Microsoft Azure Data Lake Storage is the industrial leading storage solution for big data. Our import integration helps ingest the parquet files from your Azure Data Lake Storage into Treasure Data for consolidation with other sources set up in Treasure Data.
- Copy all existing data files: You can copy all of your Azure Data Lake parquet files into Treasure Data in order to migrate from the system.
- Ingest data directly: Import data directly from the Azure Data Lake into Treasure Data instead of having to use a bridge system.
- Basic knowledge of Treasure Data
- Basic knowledge of Microsoft Azure Data Lake
- Microsoft Azure Data Lake account with sufficient permissions to create Shared Access Signatures and download files
- Supports only Azure Data Lake Storage (v2)
- Supports only one level of partition keys as a Spark Partition (https://spark.apache.org/docs/2.4.0/sql-data-sources-parquet.html#partition-discovery)
- Supports only snappy compression codec
- No data preview is available due to the time required to process the download and read the parquet file schema
- Supports only the HTTP Proxy method
- Does not support BlobStorageEvents or SoftDelete for Azure
- The delta file format is not supported. (For other common file formats such as CSV and TVS, use Microsoft Azure Blob Storage).
Parquet file size expectation
Treasure Data recommends that you limit Row Group Size to less than 3.4GB. If the Row Group size is larger than 3.4GB, your import job may encounter an "Out of Memory" error.
If this happens, you will need to re-partition your data into smaller parquet file sizes and then retry the import job.
- Navigate to Storage Account management on your Azure Portal
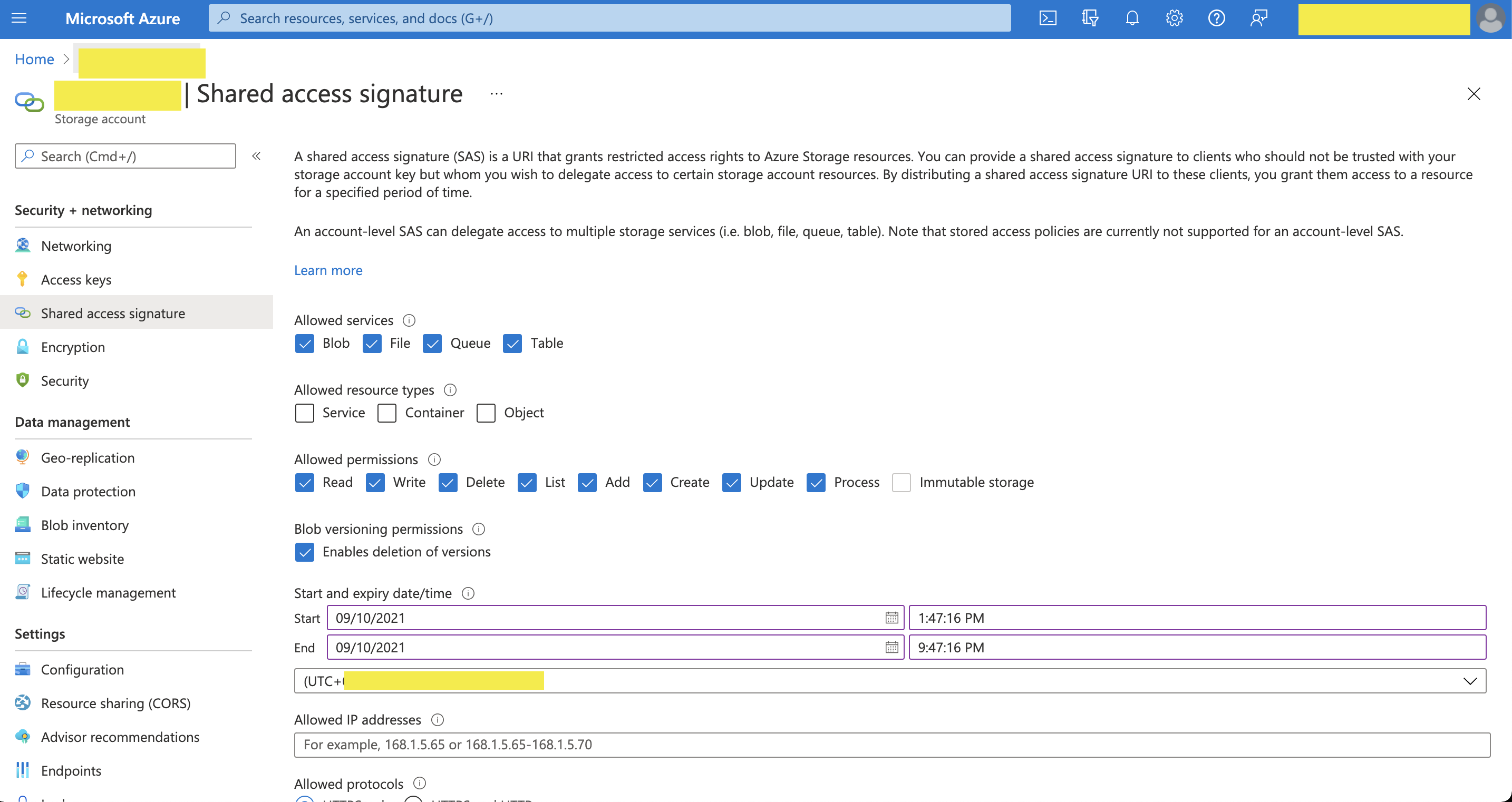
- Select Access keys or Shared access signatures
- Copy the keys to use in the TD authentication configuration
In Treasure Data, you must create and configure the data connection prior to running your query. As part of the data connection, you provide authentication to access the integration.
