This feature is in BETA version. For more information, contact your Customer Success Representative.
The Google BigQuery Connector V2 is designed to streamline the process of uploading large volumes of data to Google BigQuery. It offers the following key capabilities:
- Efficient packaging of datasets into Parquet files to handle large volumes of data uploaded to Big Query
- Optimized data uploads using BigQuery load jobs
- Flexible data sync operations, with added support for Truncate sync mode.
- Basic knowledge of Treasure Data, including the TD Toolbelt.
- A Google Cloud Platform account
- Nested or repeated data types like ARRAY are not supported as destination columns.
This connector supports the "append, replace, replace backup, truncate" modes.
To use this feature, you need:
- Project ID
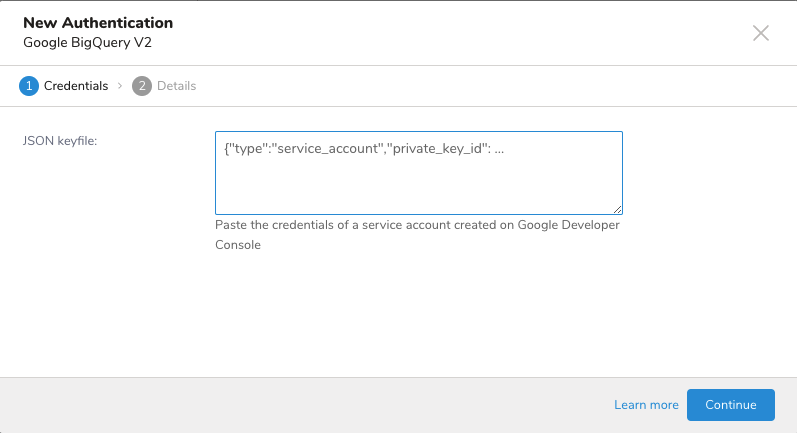
- JSON Credential
The integration with Google BigQuery is based on server-to-server API authentication.
- Navigate to your Google Developer Console.
- Select APIs & auth > Credentials.
- Select Service account.
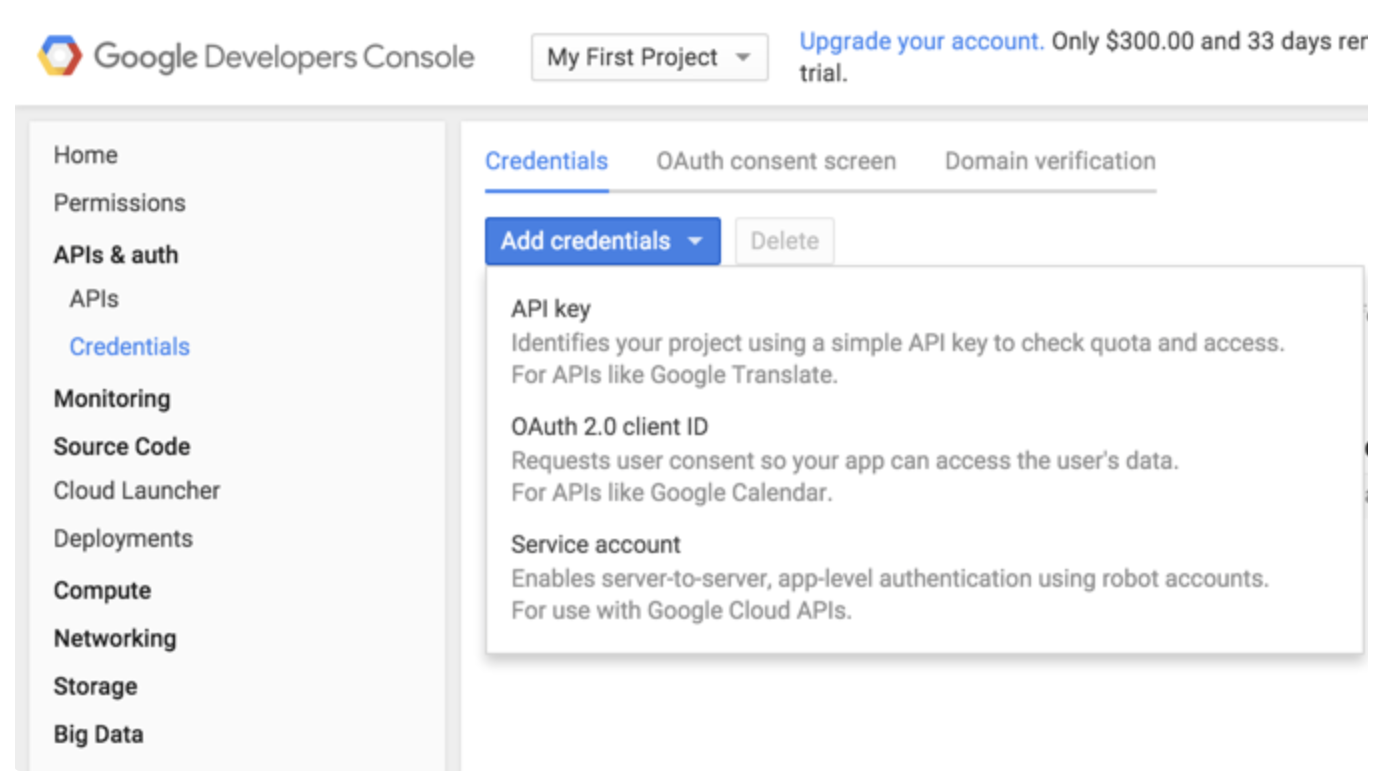 4. Select the JSON-based key type, which is recommended by Google. The key is downloaded automatically by the browser.
