Learn more about Microsoft SQL Server Import Integration.
You can write job results directly to your Microsoft SQL Server tables.
For sample workflows on exporting to your SQL Server tables, see Treasure Boxes.
- Basic knowledge of Treasure Data.
- A SQL Server instance.
Open the TD Console.
Navigate to Data Workbench > Queries.
Create a new query or select an existing query.
Select Export Results.
The Choose Integration dialog opens. Select one of two options:
Use Existing Integration. Select the existing integration.
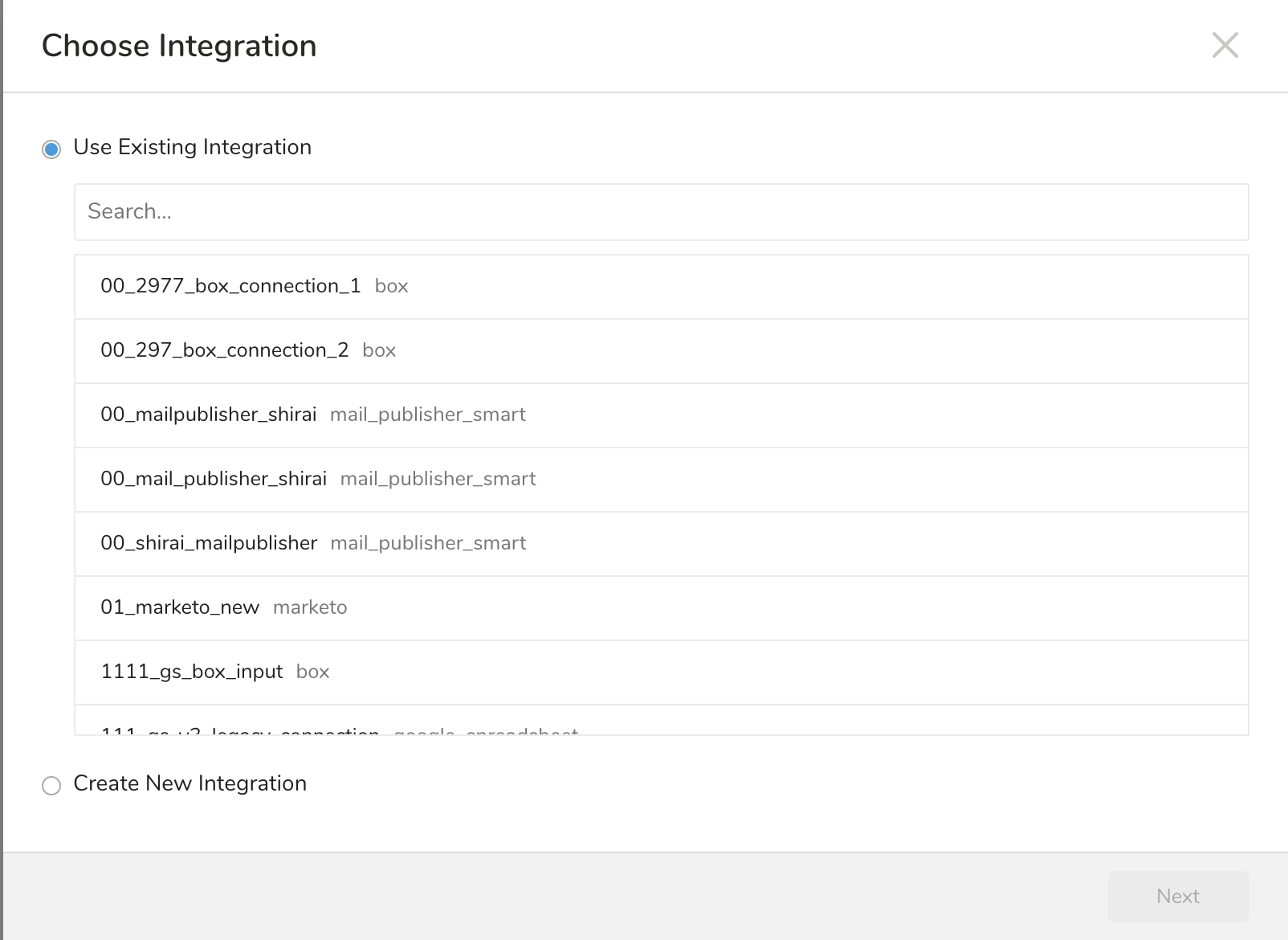
Create New Integration. Select the integration type and edit the integration Name, Host, User, and Password.
