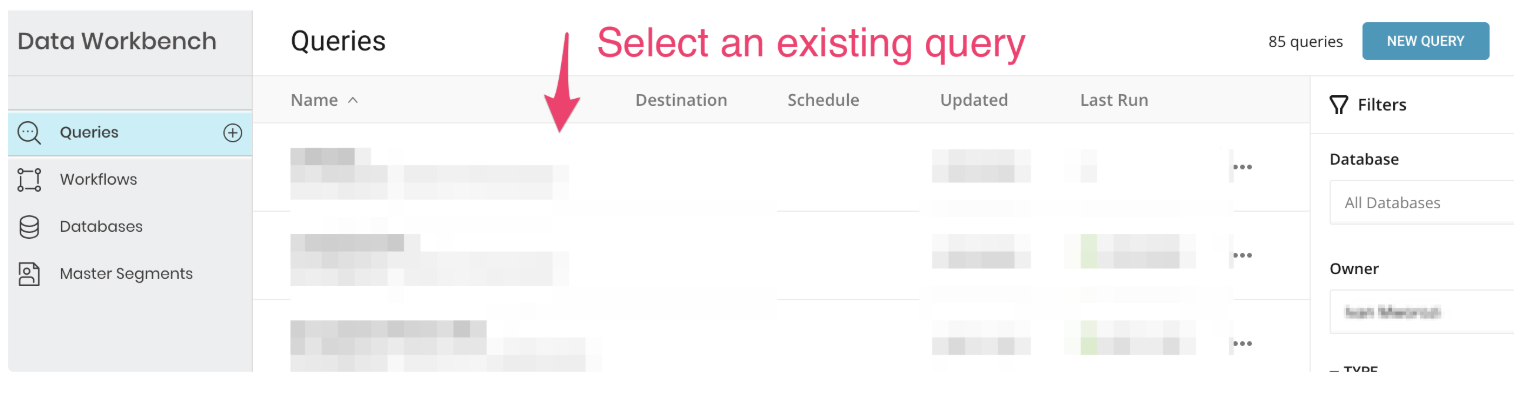
After your query setup is complete, select Export Results.
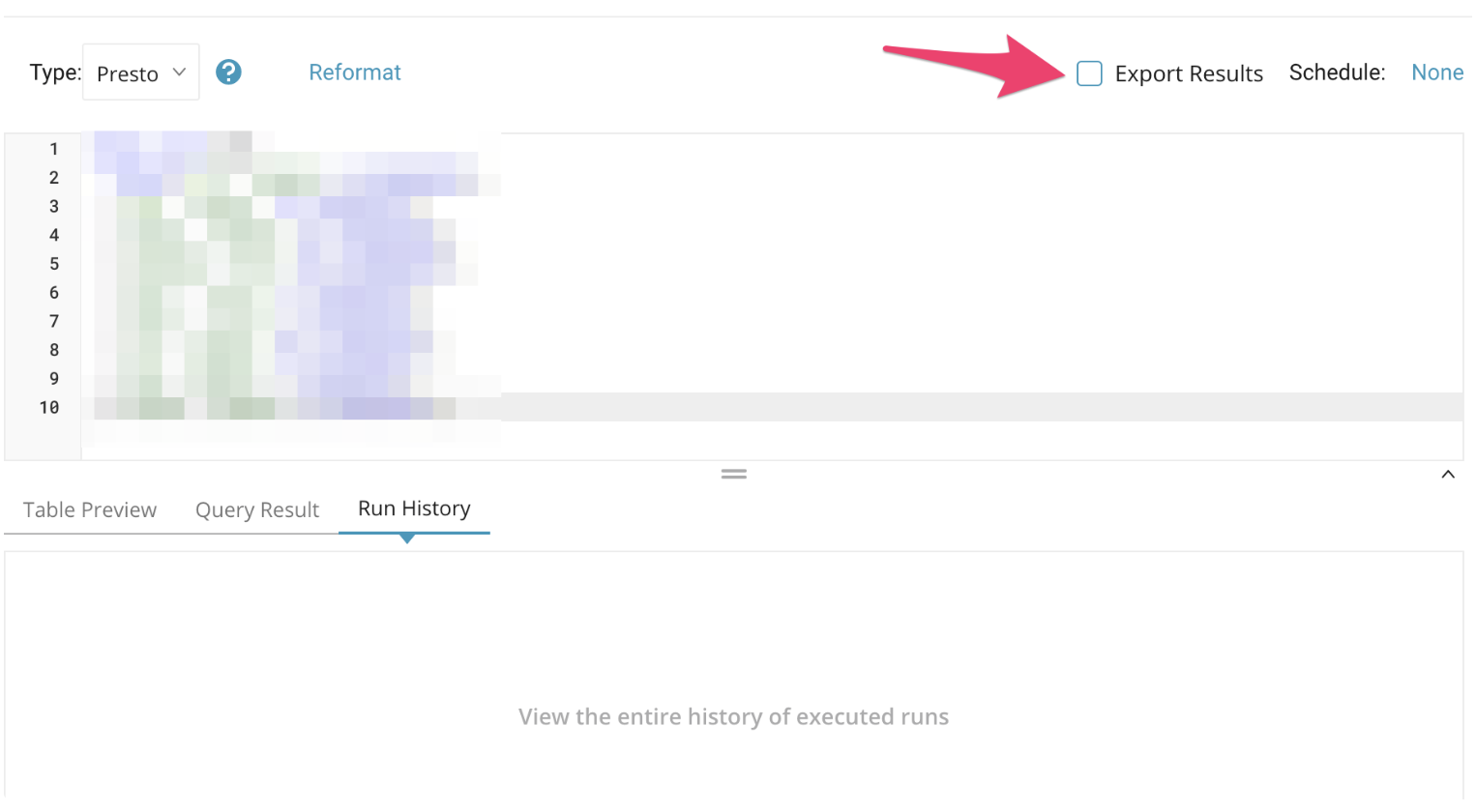
The Choose Integration dialog opens. You have two options when selecting a connection to use to export