The Data Connector for MongoDB enables importing documents (records) stored in your MongoDB server, to Treasure Data.
- Basic knowledge of Treasure Data
You can create an instance of the MongoDB data connector from the TD Console. Select create on the MongoDB connector tile.

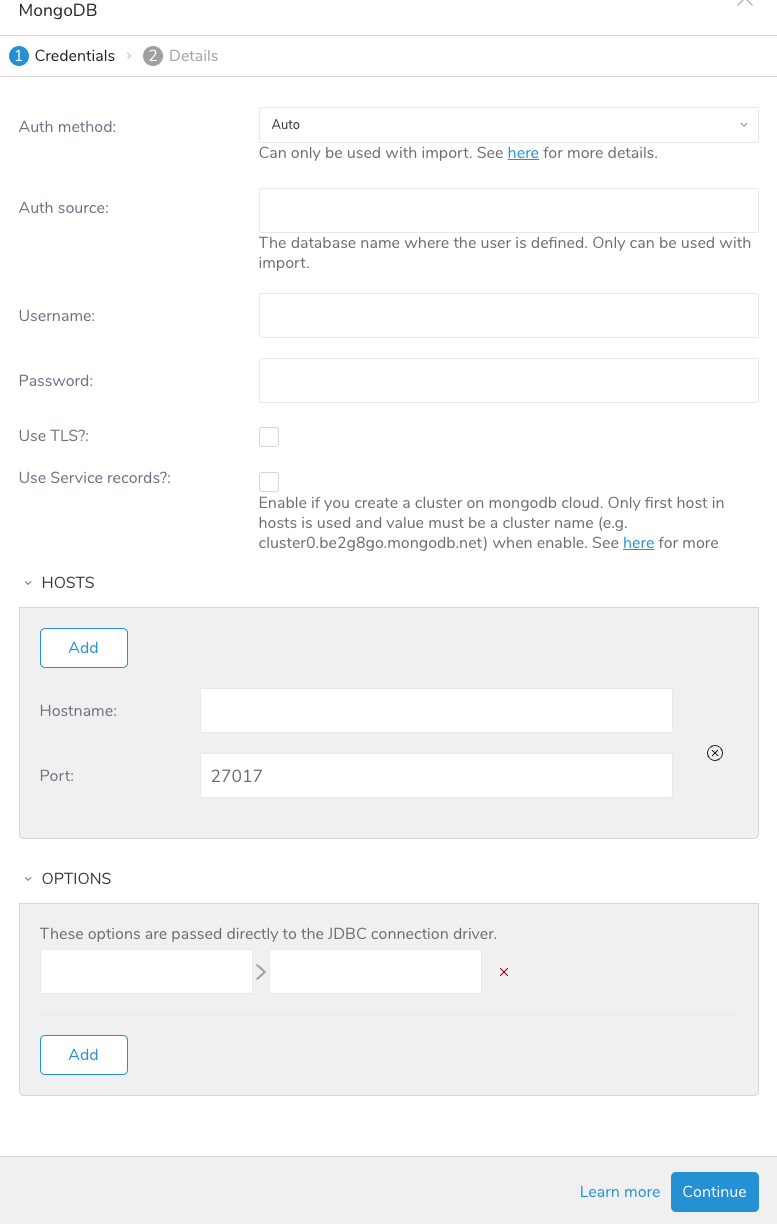
Enter the required credentials for your MongoDB instance. Set the following parameters.
Auth method: Auth method to authenticate.
If you choose "Auto", The connector negotiates the best mechanism based on the version of the server that the connector is authenticating to.
If the server version is 3.0 or higher, the driver authenticates using the SCRAM-SHA-1 mechanism.
Otherwise, the driver authenticates using the MONGODB_CR mechanism.
Auth source: The database name where the user is defined.
Username: Username to connect to the remote database.
Password: Password to connect to the remote database.
Use TLS?: Check this box to connect using TLS (SSL).
Bypass certificate validations?: Check this box to bypass all certificate validations.
Use Service records?: Enable if you create a cluster on MongoDB cloud. Only the first host in hosts is used and the value must be a cluster name (e.g. cluster0.be2g8go.mongodb.net) when enabling.