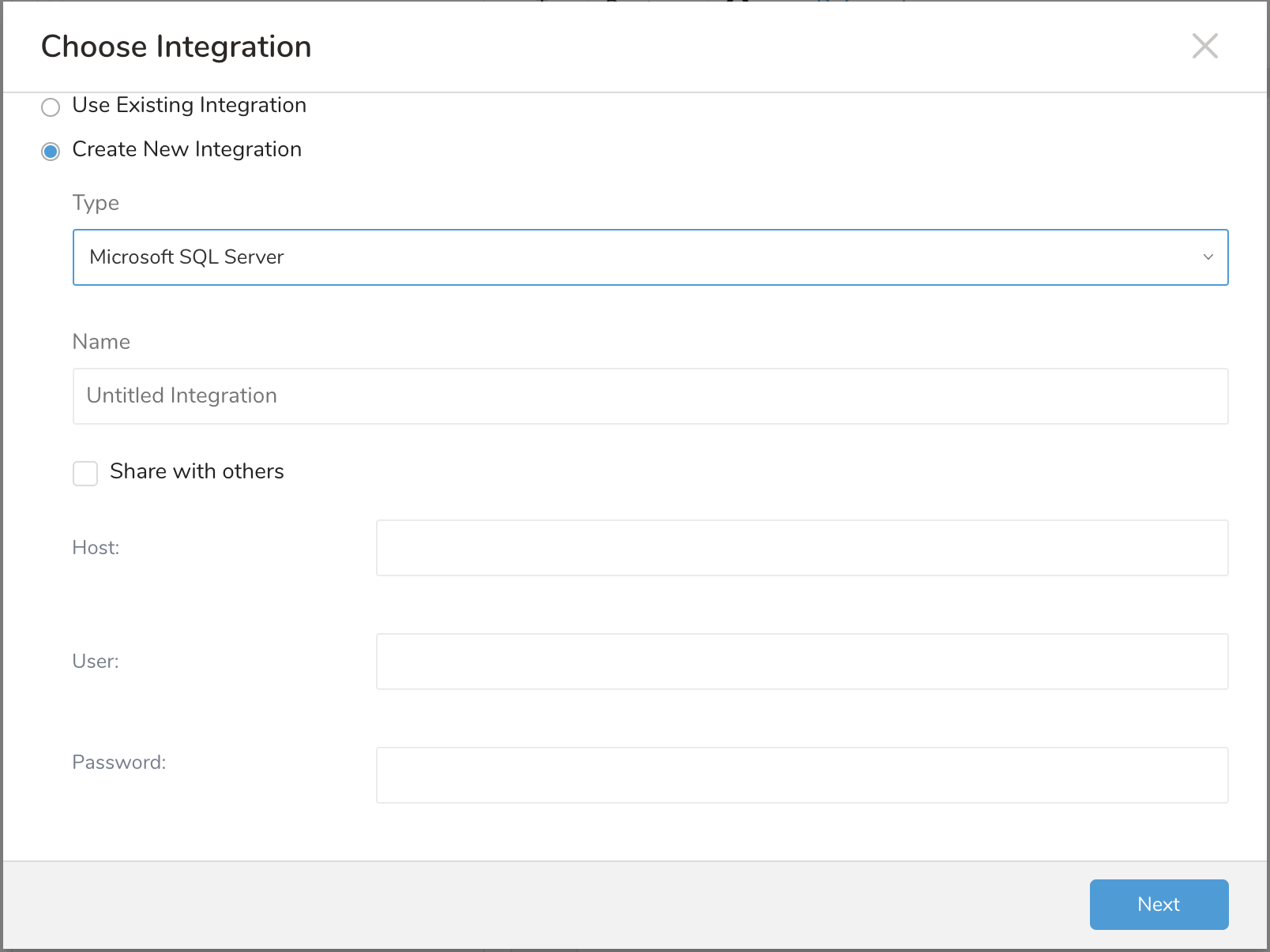
- If you are using Azure, omit the instance name and provide the port # only.