the results: Usle an Existing Condition or Create a New MySQL Connection.
Type the connection name in the search box and select your connection.
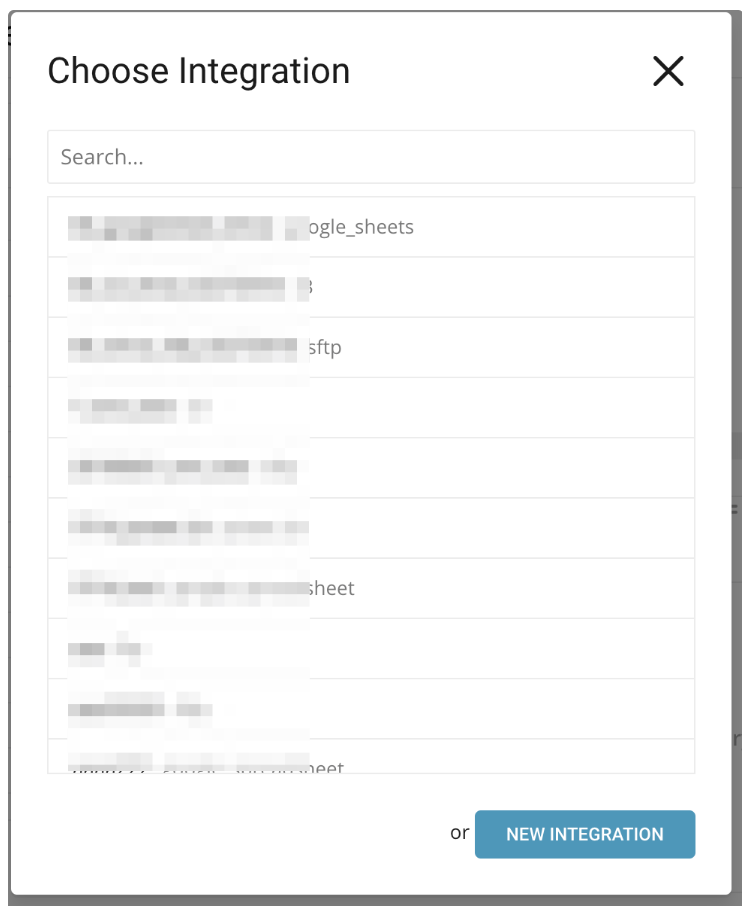
Fill in the field values to create a new connection.