4. Select the JSON-based key type, which is recommended by Google. The key is downloaded automatically by the browser.
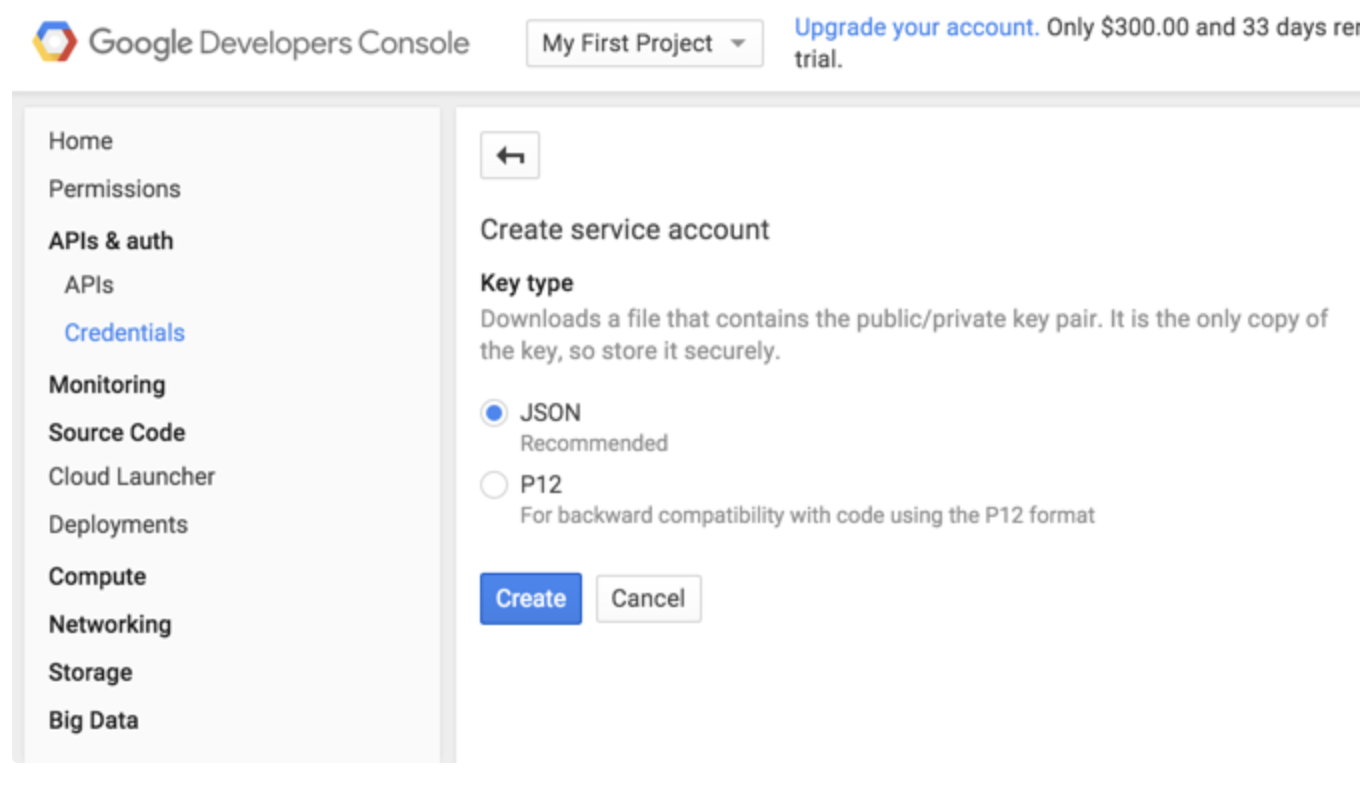
- Navigate to your Google Developer Console.