- If you are not using Azure and want to use your own instance: make sure that you can connect to the database using only the instance name, without the port. The reason for this is that when port is set, the instance name will be ignored. The JDBC library does not try to resolve from name to port but instead uses the port in configuration. Check with a database connector tool without using the given port.
Fill the output data information
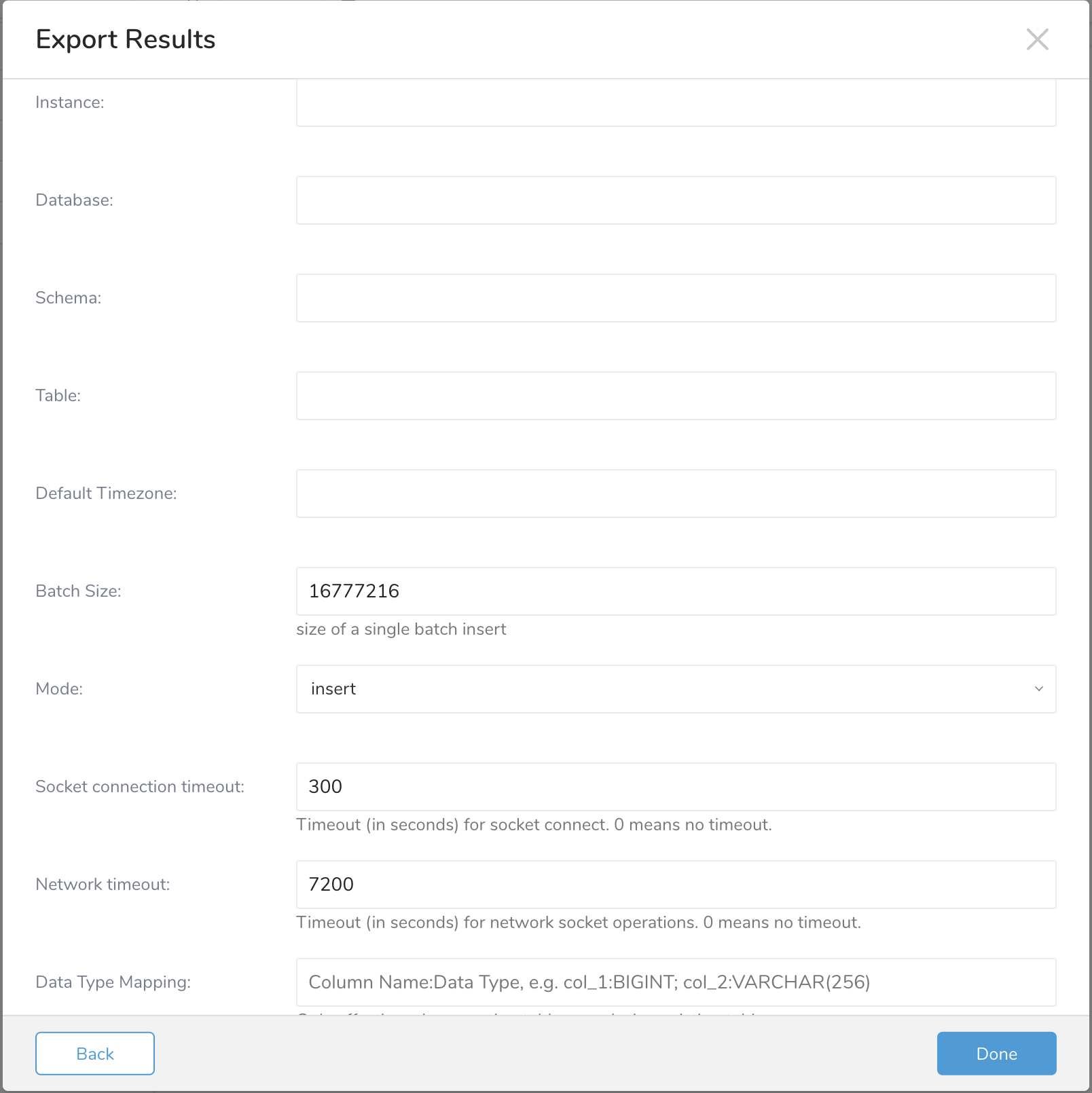
The information include:
Instance: the instance name
Database: the database name
Schema: the schema name
Table: the table name
Default Timezone: the default timezone
Batch Size: the batch size run
Mode:
- insert
- insert_direct
- truncate_insert
- replace
- merge
Socket connection timeout: the limit timeout for socket connection
Network timeout: the limit timeout for network connection
Data Type Mapping: the column data type mapping. Only effective when creating table or replacing existing table.
Save the query with a name and run, or just run the query. After successful completion of the query, the results are exported to the specified SQL Server destination.