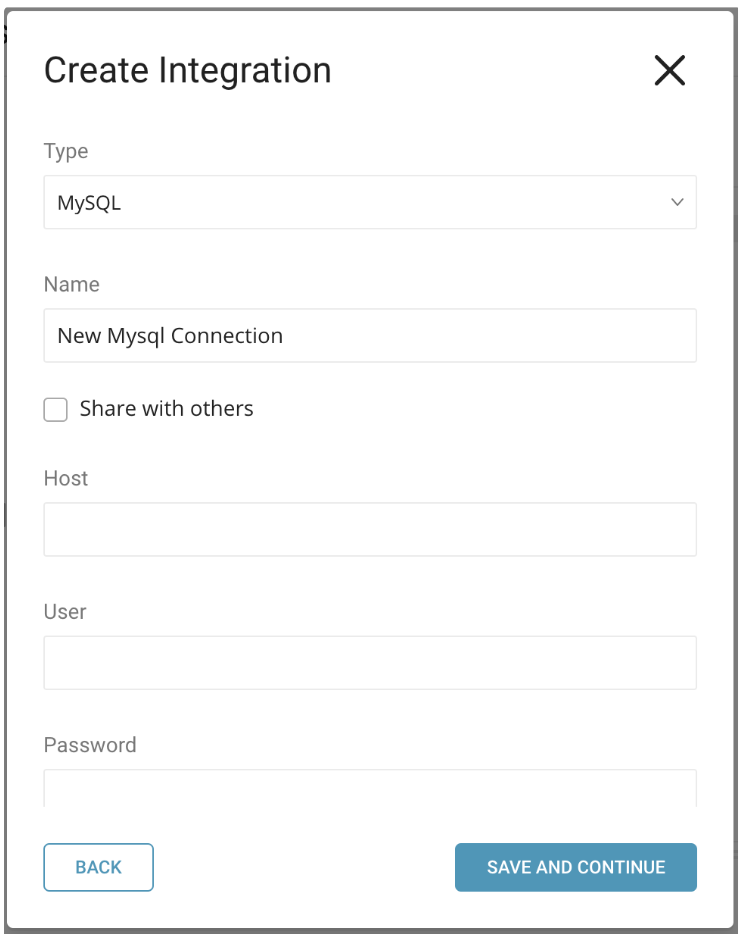
Enter the required credentials for your new MySQL connection. Set the following parameters:
- Host: The host information of the source database, such as an IP address.
- User: Username to connect to the source database.
- Password: Password to connect to the source database.
- Use SSL: Check this box to connect using SSL
- Require a valid SSL certificate?: Require that a valid SSL certificate is presented on the connection.
After setting up your connection, set the transfer parameters.