Hostname: The hostname or IP address of the remote Server. (You can add more than one IP address, depending on your MongoDB setup.)
Port: Port number of the remote server (Default is 27017).
Options: JDBC key-value pairs that are passed to the driver (see Connection Options for more information on these options)
Select Continue after entering the required connection details. Name the connection so you can find it later if you need to modify any of the connection details. If you would like to share this connection with other users in your organization, select Share with others. If this box is unchecked, this connection is visible to only you.
Select Create Connection to complete the connection. If the connection is a success, then the connection you just created appears in your list of connections with the name you provided.
After creating the connection to your remote database, you can import the data from your database into Treasure Data. You can set up an ad hoc one-time transfer or a recurring transfer at regular intervals.
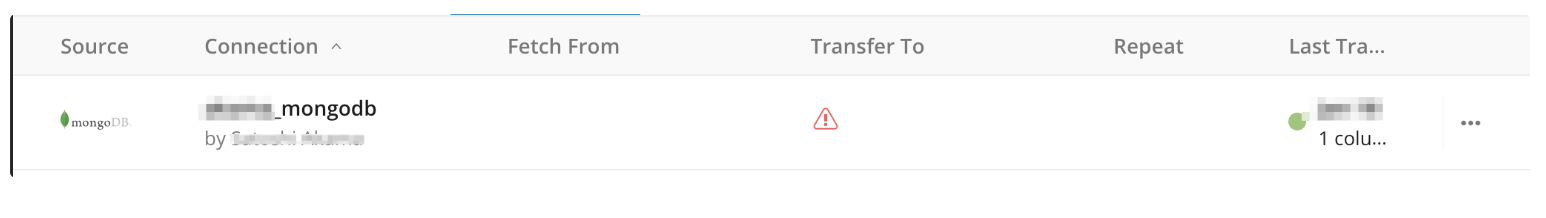
Provide the details of the database and table from which you want to ingest data.
- Database name: The name of the database from which you are transferring data. (for example,
your_database_name) - Collection Name: The name of the collection from which you are transferring data.
- JSON Query: Specifies records to return
- JSON Projection: Specifies fields to return