You can use Scheduled Jobs with Result Export to periodically write the output result to a target destination that you specify.
Treasure Data's scheduler feature supports periodic query execution to achieve high availability.
When two specifications provide conflicting schedule specifications, the specification requesting to execute more often is followed while the other schedule specification is ignored.
For example, if the cron schedule is '0 0 1 * 1', then the 'day of month' specification and 'day of week' are discordant because the former specification requires it to run every first day of each month at midnight (00:00), while the latter specification requires it to run every Monday at midnight (00:00). The latter specification is followed.
Navigate to Data Workbench > Queries
Create a new query or select an existing query.
Next to Schedule, select None.

In the drop-down, select one of the following schedule options:
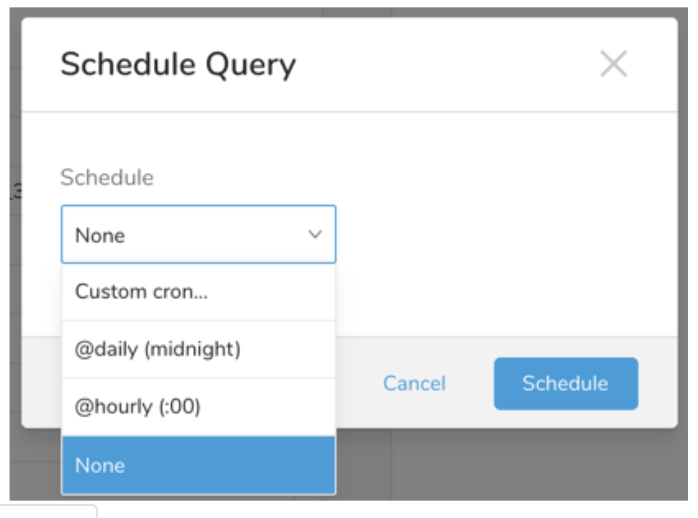
Drop-down Value Description Custom cron... Review Custom cron... details. @daily (midnight) Run once a day at midnight (00:00 am) in the specified time zone. @hourly (:00) Run every hour at 00 minutes. None No schedule.