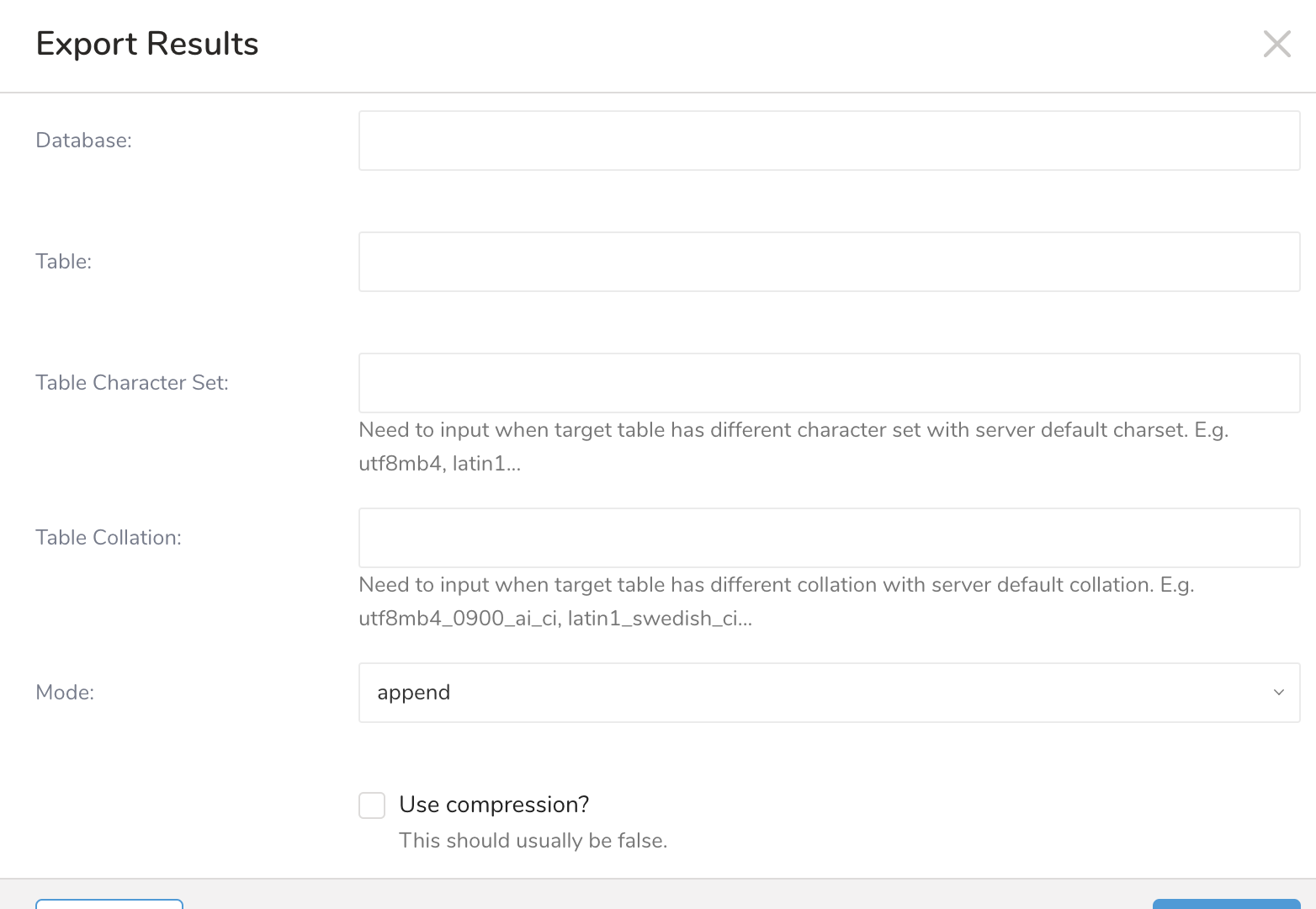
Database name: The name of the database to which you transfer data. (Ex.
your_database_name)Table: The table to which you want to export the data.
Table Charset: Need to input when target table has a different character set with server default charset. E.g. utf8mb4
Table Collation: Need to input when target table has a different collation with server default collation. E.g. utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci, utf8mb4_general_ci
Output mode. Different methods to upload the data.
