Learn more Mailchimp Import Integration.
You can create a Mailchimp list from data stored in Treasure Data. Use cases include:
- Personalization through Segmentation: Capture user behaviors from websites or mobile apps, collecting all user events into Treasure Data. Then, write personalization logic in SQL, and export the segmented mailing list to MailChimp for targeted campaigns.
- Customer Retention: For SaaS and subscription e-commerce businesses, customer retention can drive growth. Identify“at-risk” users with user events stored in Treasure Data and pushed to MailChimp. Send targeted promotions to the at-risk users to re-engage them.
For sample workflows on exporting to Mailchimp, view Treasure Boxes.
Continue to the following topics:
- Basic knowledge of Treasure Data, including the TD Toolbelt.
- A MailChimp account
- Authorized Treasure Data account access to Mailchimp
You can use the TD Console to configure your connection. You create a new connection or if you already configured a Mailchimp data connector (an input transfer or an authentication), you can skip to Configure Export Results in Your Data Connection.
Go to Integrations Hub > Catalog and search. Locate and select the Mailchimp tile.
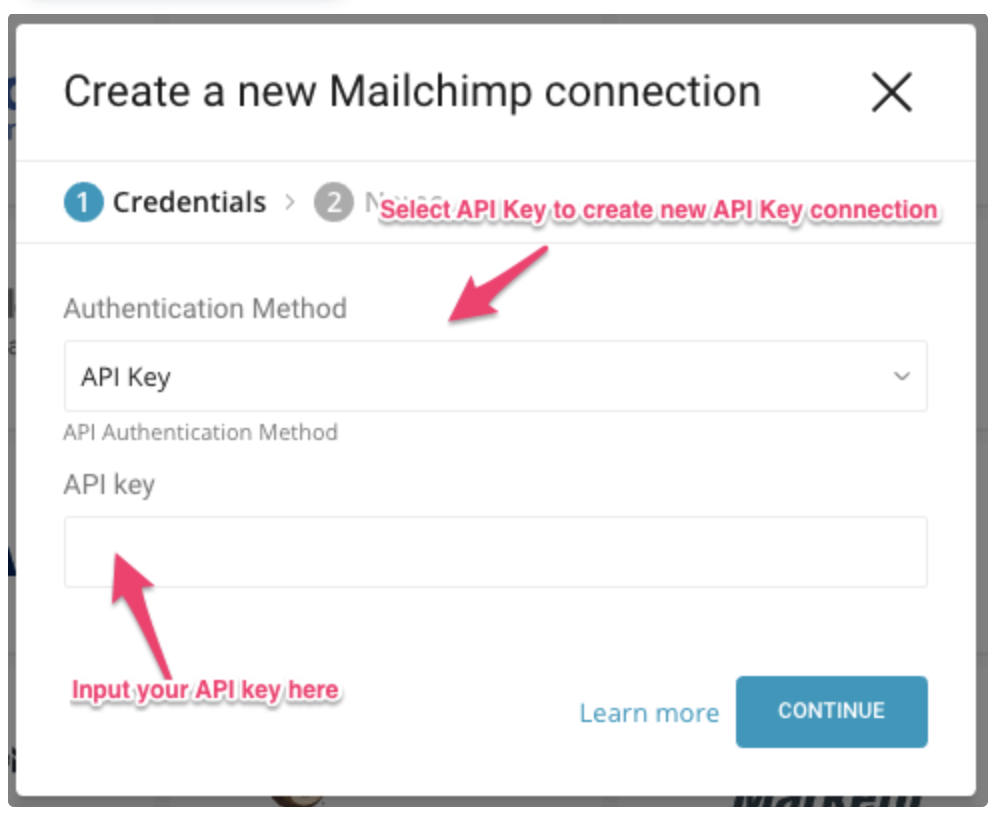