Select Next to preview the data in the next step.
If there are no errors with the connection, you see a preview of the data to be imported. If you are unable to see the preview or have any issues viewing the preview, contact support.
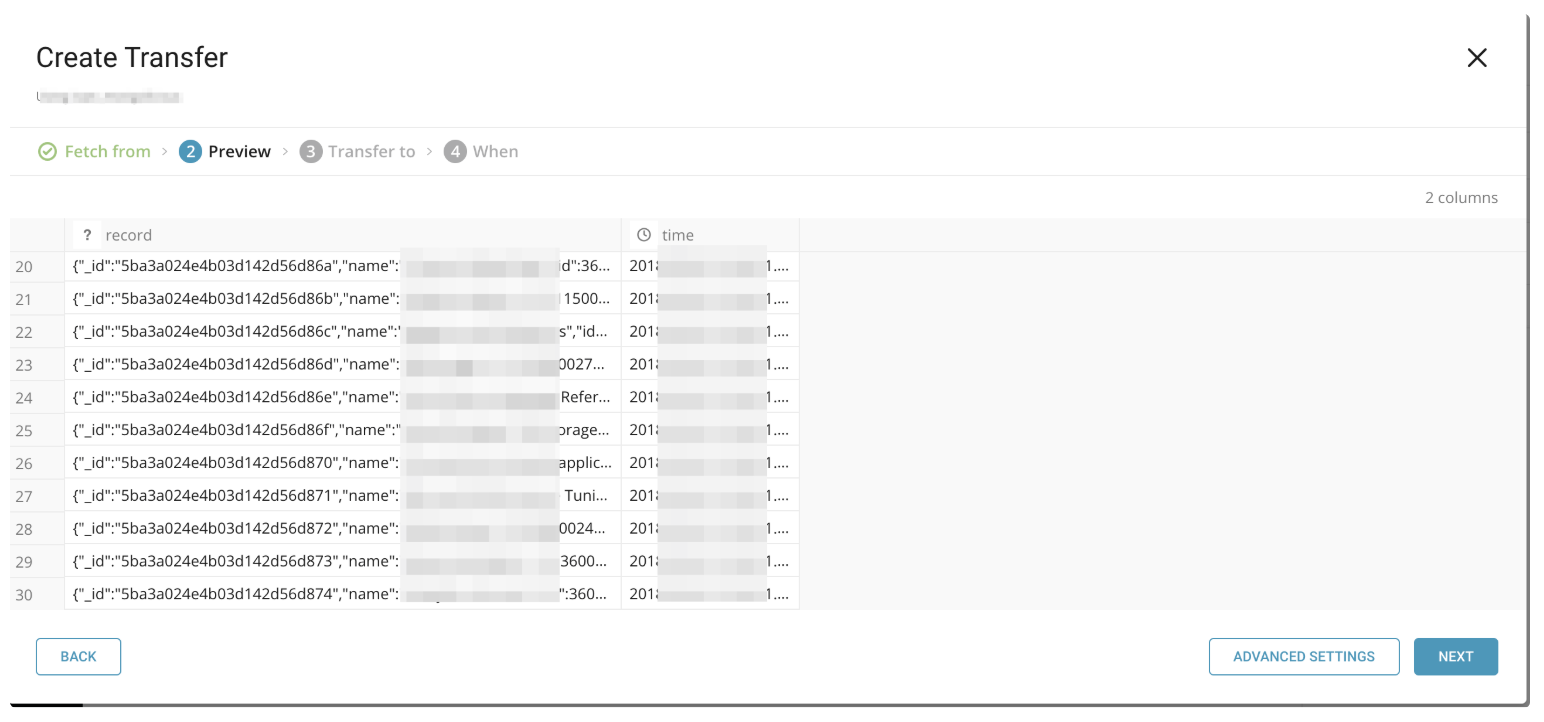
The records arw imported into one column both during the preview and when the data import is run. If you need to use non-standard options for your import, select Advanced Settings.
Advanced Settings allow to you modify aspects of your transfer to allow for special requirements. The following fields are available in Preview > Advanced Settings.
- Object ID field name: Name of Object ID field name to import.
- Load only new records each run: If checked/enabled, you must specify which fields to sort by
- Sort by: Fields to use to sort records. Required if
Load only new records each runis checked. - Aggregation query : Query string for aggregation. See also Aggregation — MongoDB Manual and Aggregation Pipeline Stages — MongoDB Manual
- Output column name: The name of the column to output the records to.
- Stop on invalid record: If checked, the transfer will stop and not complete if it encounters an invalid record.
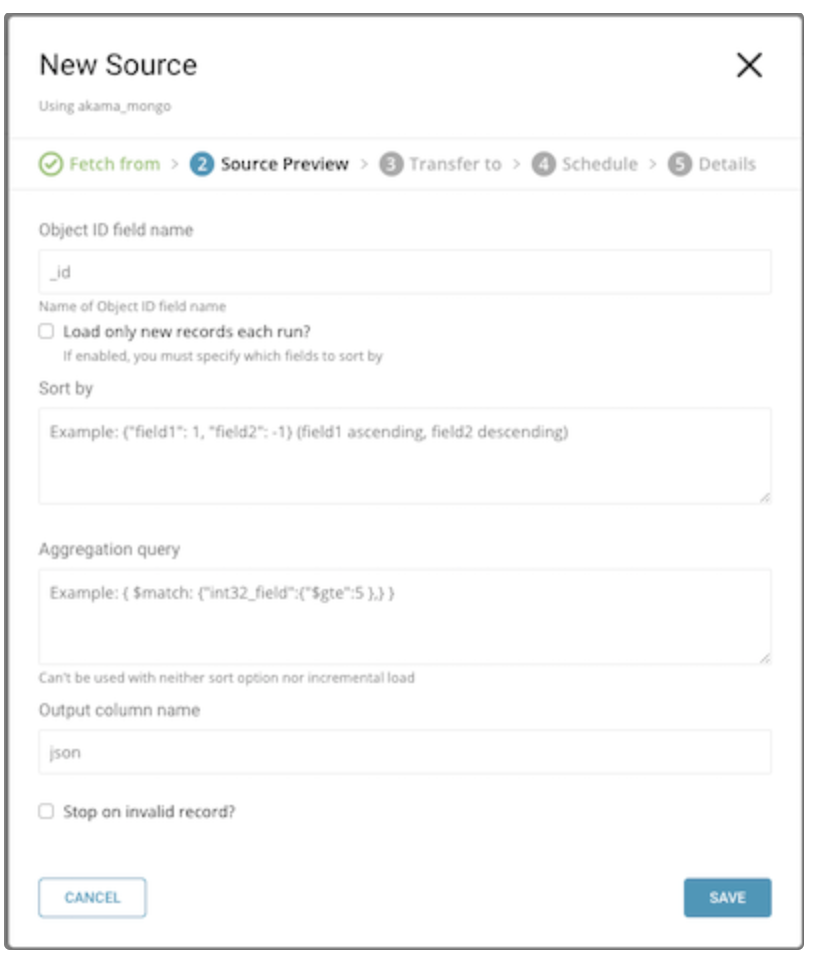
In this phase, select the Treasure Data target database and table into which you want to import your data. You can create a new database or table using Create new database or Create new table.