- Append (default used when no mode option is provided in the URL) Query results are appended to the table. If the table does not exist, a table is created. This mode is atomic. Using SQL statement
INSERT INTO target_table SELECT * FROM * temp_table;
- Replace: Replaces the entire content of an existing table with the resulting query output. If the table does not exist yet, a new table is created. The replace mode achieves atomicity (so that a consumer of the table always has consistent data) by performing the following three steps in a single transaction:
- Create a temporary table.
- Write to the temporary table.
- Replace the existing table with the temporary table using ALTER TABLE RENAME. Using replace mode may change the schema of the MySQL table. To avoid schema changes to the target table, select the Preserve schema? option.
- Using SQL statements
- if target_table does not exist: RENAME temp_table --> target_table
- if target_table exist: RENAME temp_table --> swap_table, target_table --> temp_table, swap_table --> target_table
- Truncate: The system first truncates the existing table and inserts the query results, as in Append mode. If the table does not exist yet, a new table is created. This mode is atomic.
- Update: A row is inserted unless it can cause a duplicate value in the columns specified in the “unique” parameter: in such case, an update is performed instead. The “unique” parameter is only applied when using the update mode. This mode is atomic. SQL statements
- no unique parameter or null: REPLACE INTO target_table SELECT * FROM * temp_table;
- unique parameter: do upsert
- UPDATE target_table, temp_table SET target_table.* = temp_table.* WHERE target_table.unique_keys = temp_table.unique_keys
- INSERT INTO target_table SELECT * FROM temp_table WHERE NOT EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM target_table TD WHERE target_table.unique_keys = temp_table.unique_keys)
- Append (default used when no mode option is provided in the URL) Query results are appended to the table. If the table does not exist, a table is created. This mode is atomic. Using SQL statement
Use compression: Connections to the server can use compression on the traffic between client and server to reduce the number of bytes sent over the connection.
Use UTF-8 Encoding: Backward compatible for MySQL server config with UTF-8 format.
Run the query with the 'Output Results' checkbox checked. If the query completes successfully, you will see the results in the MySQL database and table you specified when entering the transfer details.