A dialog opens in which you provide the required credentials. Specify an Authentication Method.
The method you use to authenticate Treasure Data with MailChimp affects the steps you take to enable the data connector. You can choose to authenticate using:
- an API
- OAuth
You can specify the MailChimp API Key and credential to authorize Treasure Data access. The API key grants full access to your Mailchimp account.
OAuth method is not supported for JP and IDCF customers.
You can select an existing OAuth connection for MailChimp from the drop-down or select the link under OAuth connection to create a new one.
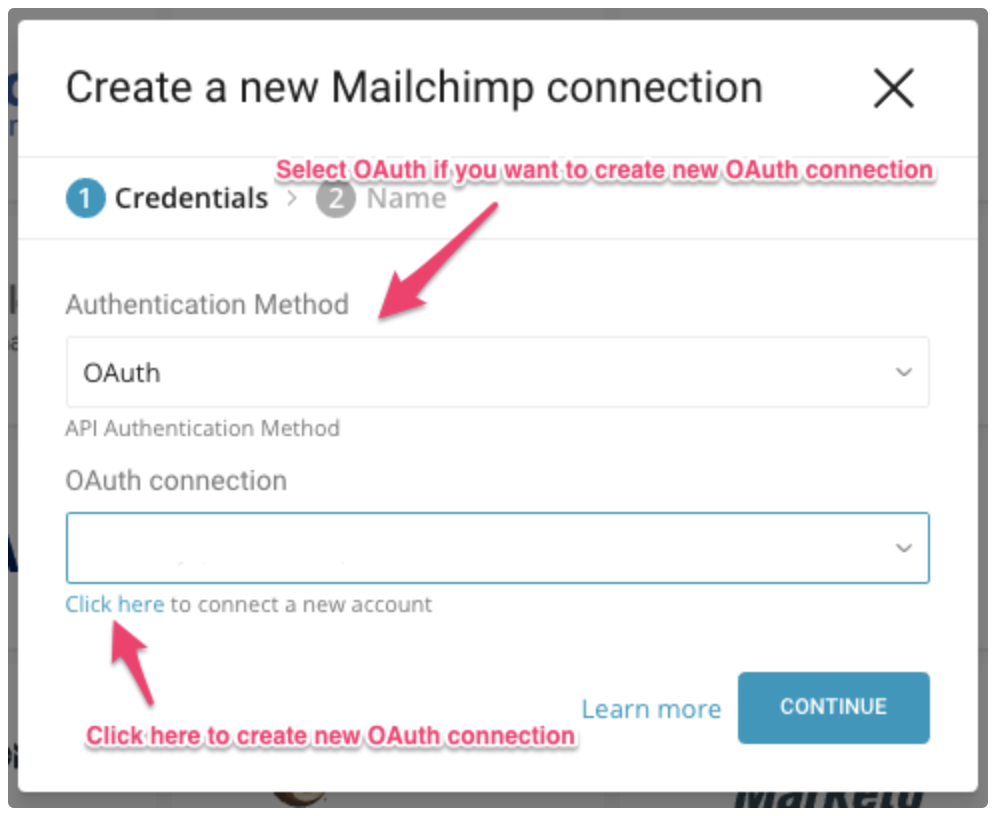
When you select Click here to connect a new account, you must sign into your MailChimp account in popup window
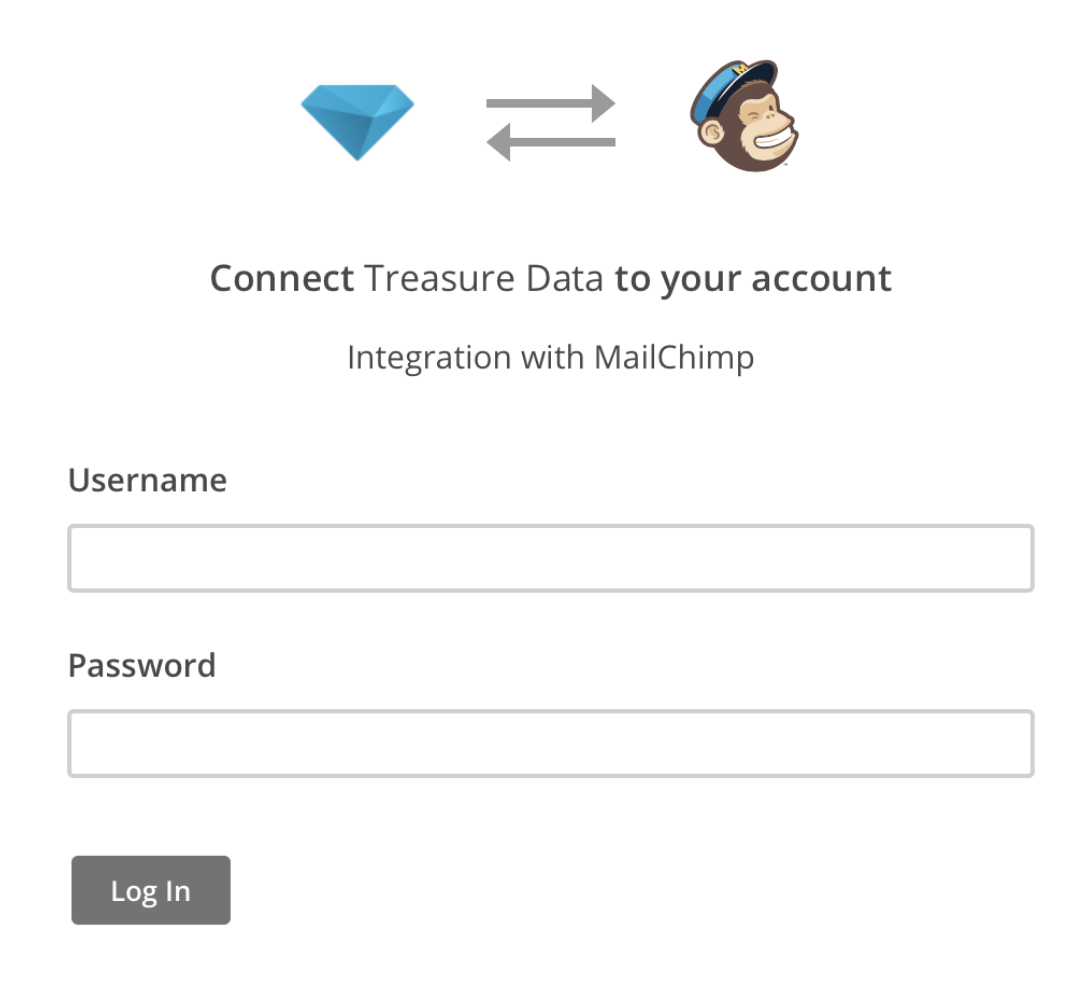
By signing into MailChimp, you are authenticating. The action of signing into Mailchimp generates an Oauth authentication.
You are redirected back to the Treasure Data Connections page. Repeat the first step (Create a New Connection) and choose your new OAuth connection, then finish creating your connection.
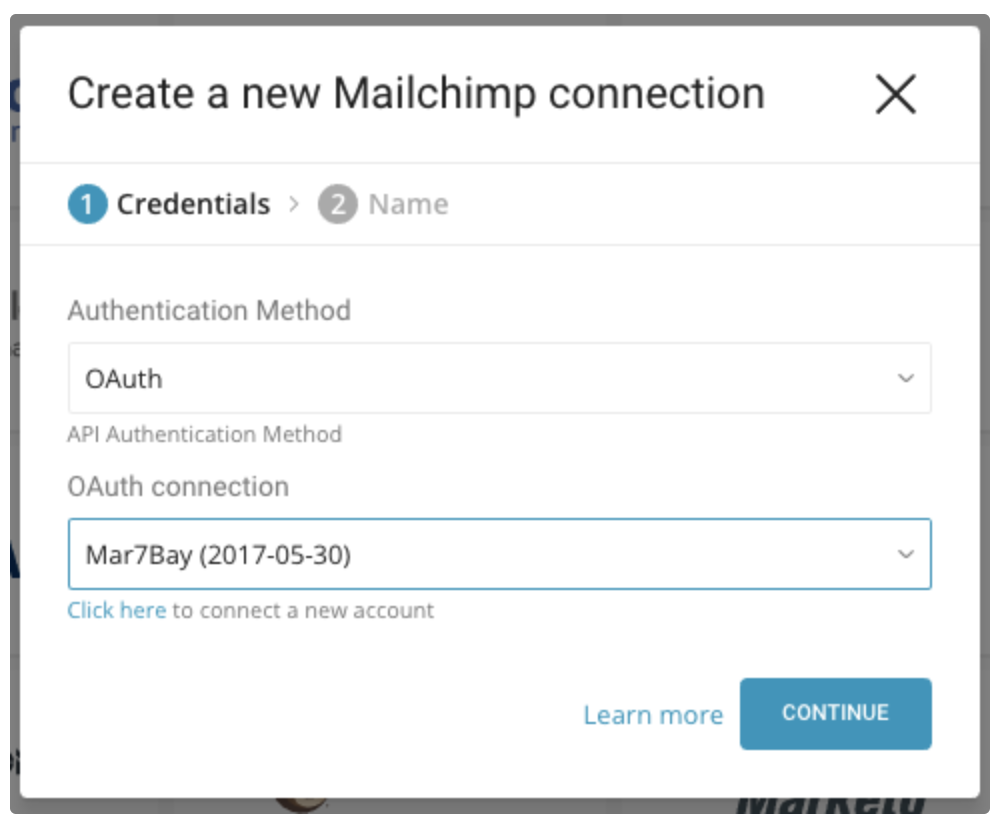
You now have an authenticated connector that you use to complete configuration for output of data in the next step.