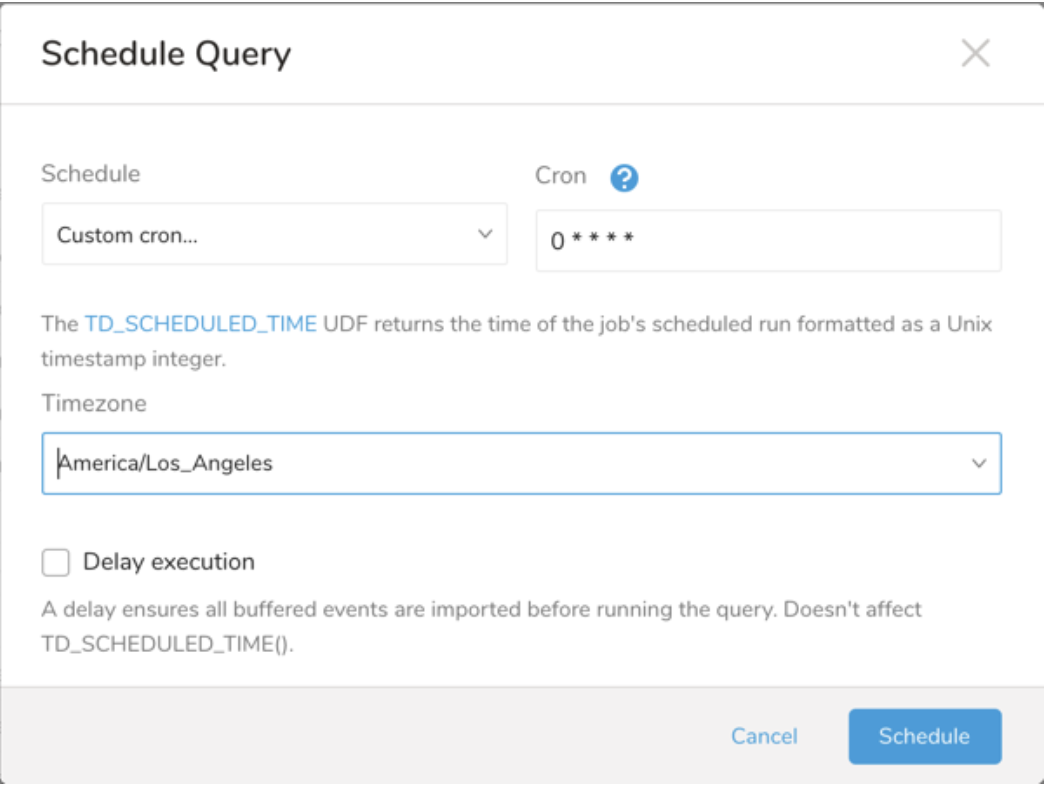
| Cron Value | Description |
|---|---|
0 * * * * | Run once an hour. |
0 0 * * * | Run once a day at midnight. |
0 0 1 * * | Run once a month at midnight on the morning of the first day of the month. |
| "" | Create a job that has no scheduled run time. |
* * * * *
- - - - -
| | | | |
| | | | +----- day of week (0 - 6) (Sunday=0)
| | | +---------- month (1 - 12)
| | +--------------- day of month (1 - 31)
| +-------------------- hour (0 - 23)
+------------------------- min (0 - 59)The following named entries can be used:
- Day of Week: sun, mon, tue, wed, thu, fri, sat.
- Month: jan, feb, mar, apr, may, jun, jul, aug, sep, oct, nov, dec.