- Database: The database into which to import the data.
- Table: The table within the database to import the data.
- Mode: Append – Allows you to add records into an existing table.
- Mode: Replace – Replace the existing data in the table with the data being imported.
- Partition Key Seed: Choose the long or timestamp column that you would like to use as the partitioning time column. If you do not specify a time column, the upload time of the transfer is used in conjunction with the addition of a
timecolumn. - Data Storage Timezone: Data Storage Timezone – Timezone in which the data is stored; data is also displayed in this timezone.
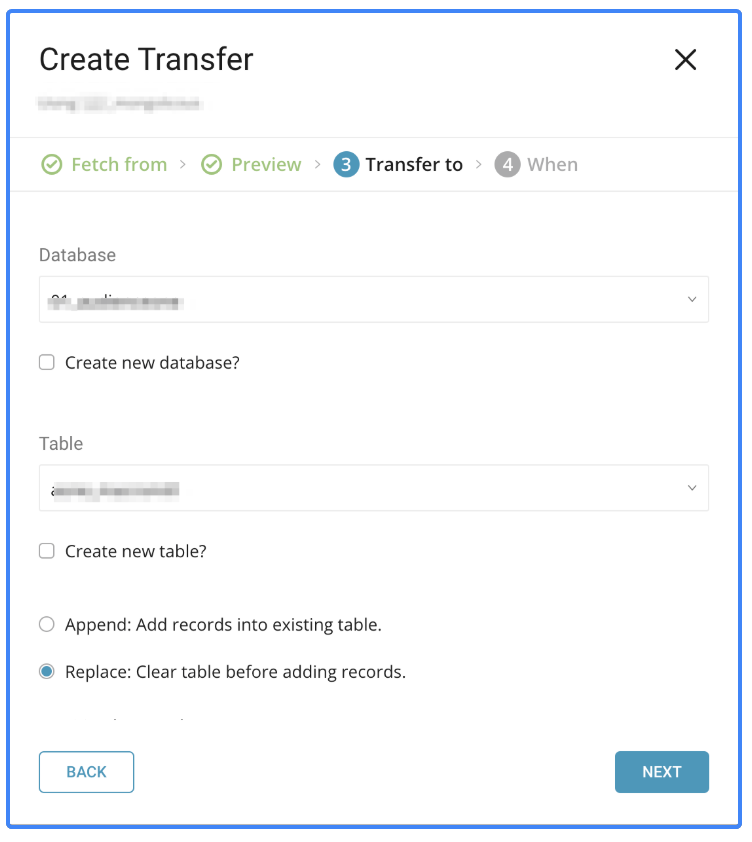
In this phase, you can choose to run the transfer only one time or schedule it to run at a specified frequency.
When
Once now: Run the transfer only once.
Repeat…
- Schedule: accepts these three options:
@hourly,@dailyand@monthlyand customcron. - Delay Transfer: add a delay of execution time.
- Schedule: accepts these three options:
Time Zone: supports extended timezone formats like ‘Asia/Tokyo’.