Select Continue. Provide a name for your connector.
You create a query, or use an existing query, that retrieves data to be exported and placed into a Mailchimp list. In the query, you specify the Treasure Data Mailchimp data connector.
Go to the TD Console and go to the query editor. Access or write the query that you plan to use to export data. Select Output results.
You can see a simple sample query in the following image:
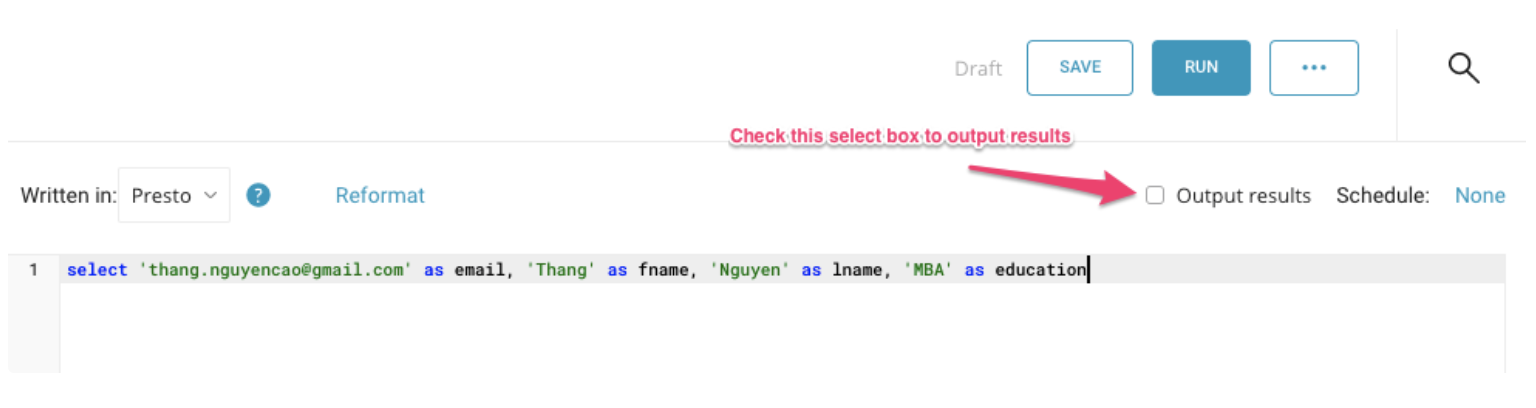
Read more about writing a query for Mailchimp in the Appendix.
When you select the Output Results checkbox and select Save, The Choose Saved Connection dialog opens.
The Choose Saved Connection dialog opens. Type the connection name in the search box to filter and select your connection.
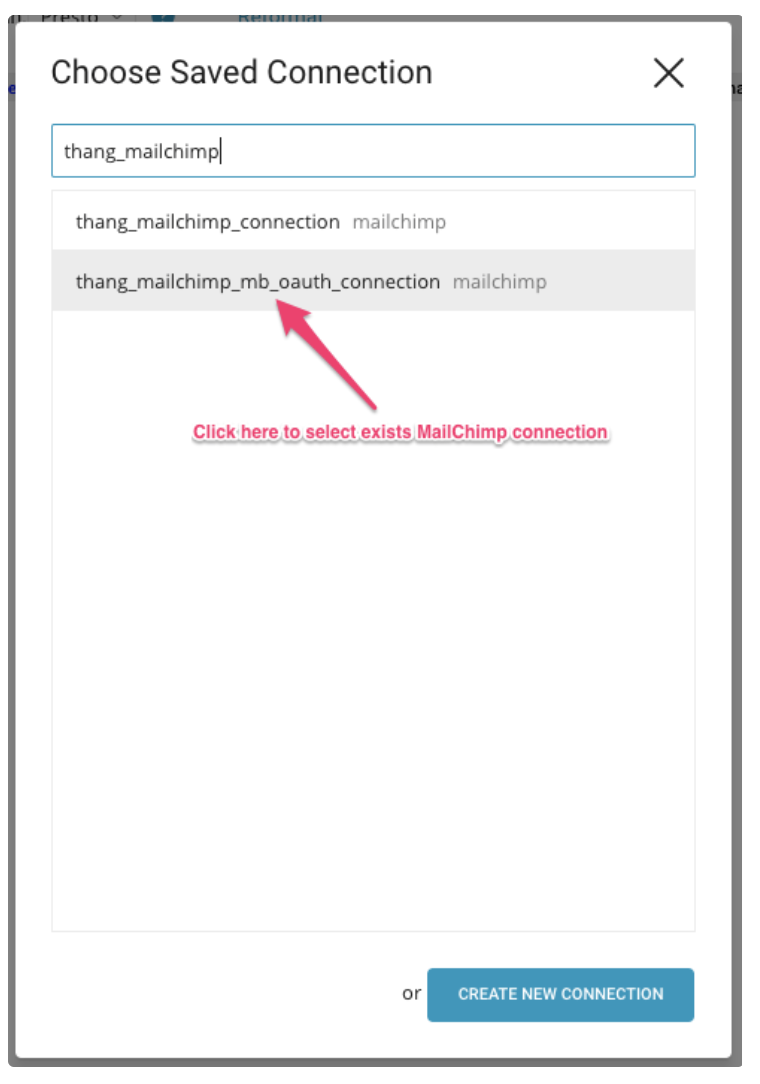
Select Create New Connection.