- Select Home.
- Locate your Project ID.
Create your Dataset and Table from your BigQuery console.
- Navigate to TD Console.
- Navigate to Integrations Hub > Catalog.
- Select Google Big Query V2.
 4. Complete all the information as follows:
4. Complete all the information as follows:
The TD Console supports multiple ways to export data. Follow these steps to export data from the Data Workbench.
- Navigate to Data Workbench > Queries.
- Select New Query, and define your query.
- Select Export Results to configure the data exporting.
- Select an existing Snapchat CAPI authentication or create a new one described previously
- Select Done.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Sync Mode | Determines how data will be written to the destination table. Available options: Append Mode: Adds new data from the query result to the existing table without modifying existing records. Replace Mode: Completely drops the existing destination table and creates a new one using the schema and data from the query result. Truncate Mode: Preserves the existing table structure but removes all data, then inserts new data from the query result. The existing table schema is maintained, and any schema definitions from the query result or JSON Schema File are ignored. Replace_Backup: Replaces the destination table while safely preserving the existing data through a backup method. When this mode is selected, an additional field “Table Backup Operation Type” appears for selecting the backup method. |
| Table Backup Operation Type (Only appears when Replace_Backup mode is selected) | Specifies how the existing table should be backed up before replacement. Two options are available: Existing Table Rename: Creates an editable backup by renaming the existing table with a timestamp prefix (e.g., backup_{timestamp}_). A new table is then created with the original name using the query result’s schema, and data is loaded from the query result. Existing Table Snapshot: Creates a read-only point-in-time copy of the existing table using BigQuery’s snapshot feature. After creating the snapshot, the existing table is dropped, and a new table is created with the query result’s schema and data. This method is more storage-efficient but the backup is read-only. |
| Google Cloud Project ID | The unique identifier for your Google Cloud project where the BigQuery dataset resides. This can be found at the top of your Google Developer Console page. |
| Dataset Name | The name of the BigQuery dataset where you want to store your data. This is a collection of tables within your Google Cloud project. |
| Data Location | Specifies the geographic location where your BigQuery data will be stored. Important for data residency requirements. If your data needs to be stored outside the US or EU multi-region, you must specify the location explicitly. |
| Table Name | The name of the specific table within your chosen dataset where the data will be written. |
| Auto-create table? | When checked, the system will automatically create the destination table if it doesn’t exist. This option is ignored for Truncate sync mode. |
| Add missing columns? | When enabled, any columns in the source data that don’t exist in the destination table will be added. When disabled, these columns will be ignored. |
| Json Schema File | Defines the structure of your data using JSON format, specifying column names, data types, and constraints. Each column definition requires a name and type field. The example shows a schema with two columns: an INTEGER “id” field marked as REQUIRED, and a STRING “comment” field. |
| Skip on invalid records? | When enabled, the job will continue processing even if it encounters records that fail validation, skipping the invalid records. When disabled, the job will stop completely if it encounters any invalid records. |
The connector implements a schema reconciliation or consolidation process that harmonizes schemas from multiple sources to determine the final table structure or schema. This process ensures data integrity while supporting schema evolution scenarios based on configured sync modes and user preferences.
The connector determines the final table schema by evaluating three potential schema sources in a hierarchical order. This hierarchy is crucial for understanding how your data schema will be materialized in the destination BigQuery table.
- Destination Table Schema (Highest Precedence)
If the destination table exists, its schema serves as the primary authority for data loading operations.
When it applies:
- During APPEND operations to existing tables
- During TRUNCATE operations
Practical Example: Numeric Type Handling
- Query Resut Data
| user_id | transaction_amount | transaction_date |
|---|---|---|
| 1001 | 99.99 | 2024-01-15 |
| 1002 | 150.50 | 2024-01-16 |
Destination Table Schema
user_id: INT64transaction_amount: NUMERIC(38,9)transaction_date: DATE
Result: Even if query result data comes as FLOAT64 for transaction_amount, it will be converted to NUMERIC as per destination schema.
- User-Defined JSON Schema (Second Precedence)
When provided through the JSON Schema File configuration, this schema overrides type inference from query results and provides explicit column definitions.