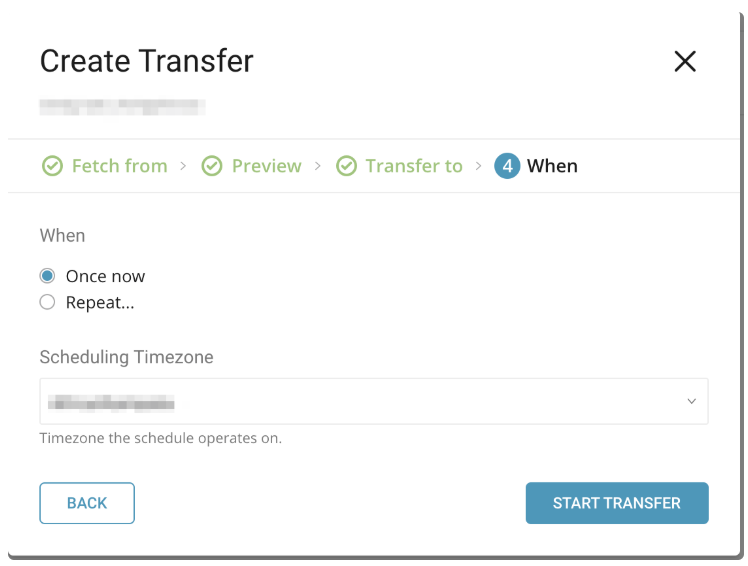
After selecting the frequency, select Start Transfer to begin the transfer. If there are no errors, the transfer into Treasure Data will complete and the data will be available.
If you need to review the transfer you have just completed for other data connector jobs, you can view a list of your transfers in the My Input Transfers section.
You can also use the MongoDB data connector from the command line interface. The following instructions show you how to import data using the CLI.
Install the newest TD Toolbelt.
$ td --version
0.11.10First, prepare seed.yml as shown, with your MongoDB details. Create seed.yml with the following content.
in:
type: mongodb
hosts:
- {host: HOST, port: PORT}
auth_method: auto
#auth_source: AUTH_SOURCE_DB
user: USER
password: PASSWORD
database: DATABASE
collection: COLLECTION
options:
connectTimeoutMS: 10000
socketTimeoutMS: 10000
projection: '{"_id": 0}'
query: '{}'
sort: '{}'
stop_on_invalid_record: true
out:
mode: append
exec: {}The Data Connector for MongoDB imports all documents that are stored in a specified collection. You may filter fields, specify queries, or sort with the following options.
A JSON document used for projection on query results. Fields in a document are used only if they match with this condition.
projection: '{ "_id": 1, "user_id": 1, "company": 1 }'A JSON document used for querying on the source collection. Documents are loaded from the collection if they match with this condition.
query: '{ user_id: { $gte: 20000 } }'Order of result
sort: '{ "field1": 1, "field2": -1}' # field1 ascending, field2 descendingThis option can't be used with aggregation option.
For more details on available out modes, see Appendix.
Aggregation query
aggregation: '{ $match: { field1: { $gt: 1}} }' # where field1 is greater than 1This option can't be used with sort option.
For more details on available out modes, see Appendix.
The Data Connector MongoDB loads MongoDB’s documents as a single column and therefore doesn’t support connector:guess. Edit all settings in your load.yml.
You can preview how the system parses the documents by using the preview command.
$ td connector:preview load.yml
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| record:json |
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| "{\"user_id\":11200,\"company\":\"AA Inc.\",\"customer\":\"David\",\"created_at\":\"2015-03-31T06:12:37.000Z\"}" |
| "{\"user_id\":20313,\"company\":\"BB Imc.\",\"customer\":\"Tom\",\"created_at\":\"2015-04-01T01:00:07.000Z\"}" |
| "{\"user_id\":32132,\"company\":\"CC Inc.\",\"customer\":\"Fernando\",\"created_at\":\"2015-04-01T10:33:41.000Z\"}" |
| "{\"user_id\":40133,\"company\":\"DD Inc.\",\"customer\":\"Cesar\",\"created_at\":\"2015-04-02T05:12:32.000Z\"}" |
| "{\"user_id\":93133,\"company\":\"EE Inc.\",\"customer\":\"Jake\",\"created_at\":\"2015-04-02T14:11:13.000Z\"}" |
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+The data connector supports parsing of “boolean”, “long”, “double”, “string”, and “timestamp” types.
You also must create a local database and table prior to executing the data load job.