A single space is required between each field. The values for each field can be composed of:
| Field Value | Example | Example Description |
|---|---|---|
| A single value, within the limits displayed above for each field. | ||
A wildcard '*' to indicate no restriction based on the field. | '0 0 1 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) on the first day of each month. |
A range '2-5', indicating the range of accepted values for the field. | '0 0 1-10 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) on the first 10 days of each month. |
A list of comma-separated values '2,3,4,5', indicating the list of accepted values for the field. | 0 0 1,11,21 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) every 1st, 11th, and 21st day of each month. |
A periodicity indicator '*/5' to express how often based on the field's valid range of values a schedule is allowed to run. | '30 */2 1 * *' | Configures the schedule to run on the 1st of every month, every 2 hours starting at 00:30. '0 0 */5 * *' configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) every 5 days starting on the 5th of each month. |
A comma-separated list of any of the above except the '*' wildcard is also supported '2,*/5,8-10'. | '0 0 5,*/10,25 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) every 5th, 10th, 20th, and 25th day of each month. |
- (Optional) You can delay the start time of a query by enabling the Delay execution.
Save the query with a name and run, or just run the query. Upon successful completion of the query, the query result is automatically exported to the specified destination.
Scheduled jobs that continuously fail due to configuration errors may be disabled on the system side after several notifications.
(Optional) You can delay the start time of a query by enabling the Delay execution.
You can also send segment data to the target platform by creating an activation in the Audience Studio.
- Navigate to Audience Studio.
- Select a parent segment.
- Open the target segment, right-mouse click, and then select Create Activation.
- In the Details panel, enter an Activation name and configure the activation according to the previous section on Configuration Parameters.
- Customize the activation output in the Output Mapping panel.
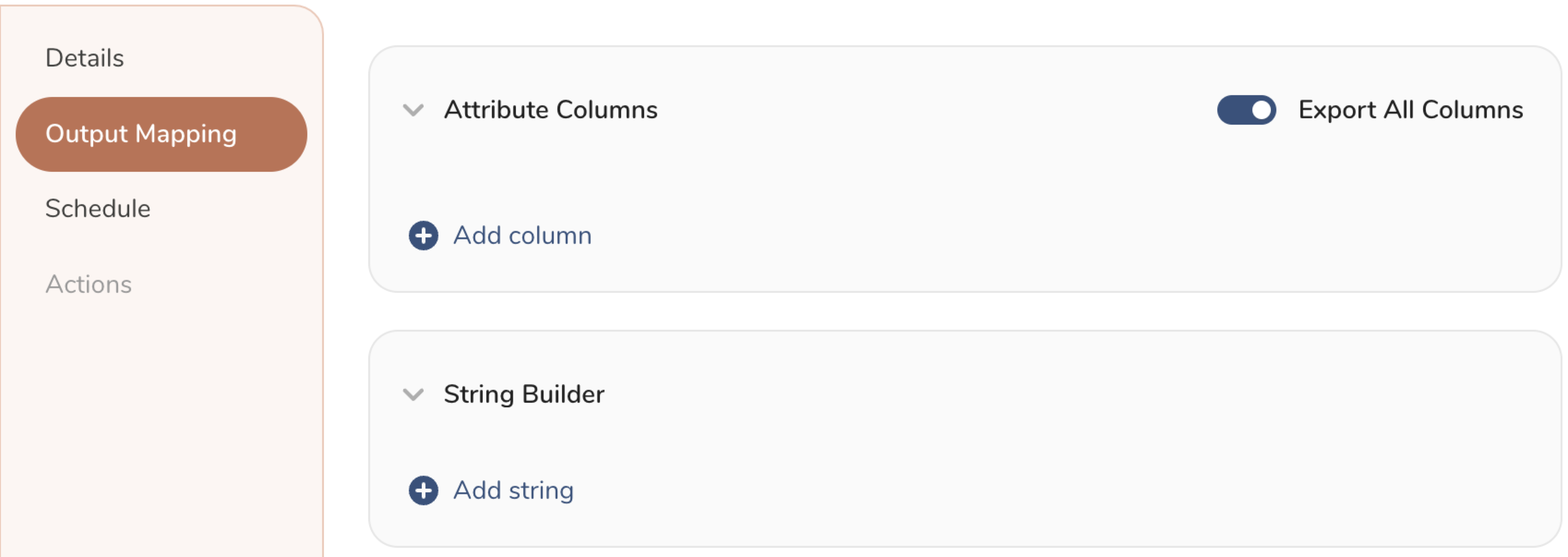
- Attribute Columns
- Select Export All Columns to export all columns without making any changes.