When it applies:
- During table creation (new tables)
- When adding new columns to existing tables
- For explicit type casting and column property definition
Practical Example: Timestamp and Date Conversions
- Source Data
| event_time | registration_date |
|---|---|
| 2024-01-15 14:30:00 | 2024-01-15 14:30:00+02:00 |
| 2024-01-16 09:15:00 | 2024-01-16 09:15:00+08:00 |
User-Defined Schema
event_time: TIMESTAMPregistration_date: DATEEffects
event_time:
- Source data will be parsed as TIMESTAMP
- Maintains microsecond precision
- Stores in UTC
- Query Result Schema (Lowest Precedence)
The schema derived from your source data structure. This serves as the baseline schema when no other schemas are specified.
When it applies:
- When creating new tables without a JSON schema definition
- When adding new columns without explicit type definitions
- As a source for type inference when no overrides exist
Practical Example: Integer to String Conversion
- Query Result Data
| product_id | status_code |
|---|---|
| “SKU-001” | 200 |
| “SKU-002” | 404 |
Query Result Schema
product_id: STRINGstatus_code: IntPossible Target Conversions
- status_code as STRING:
- INT64 → STRING (Compatible conversion)
- Result: “200”, “404”
- status_code as INT64:
- Maintains original type
- Result: 200, 404
Find below a structured reference table showing exactly how schemas are handled in each scenario, organized by sync mode, table state, and configuration settings.
| Sync Mode | Destination Table | Add Missing Columns | Column Type | Schema Handling Logics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Append | Exists | Enabled | Original columns in destination table | Use destination table schema |
| New columns from query result data | Use query result + user-defined schema | |||
| Disabled | Original columns in destination table | Use destination table schema | ||
| New columns from query result data | Ignore these columns | |||
| Create New | N/A | All Columns | Use query result + user-defined schema | |
| Replace/Replace_Backup | Exists | N/A | All Columns | Use query result + user-defined schema |
| Create New | N/A | All Columns | Use query result + user-defined schema | |
| Truncate | Exists | Enabled | Original columns in destination table | Use destination table schema |
| New columns from query result data | Use query result + user-defined schema | |||
| Disabled | Original columns in destination table | Use destination table schema | ||
| New columns from query result data | Ignore these columns | |||
| Create New | N/A | All Columns | Error: Table must exist |
The connector implements a comprehensive type system mapping between source data types and BigQuery native types, with three categories of conversions:
- Default Mappings (Lossless Conversions)
| Query Result Type | BigQuery Type | Implementation Details |
|---|---|---|
| int32/int64 | INT64 | Native BigQuery integer, 64-bit signed |
| double | FLOAT64 | IEEE 754 double precision floating point |
| boolean | BOOL | 1-bit boolean value |
| timestamp | TIMESTAMP | Microsecond precision, UTC timezone |
| string | STRING | UTF-8 encoded character sequence |
- Compatible Mappings (Type Coercion)
| Query Result Type | BigQuery Type | Technical Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| int64 | NUMERIC | Precision: 38 digits, Scale: 9 decimal places |
| int64 | BIGNUMERIC | Precision: 76.76 digits, Scale: 38 decimal places |
| double | STRING | Formatted using toString() with full precision |
| boolean | STRING | Literal “true”/“false” representation |
| timestamp | STRING | ISO 8601 format with timezone |
- Potentially Lossy Mappings (Requires Validation)
| Query Result Type | BigQuery Type | Data Loss Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| timestamp | DATE | Truncates time component, timezone information lost |
| string | DATE | Must match ‘YYYY-MM-DD’, invalid formats become NULL |
| FLOAT64 | INT64 | Decimal truncation, possible precision loss |
| TIMESTAMP | DATE | Time granularity lost, timezone normalization |
You can use Scheduled Jobs with Result Export to periodically write the output result to a target destination that you specify.
Treasure Data's scheduler feature supports periodic query execution to achieve high availability.
When two specifications provide conflicting schedule specifications, the specification requesting to execute more often is followed while the other schedule specification is ignored.
For example, if the cron schedule is '0 0 1 * 1', then the 'day of month' specification and 'day of week' are discordant because the former specification requires it to run every first day of each month at midnight (00:00), while the latter specification requires it to run every Monday at midnight (00:00). The latter specification is followed.
Navigate to Data Workbench > Queries
Create a new query or select an existing query.
Next to Schedule, select None.