- Open the TD Console.
- Navigate to the Integrations Hub > Catalog.
- Click the search icon on the far-right of the Catalog screen, and enter Azure Lake.
- Hover over the Microsoft Azure Data Lake connector and selectCreate Authentication.
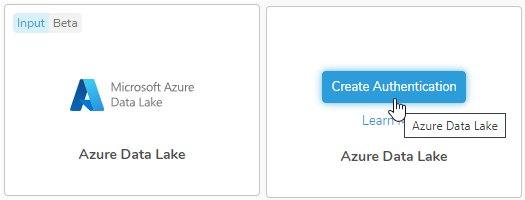
- Choose one of the following authentication methods:
Account Key authentication method Shared Access Signatures authentication method Proxy Setting (Optional) On Premises Setting (Optional)
- Select Shared Access Signature from the Authentication Mode dropdown menu.

Enter your storage Account Name.
Enter your Account Key copied from the Azure Portal.
Select Shared Access Signature from the Authentication Mode dropdown menu.

Enter your storage Account Name.
Enter your Account Key copied from the Azure Portal.
If you want to run through your HTTP Proxy, select your Proxy Type.
 **
**
Enter Proxy Host, Proxy Port, Proxy Username, and Proxy Password
If your Data Lake is on premise, specify your On Premises Setting

- Enter the Premises Host. For On Premises Setting, only Shared Access Signatures authentication method is supported.
- Enter a name for your connection.
- Choose to share the authentication with others or not.
- Select Continue.
After creating the authenticated connection, you are automatically taken to Authentications.
- Search for the connection you created.
- Select New Source.
- Type a name for your Source in the Data Transfer field**.**
- Select Next. The Source Table dialog opens
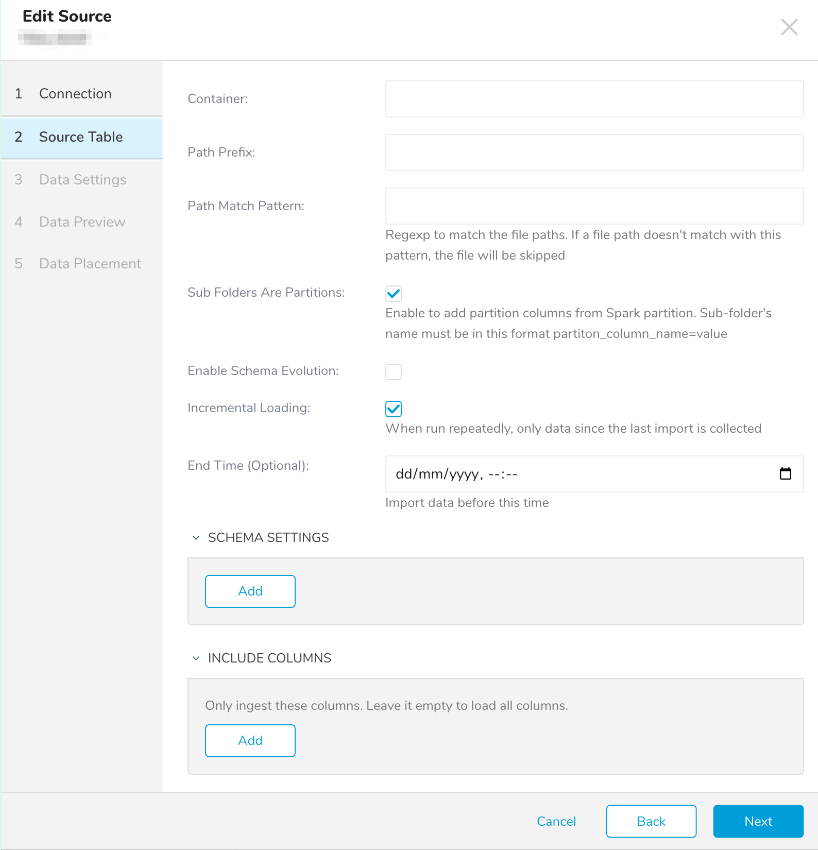
- Edit the following parameters:
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Container | The container name of the Data Lake |
| Path Prefix | The path to the folders container with all your files to ingest |
| Path Match Pattern (optional) | Only import the files with this Regular Expression pattern |
| Sub folders are partitions | Enable to specify that you use Spark Partition folder structure. The sub folder must have a name in this format <column_name>=value |
| Enable Schema Evolution | Enable schema evolution for parquet |
| Incremental Loading | Enable incremental mode. |
| End time | Only files that have been modified after the time specified will be imported. |
| Schema Settings | If "Sub Folders Are Partitions" is enabled, you must provide the column name and data type of that partition column |
| Include Columns | Limits the columns that will be imported. Only columns specified in the list will be imported. If the list is empty, all columns will be imported. |