$ td database:create td_sample_db
$ td table:create td_sample_db td_sample_tableFinally, submit the load job. It may take a couple of hours depending on the size of the data. Specify the Treasure Data database and table where the data should be stored.
Specify --time-column option, because Treasure Data’s storage is partitioned by time (see Data Partitioning in Treasure Data). If the option is not provided, the Data Connector will choose the first long or timestamp column as the partitioning time. The type of the column specified by --time-column must be either of long or timestamp type.
If your data doesn’t have a time column you can add it using add_time filter option. For more details see add_time filter plugin.
If you want to expand the JSON column, you may add it using the expand_json filter option. More details at expand_json filter plugin
$ td connector:issue load.yml --database td_sample_db --table td_sample_table --time-column created_atThe connector:issue command assumes that you have already created a database*(td_sample_db)* and a table*(td_sample_table)*. If the database or the table do not exist in TD, the connector:issue command will fail, so create the database and table manually or use the --auto-create-table option with the td connector:issue command to auto-create the database and table:
$ td connector:issue load.yml --database td_sample_db --table td_sample_table --time-column created_at --auto-create-tableThe Data Connector does not sort records on server-side. To use time-based partitioning effectively, sort records beforehand.
If you have a field called time, you don’t have to specify the --time-column option.
td connector:issue load.yml --database td_sample_db --table td_sample_tableYou can load records incrementally by specifying a field in your table that contains date information by utilizing the incremental_field and last_record options.
in:
type: mongodb
hosts:
- {host: HOST, port: PORT}
user: USER
password: PASSWORD
database: DATABASE
collection: COLLECTION
projection: '{"_id": 0}'
incremental_field:
- "field1"
last_record: {"field1": {"$date": "2015-01-25T13:23:15.000Z"}}
stop_on_invalid_record: true
out:
mode: append
exec: {}The connector automatically creates the query and sort values.
query '{ field1: { $gt: {"$date": "2015-01-25T13:23:15.000Z"} }}' # field1 > "2015-01-25T13:23:15.000Z"
sort '{"field1", 1}' # field1 ascendingYou can also specify multiple fields for incremental_fields.
incremental_field:
- "field1"
- "field2"
last_record: {"field1": {"$date": "2015-01-25T13:23:15.000Z"}, "field2": 13215}The connector creates query and sort values using ‘AND’ condition.
query '{ field1: { $gt: {"$date": "2015-01-25T13:23:15.000Z"} }, field2: { $gt: 13215}}' # field1 > "2015-01-25T13:23:15.000Z" AND field2 > 13215
sort '{"field1", 1, "field2", 1}' # field1 ascending, field2 ascendingThe sort option can't be used when you specify incremental\_field. The aggregation option can't be used when you specify incremental\_field.
You must specify last\_record with special characters when the field type is ObjectId or DateTime.
- ObjectId field
in:
type: mongodb
incremental_field:
- "_id"
last_record: {"_id": {"$oid": "5739b2261c21e58edfe39716"}}- DateTime field
in:
type: mongodb
incremental_field:
- "time_field"
last_record: {"time_field": {"$date": "2015-01-25T13:23:15.000Z"}}You can schedule periodic data connector executions for MongoDB data imports. We configure our scheduler carefully to ensure high availability. By using this feature, you no longer need a cron daemon on your local data center.
A new schedule can be created using the td connector:create command. The following are required: the name of the schedule, the cron-style schedule, the database and table where the data will be stored, and the Data Connector configuration file.
$ td connector:create \
daily_import \
"10 0 * * *" \
td_sample_db \
td_sample_table \
load.ymlIt’s also recommended to specify the --time-column option since Treasure Data’s storage is partitioned by time (see data partitioning).
$ td connector:create \
daily_import \
"10 0 * * *" \
td_sample_db \
td_sample_table \
load.yml \
--time-column created_atThe cron parameter also accepts three special options: @hourly, @daily and @monthly. By default, schedule is setup in UTC timezone. You can set the schedule in a timezone using -t or --timezone option. Note that --timezone option supports only extended timezone formats like 'Asia/Tokyo', 'America/Los_Angeles' etc. Timezone abbreviations like PST, CST are not supported and may lead to unexpected schedules.