Here is a sample configuration.
In this example, the default column names are overridden with “last_name” and “first_name”. Also, you can specify the Mailchimp “column name for group detail” as values. In the following example, the column names values are: “region, age”. For more information on Mailchimp groups, see the Appendix: "More About the Mailchimp Group Category".
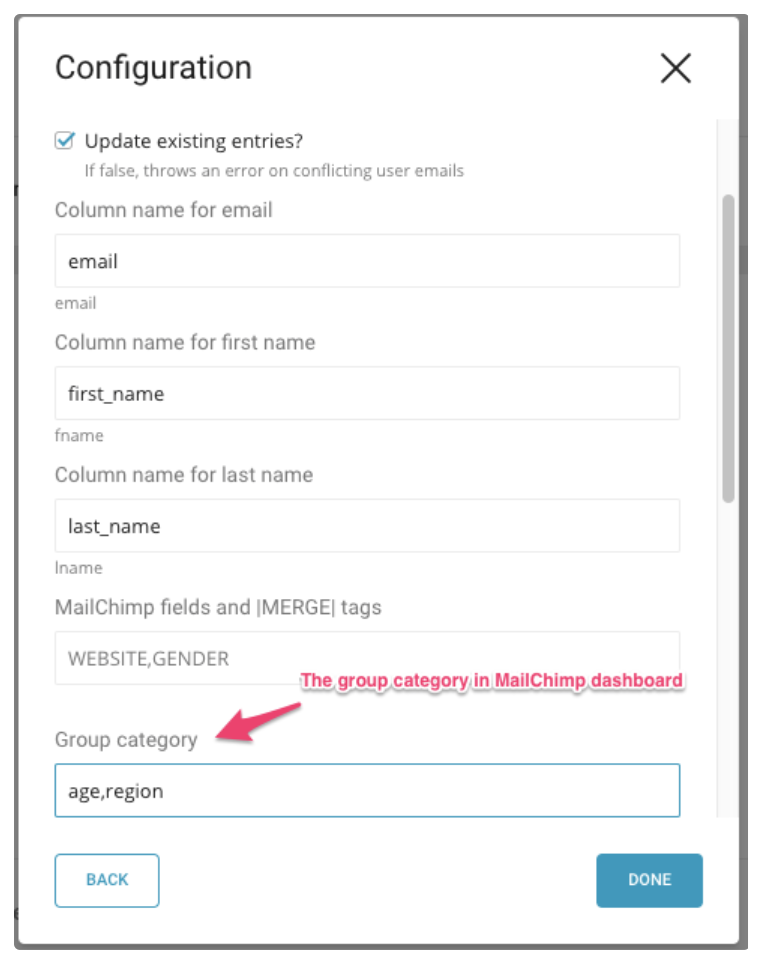
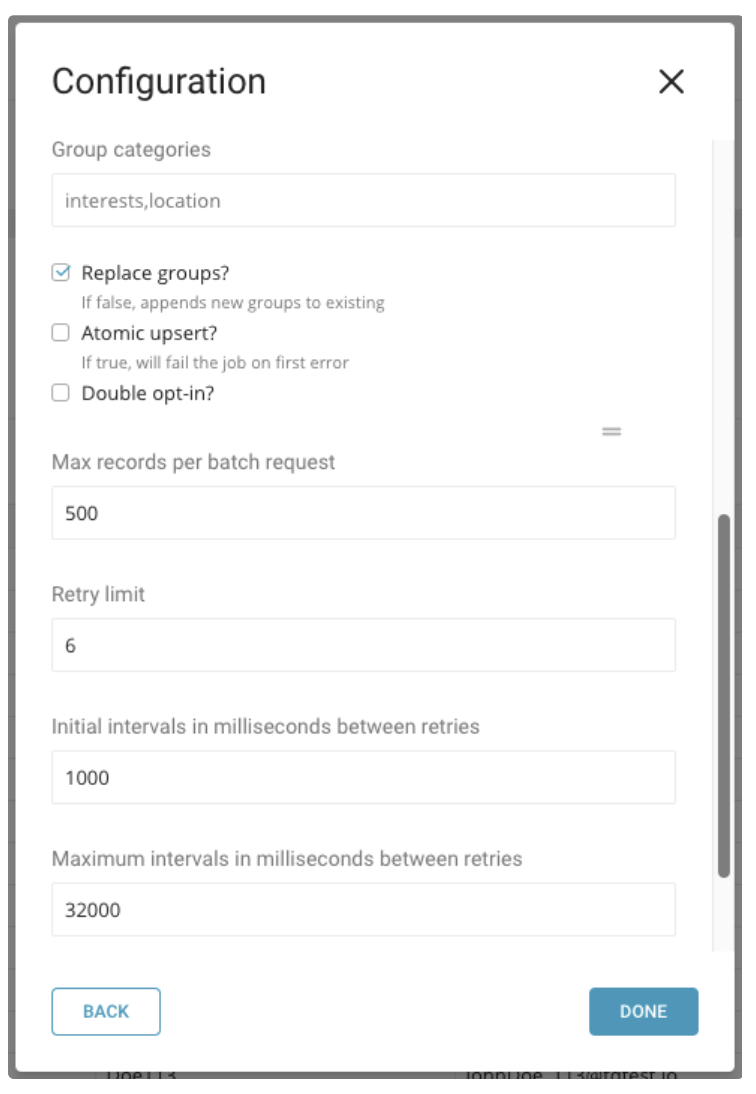
Specify the parameters.