Select Next. The Data Settings page can be modified for your needs or you can skip the page.
Optionally, edit the following parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Retry Limit | Maximum number of retries |
| Initial retry interval in millis | The initial retry interval in milliseconds |
| Max retry wait in millis | The maximum retry interval. After the initial retry, the wait interval will be doubled until this maximum is reached. |
| repartition_number | Split input file into smaller files to bypass Out Of Memory exception. This apply to large data files. Default value is 100. |
- Select Next.
Data Preview is not supported with this integration. The preview only displays example data.
For data placement, select the target database and table where you want your data placed and indicate how often the import should run.
Select Next. Under Storage, you will create a new or select an existing database and create a new or select an existing table for where you want to place the imported data.
Select a Database > Select an existing or Create New Database.
Optionally, type a database name.
Select a Table> Select an existing or Create New Table.
Optionally, type a table name.
Choose the method for importing the data.
- Append (default)-Data import results are appended to the table. If the table does not exist, it will be created.
- Always Replace-Replaces the entire content of an existing table with the result output of the query. If the table does not exist, a new table is created.
- Replace on New Data-Only replace the entire content of an existing table with the result output when there is new data.
Select the Timestamp-based Partition Key column. If you want to set a different partition key seed than the default key, you can specify the long or timestamp column as the partitioning time. As a default time column, it uses upload_time with the add_time filter.
Select the Timezone for your data storage.
Under Schedule, you can choose when and how often you want to run this query.
- Select Off.
- Select Scheduling Timezone.
- Select Create & Run Now.
- Select On.
- Select the Schedule. The UI provides these four options: @hourly, @daily and @monthly or custom cron.
- You can also select Delay Transfer and add a delay of execution time.
- Select Scheduling Timezone.
- Select Create & Run Now.
After your transfer has run, you can see the results of your transfer in Data Workbench > Databases.
Within Treasure Workflow, you can specify the use of this data connector within a workflow.
Learn more at Using Workflows to Export Data with the TD Toolbelt.