You can also send segment data to the target platform by creating an activation in the Audience Studio.
- Navigate to Audience Studio.
- Select a parent segment.
- Open the target segment, right-mouse click, and then select Create Activation.
- In the Details panel, enter an Activation name and configure the activation according to the previous section on Configuration Parameters.
- Customize the activation output in the Output Mapping panel.
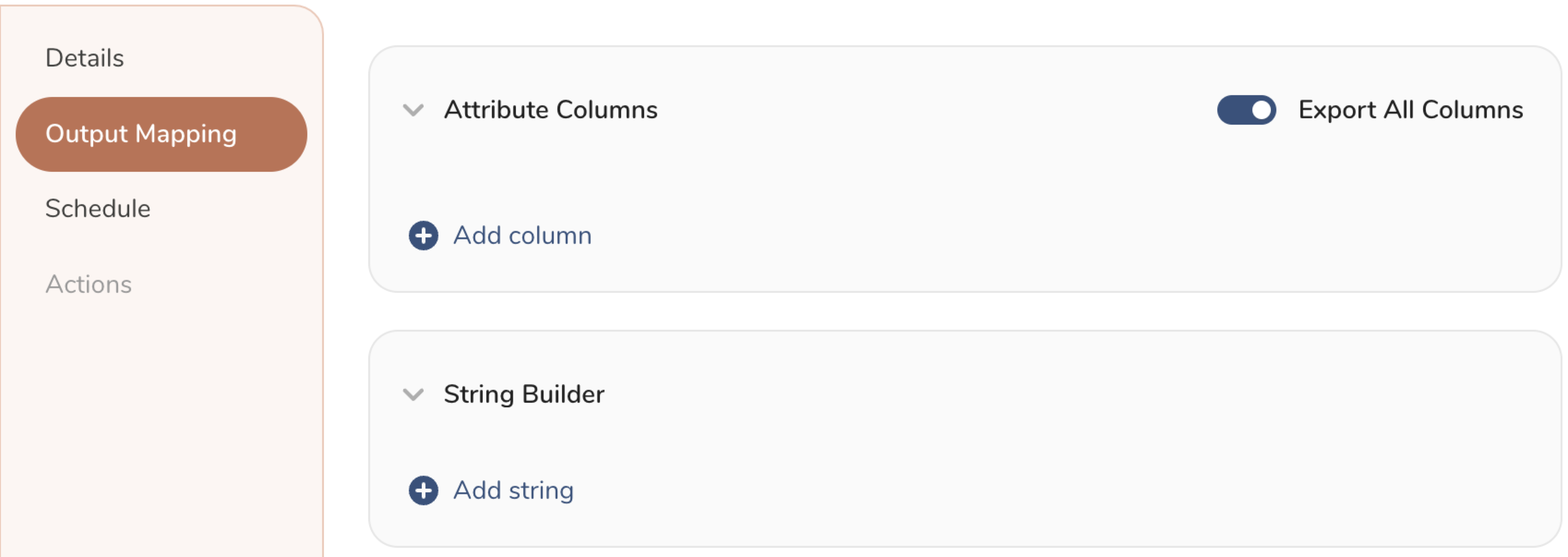
- Attribute Columns
- Select Export All Columns to export all columns without making any changes.
- Select + Add Columns to add specific columns for the export. The Output Column Name pre-populates with the same Source column name. You can update the Output Column Name. Continue to select + Add Columnsto add new columns for your activation output.
- String Builder
- + Add string to create strings for export. Select from the following values:
- String: Choose any value; use text to create a custom value.
- Timestamp: The date and time of the export.
- Segment Id: The segment ID number.
- Segment Name: The segment name.
- Audience Id: The parent segment number.
- + Add string to create strings for export. Select from the following values:
- Set a Schedule.
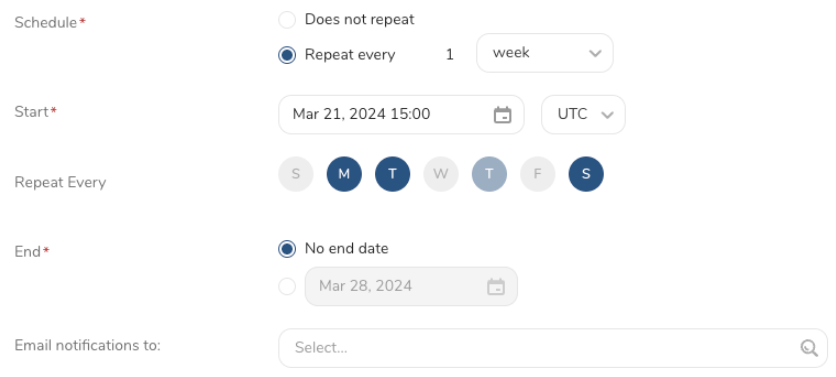
- Select the values to define your schedule and optionally include email notifications.
- Select Create.
Scheduled Jobs with Result Output periodically writes the output result to a specified MySQL instance.
Within Treasure Workflow, you can specify the use of this data connector to output data.
timezone: UTC
_export:
td:
database: sample_datasets
+td-result-output-mysql:
td>: queries/sample.sql
result_connection: your_connections_name
result_settings:
database: database_name
table: table_name
mode: appendIn MySQL 5.7, the default collation was utf8mb4_general_ci. In MySQL 8, however, the default character set is utf8mb4, and the default collation is utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
The MySQL output connector may not work in update mode (with unique setting) when the server default collation (used to create temp table) is different from the target table collation (illegal mix of collations error)
Then we need to use two settings (table_charset and table_collation) to make sure the temp table will have the same charset and collation as the target table
(The "illegal mix of collations" error in MySQL occurs when you try to compare or combine text columns with incompatible collations (collations are a set of rules for comparing characters in a character set).