| Parameters | Description | Default values |
|---|---|---|
| MailChimp list ID | This is the ID of the Mailchimp list that you want to populate with Treasure Data’s query results. Here is how to look it up | |
| Update existing entries? | When toggled on, existing entries are updated with their email addresses as keys. If not, new entries are appended to the MailChimp List | Yes |
| Column name for email | The value of this columns is used to populate the email field of the target MailChimp List | email |
| Column name for fname | The value of this columns is used to populate the fname field of the target MailChimp List | fname |
| Column name for lname | The value of this columns is used to populate the lname field of the target MailChimp List | lname |
| Additional MailChimp fields and MERGE tags | The values of additional merge fields are used to populate groups in the target MailChimp List. Multiple fields can be configured by separating them by “,”. E.g: WEBSITE,GENDER | |
| Group categories | The values of interest categories are used to populate groups in the target MailChimp List. Multiple groups can be configured by separating them by “,”. E.g interests,location | |
| Replace group? | When toggled on, the value of the groups for each subscriber is replaced. Otherwise, new values are appended to the subscriber’s interest group. | Yes |
| Double opt-in? | When toggled on, each subscriber will received confirmation email and they have to confirm the subscription. Otherwise, each subscriber will be subscribed automatically | No |
| Atomic Upsert? | A composite of UPDATE and INSERT operations. If the UPDATE fails because the target row does not exist, the INSERT is automatically executed. When 'yes' (true), the query results returns the job's status as 'success' when all the records are processed successfully within MailChimp. (An error indicates a target row does not exists and an INSERT is automatically executed but failed.) | No |
| The timeout expires in Milliseconds | The time to wait for response from MailChimp API. This value is useful in the network issues | 60000 |
| Max records per request | The max records per batch request from MailChimp API. MailChimp API enables max records is 500 per batch request. This value is useful when you upload the large data. | 500 |
You can use Scheduled Jobs with Result Export to periodically write the output result to a target destination that you specify.
Treasure Data's scheduler feature supports periodic query execution to achieve high availability.
When two specifications provide conflicting schedule specifications, the specification requesting to execute more often is followed while the other schedule specification is ignored.
For example, if the cron schedule is '0 0 1 * 1', then the 'day of month' specification and 'day of week' are discordant because the former specification requires it to run every first day of each month at midnight (00:00), while the latter specification requires it to run every Monday at midnight (00:00). The latter specification is followed.
Navigate to Data Workbench > Queries
Create a new query or select an existing query.
Next to Schedule, select None.

In the drop-down, select one of the following schedule options:
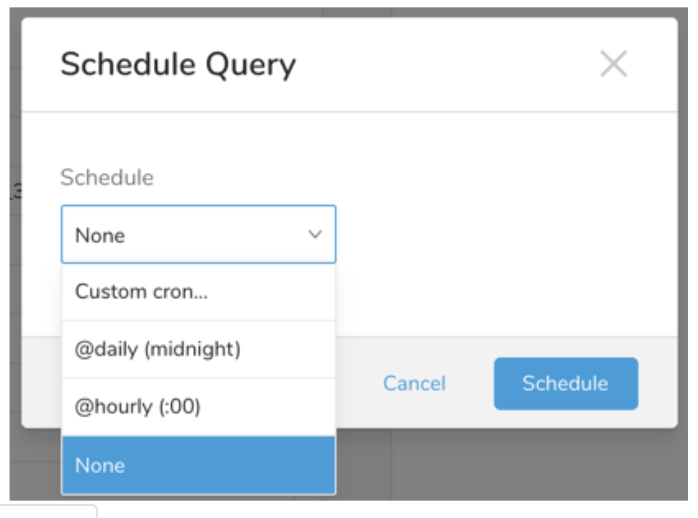
Drop-down Value Description Custom cron... Review Custom cron... details. @daily (midnight) Run once a day at midnight (00:00 am) in the specified time zone. @hourly (:00) Run every hour at 00 minutes. None No schedule.
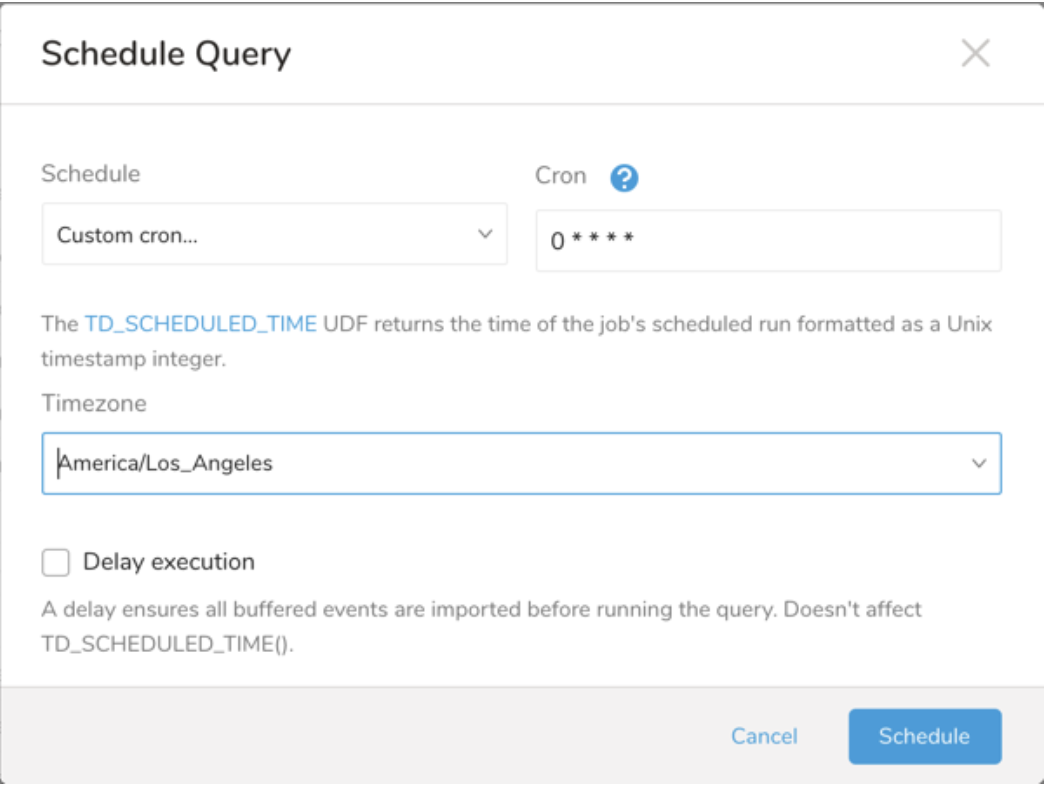
| Cron Value | Description |
|---|---|
0 * * * * | Run once an hour. |
0 0 * * * | Run once a day at midnight. |
0 0 1 * * | Run once a month at midnight on the morning of the first day of the month. |
| "" | Create a job that has no scheduled run time. |
* * * * *
- - - - -
| | | | |
| | | | +----- day of week (0 - 6) (Sunday=0)
| | | +---------- month (1 - 12)
| | +--------------- day of month (1 - 31)
| +-------------------- hour (0 - 23)
+------------------------- min (0 - 59)The following named entries can be used:
- Day of Week: sun, mon, tue, wed, thu, fri, sat.