+setup:
echo>: start ${session_time}
+import-with-sql:
td_load>: config.yml
database: ${td.some_database}
table: ${td.some_table2}
+teardown:
echo>: finish ${session_time}
The following is an example configuration file to fetch files from Azure Data Lake:
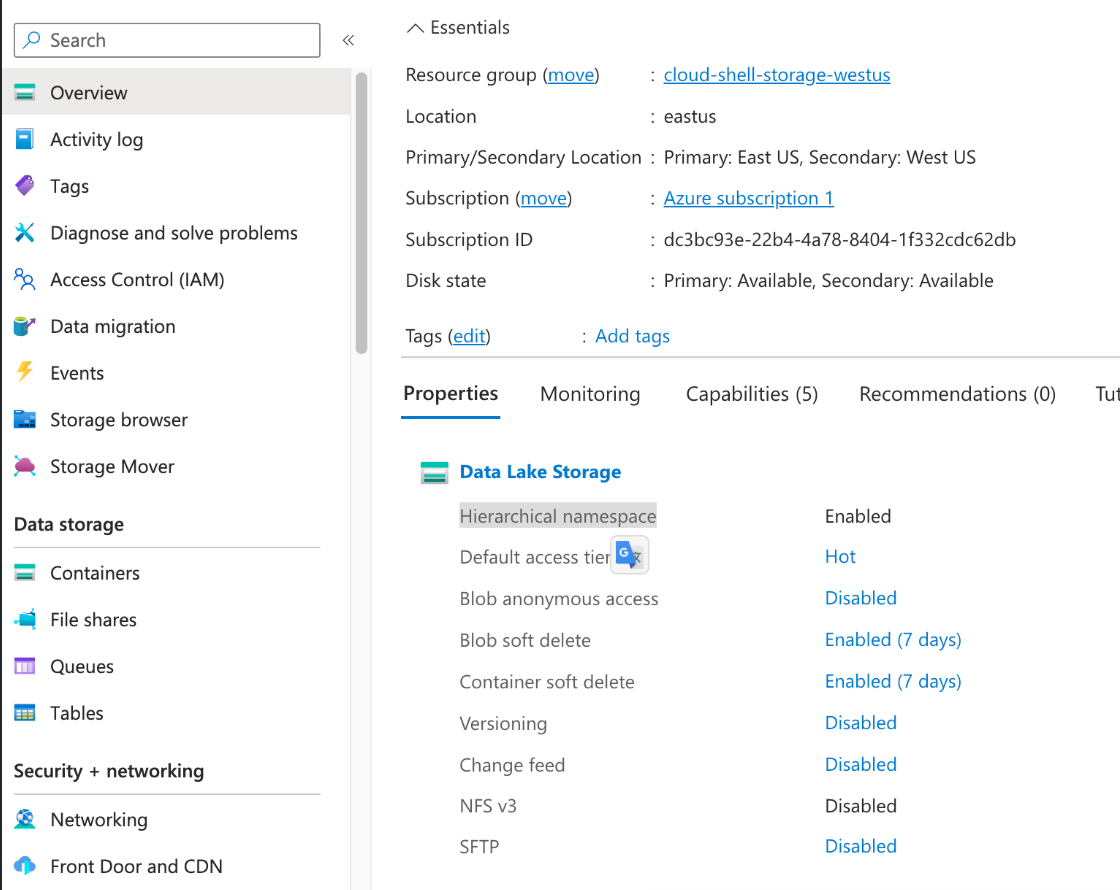
input: type: azure_datalake authentication_mode: account_key account_name: tdadl account_key: fjZliu61iZV sas_token: ?sv=sas_token container_name: test path_prefix: /traffic_data/partition/collisionrecords2/ path_match_pattern: /traffic_data/partition/collisionrecords2/* subfolder_partitions: true proxy_type: none proxy_host: host proxy_port: 3128 proxy_username: tdpy proxy_password: 321tre repartition_number: 100 schema_evolution: false incremental: true last_updated_at: "2023-12-20T03:51:20.937Z" include_columns: [ col0, col3, col4, ]When you enable the `"Soft delete for blobs" feature, the connector doesn't work, because it uses the REST API.
To use this feature, login in the Azure Portal, and from the Overview page, change the Properties of Data Lake Storage so that "Hierarchical namespace" is Enabled.
Error example looks like this.
Caused by: org.apache.hadoop.fs.azurebfs.contracts.exceptions.AbfsRestOperationException: Operation failed: "Server failed to authenticate the request. Make sure the value of Authorization header is formed correctly including the signature.", 403, HEAD, https://kfcusprdanalyticsadl.dfs.core.windows.net/data-science-container/?upn=false&action=getAccessControl&timeout=90&sp=racwdlmep&st=2024-08-26T15:03:55Z&se=2024-10-15T23:03:55Z&spr=https&sv=2022-11-02&sr=d&sig=XXXXX&sdd=2s, rId: 596f51a1-601f-000d-6fe0-f7dd2e000000