- Select + Add Columns to add specific columns for the export. The Output Column Name pre-populates with the same Source column name. You can update the Output Column Name. Continue to select + Add Columnsto add new columns for your activation output.
- String Builder
- + Add string to create strings for export. Select from the following values:
- String: Choose any value; use text to create a custom value.
- Timestamp: The date and time of the export.
- Segment Id: The segment ID number.
- Segment Name: The segment name.
- Audience Id: The parent segment number.
- + Add string to create strings for export. Select from the following values:
- Set a Schedule.
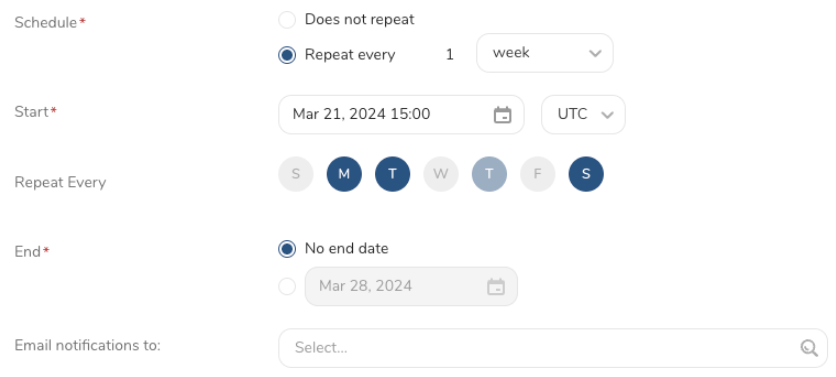
- Select the values to define your schedule and optionally include email notifications.
- Select Create.
If you need to create an activation for a batch journey, review Creating a Batch Journey Activation.
The following command enables you to set a scheduled query with Result Output exported to SQL Server.
Designate your json_key and escape newline with backslash.
For example:
td sched:create scheduled_sqlserver "10 6 * * *" \
-d dataconnector_db "SELECT id,account,purchase,comment,time FROM payment_history" \
-r '{ "type":"sqlserver", "user":"user", "database":"mydb", "table":"payments", "batch_size":16777216, "mode":"insert"}'| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| insert | This mode writes rows to some intermediate tables first. If all those tasks run correctly, runs INSERT INTO target_table SELECT * FROM intermediate_table_1 UNION ALL SELECT * FROM intermediate_table_2 UNION ALL ... query. If the target table doesn't exist, it is created automatically. |
| insert_direct | This mode inserts rows to the target table directly. If the target table doesn't exist, it is created automatically. |
| truncate_insert | Same with insert mode excepting that it truncates the target table right before the last INSERT ... query. |
| replace | This mode writes rows to an intermediate table first. If all those tasks run correctly, drops the target table and alters the name of the intermediate table into the target table name. |
| merge | This mode writes rows to some intermediate tables first. If all those tasks run correctly, runs MERGE INTO ... WHEN MATCHED THEN UPDATE ... WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN INSERT ... query. Namely, if merge keys of a record in the intermediate tables already exist in the target table, the target record is updated by the intermediate record, otherwise the intermediate record is inserted. If the target table doesn't exist, it is created automatically. |
MS SQL Server Result Output fails with “Connection reset” failure while exporting to Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Database is a multi-tenant service. Timeout sometimes occurs due to resource problems. To avoid this problem, we recommend you to try the following workarounds:
- First dump to Azure Blob Storage with Azure Blob Storage Data Result Output, then export to Azure SQL Database.
- Decrease batch_size option's value to something like 3000 to reduce byte size of every insert request. Note that this change may cause long job running time.