- Month: jan, feb, mar, apr, may, jun, jul, aug, sep, oct, nov, dec.
A single space is required between each field. The values for each field can be composed of:
| Field Value | Example | Example Description |
|---|---|---|
| A single value, within the limits displayed above for each field. | ||
A wildcard '*' to indicate no restriction based on the field. | '0 0 1 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) on the first day of each month. |
A range '2-5', indicating the range of accepted values for the field. | '0 0 1-10 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) on the first 10 days of each month. |
A list of comma-separated values '2,3,4,5', indicating the list of accepted values for the field. | 0 0 1,11,21 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) every 1st, 11th, and 21st day of each month. |
A periodicity indicator '*/5' to express how often based on the field's valid range of values a schedule is allowed to run. | '30 */2 1 * *' | Configures the schedule to run on the 1st of every month, every 2 hours starting at 00:30. '0 0 */5 * *' configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) every 5 days starting on the 5th of each month. |
A comma-separated list of any of the above except the '*' wildcard is also supported '2,*/5,8-10'. | '0 0 5,*/10,25 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) every 5th, 10th, 20th, and 25th day of each month. |
- (Optional) You can delay the start time of a query by enabling the Delay execution.
Save the query with a name and run, or just run the query. Upon successful completion of the query, the query result is automatically exported to the specified destination.
Scheduled jobs that continuously fail due to configuration errors may be disabled on the system side after several notifications.
(Optional) You can delay the start time of a query by enabling the Delay execution.
You can also send segment data to the target platform by creating an activation in the Audience Studio.
- Navigate to Audience Studio.
- Select a parent segment.
- Open the target segment, right-mouse click, and then select Create Activation.
- In the Details panel, enter an Activation name and configure the activation according to the previous section on Configuration Parameters.
- Customize the activation output in the Output Mapping panel.
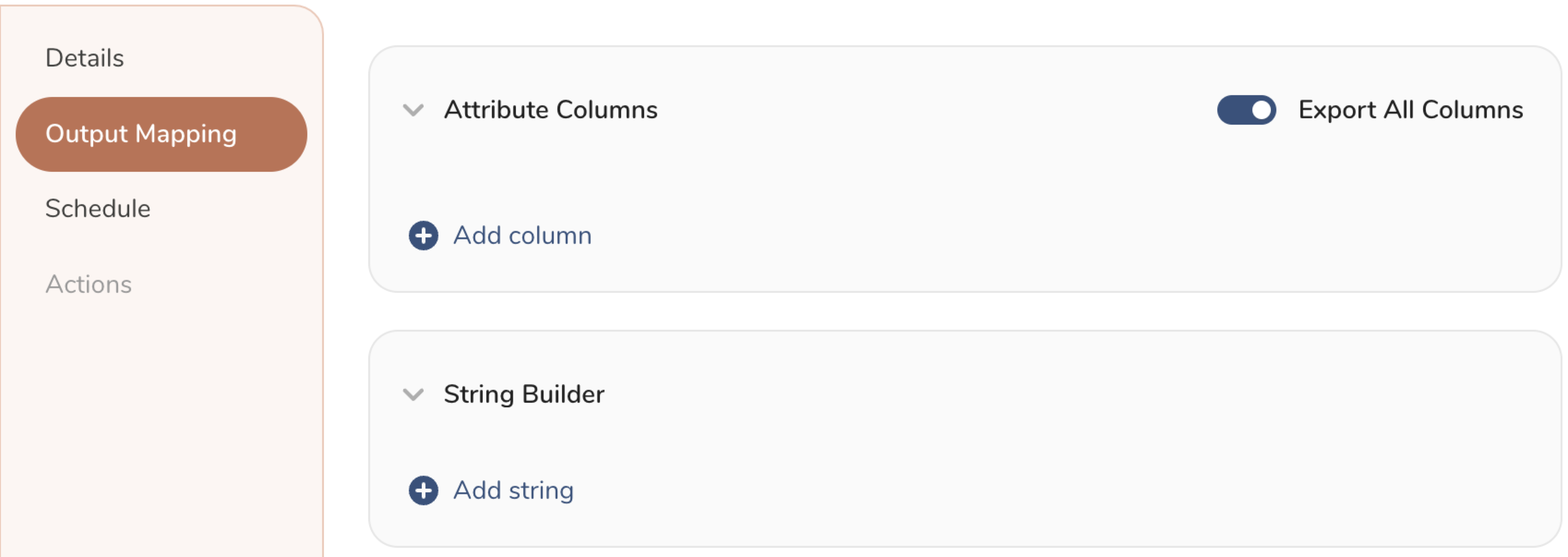
- Attribute Columns
- Select Export All Columns to export all columns without making any changes.
- Select + Add Columns to add specific columns for the export. The Output Column Name pre-populates with the same Source column name. You can update the Output Column Name. Continue to select + Add Columnsto add new columns for your activation output.
- String Builder
- + Add string to create strings for export. Select from the following values:
- String: Choose any value; use text to create a custom value.
- Timestamp: The date and time of the export.
- Segment Id: The segment ID number.
- Segment Name: The segment name.
- Audience Id: The parent segment number.
- + Add string to create strings for export. Select from the following values:
- Set a Schedule.
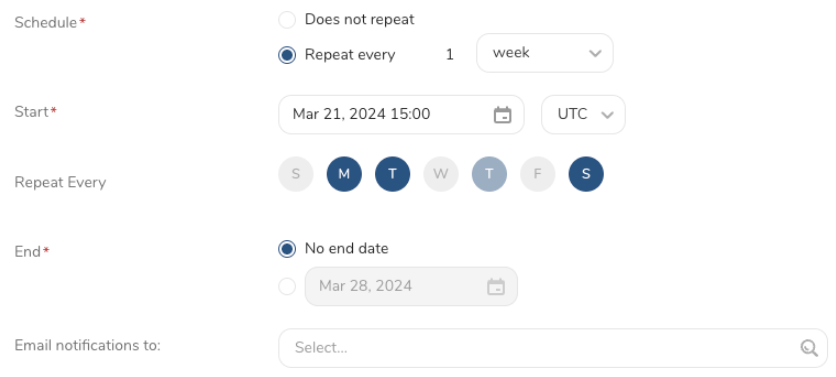
- Select the values to define your schedule and optionally include email notifications.
- Select Create.
If you need to create an activation for a batch journey, review Creating a Batch Journey Activation.
If you work in Treasure Workflow, you can specify the use of this data connector to output data.
timezone: UTC
_export:
td:
database: sample_datasets
+td-result-into-target:
td>: queries/sample.sql
result_connection: your_connections_name
result_settings:
list_id: your_list_id
email_column: email
fname_column: first_name
lname_column: last_name
update_existing: true
grouping_columns: age, regionSpecify the result_settings parameters.
| Parameters | Description | Default values |
|---|---|---|
| list_id | This is the ID of the Mailchimp list that you want to populate with Treasure Data’s query results. Here is how to look it up | |
| update_existing | When toggled on, existing entries are updated with their email addresses as keys. If not, new entries are appended to the MailChimp List | false |
| email_column | The value of this columns is used to populate the email field of the target MailChimp List | email |
| fname_column | The value of this columns is used to populate the fname field of the target MailChimp List | fname |
| lname_column | The value of this columns is used to populate the lname field of the target MailChimp List | lname |
| merge_fields | The values of additional merge fields are used to populate groups in the target MailChimp List. Multiple fields can be configured by separating them by “,”. E.g: WEBSITE,GENDER | |
| grouping_columns | The values of interest categories are used to populate groups in the target MailChimp List. Multiple groups can be configured by separating them by “,”. E.g interests,location | |
| replace_interests | When toggled on, the value of the groups for each subscriber is replaced. Otherwise, new values are appended to the subscriber’s interest group. | true |
| double_optin | When toggled on, each subscriber will received confirmation email and they have to confirm the subscription. Otherwise, each subscriber will be subscribed automatically | false |
| atomic_upsert | A composite of UPDATE and INSERT operations. If the UPDATE fails because the target row does not exist, the INSERT is automatically executed. When 'yes' (true), the query results returns the job's status as 'success' when all the records are processed successfully within MailChimp. (An error indicates a target row does not exists and an INSERT is automatically executed but failed.) | false |
| sleep_between_requests_millis | The time to wait for response from MailChimp API. This value is useful in the network issues | 30000 |
| max_records_per_request | The max records per batch request from MailChimp API. MailChimp API enables max records is 500 per batch request. This value is useful when you upload the large data. | 500 |
Learn more about using data connectors in the workflow to export data.
Here is an example MailChimp list before the query results are exported to Mailchimp:
The preceding list is configured with two MailChimp Groups: Age and Region. They have the following categories:
- 0-20
- 21-30
- 31-40
- 41 and above
- Americas
- Asia
- EMEA
Back in the Treasure Data Query page, write and run the following query with MailChimp as Result Export:
SELECT email, first_name, last_name, region, age FROM (
VALUES ('k@gmail.com', 'K', 'T', 'Asia', '41 and above'),
('r@gmail.com', 'R', 'P', 'Americas', '21-30'),
('m@gmail.com', 'M', 'C', 'EMEA', '41 and above')
) tbl (email, first_name, last_name, region, age)The preceding query requires no source table (for the ease of testing out this feature), but you still must choose your database, so pick “sample_datasets” or any other arbitrary table. Also, make sure that Presto is chosen as the SQL dialect.
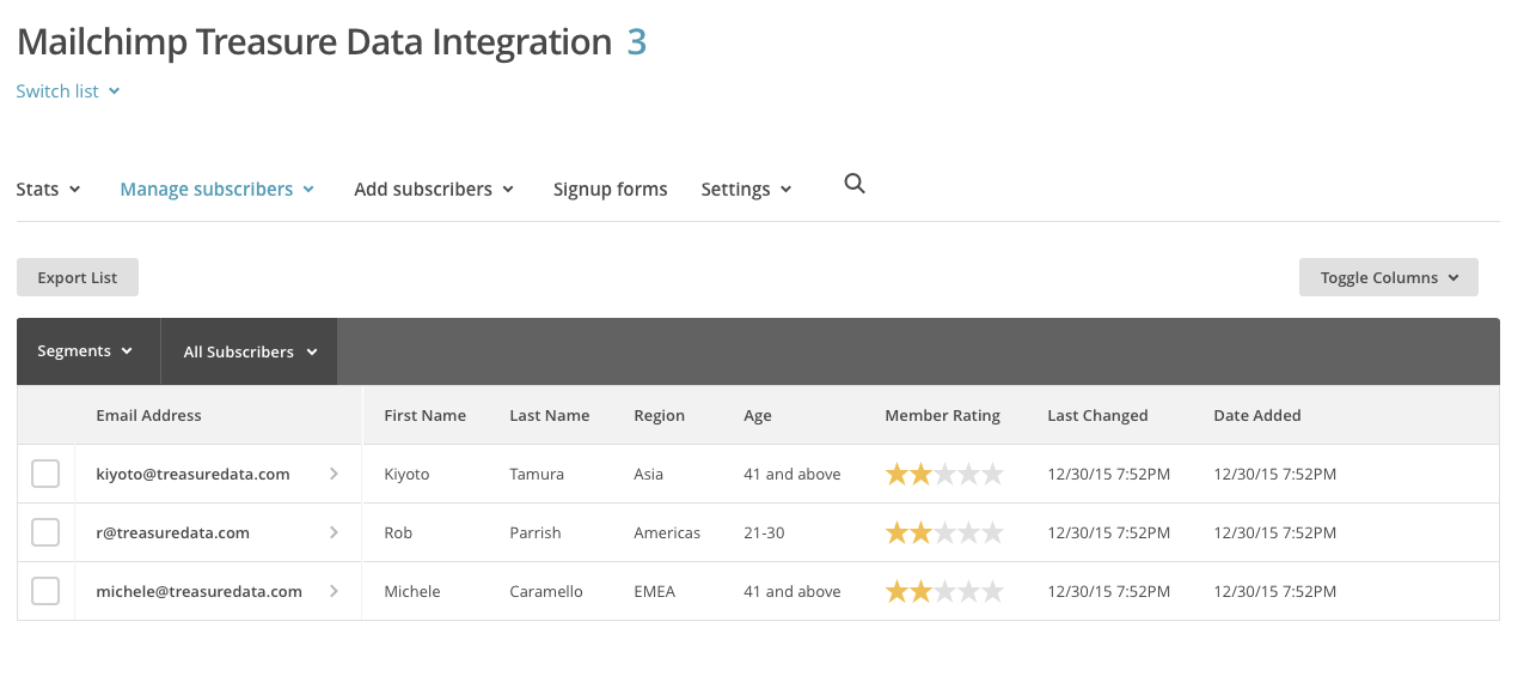
The query should complete in a few seconds. After that, check Mailchimp’s List:
If you have a MERGE field that is using the type address, you must put the values into a JSON type. The following query with MailChimp exports data with the MERGE field’s type address:
SELECT
'y@gmail.com' as email,
'y' as fname, 'L' as lname,
CAST(MAP(ARRAY['addr1', 'city', 'state', 'zip', 'country'], ARRAY['1234', 'mountain view', 'CA', '95869', 'US']) as JSON) as address,
'US' as locationIn Mailchimp, from the dashboard, you can access Lists and specify group options.
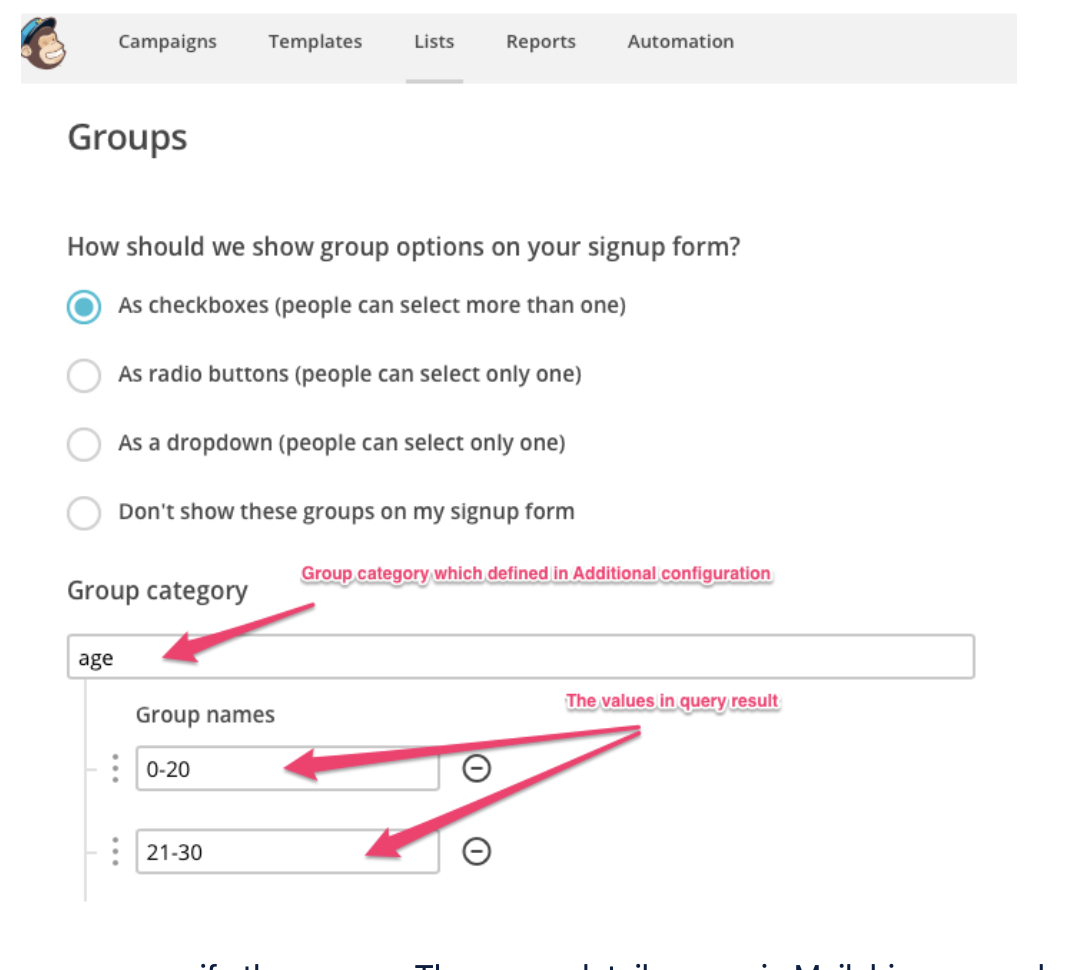
In Treasure Data, you can specify the groups. The group detail names in Mailchimp are column names in the query.