In the drop-down, select one of the following schedule options:
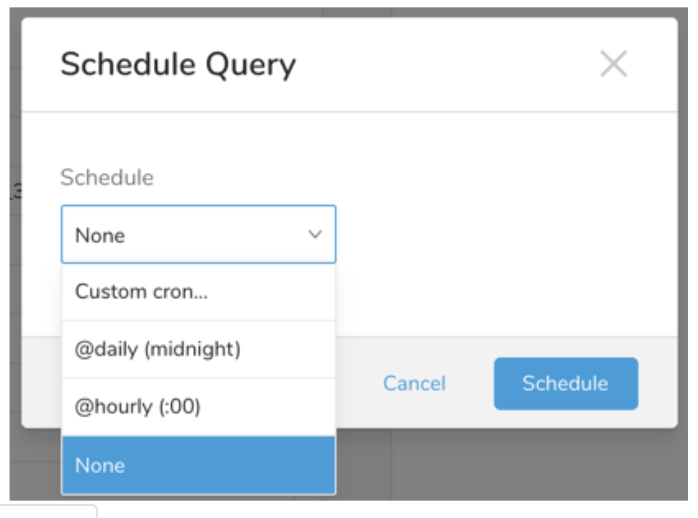
Drop-down Value Description Custom cron... Review Custom cron... details. @daily (midnight) Run once a day at midnight (00:00 am) in the specified time zone. @hourly (:00) Run every hour at 00 minutes. None No schedule.
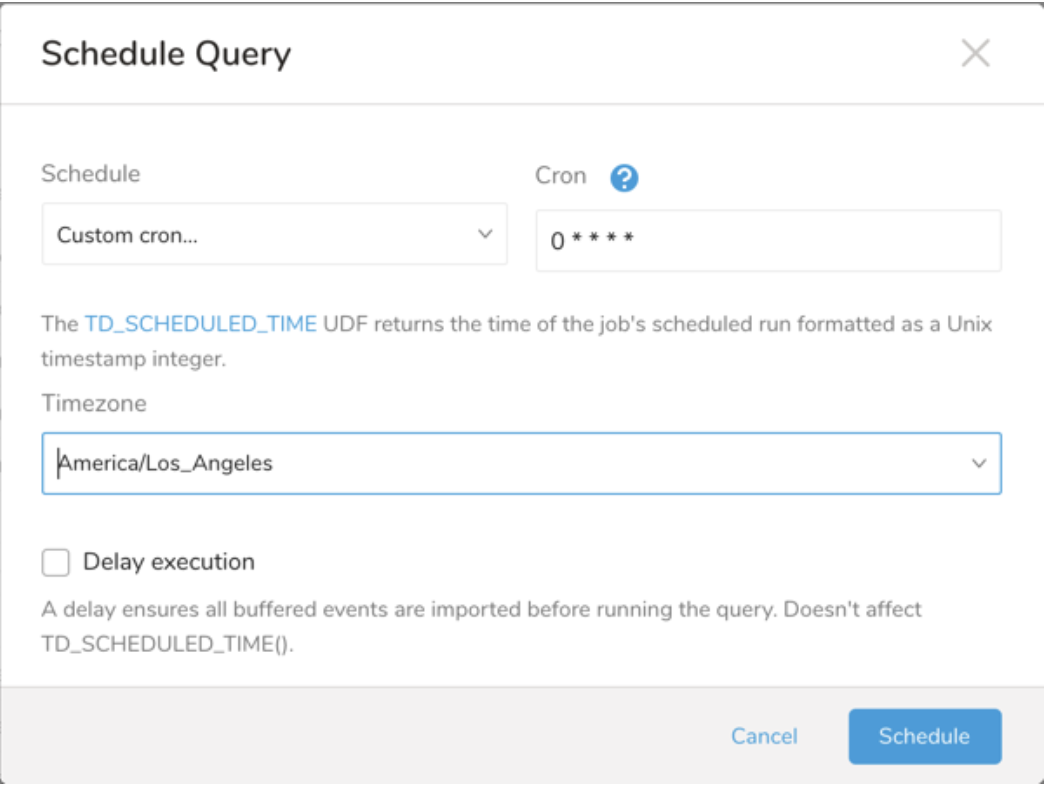
| Cron Value | Description |
|---|---|
0 * * * * | Run once an hour. |
0 0 * * * | Run once a day at midnight. |
0 0 1 * * | Run once a month at midnight on the morning of the first day of the month. |
| "" | Create a job that has no scheduled run time. |
* * * * *
- - - - -
| | | | |
| | | | +----- day of week (0 - 6) (Sunday=0)
| | | +---------- month (1 - 12)
| | +--------------- day of month (1 - 31)
| +-------------------- hour (0 - 23)
+------------------------- min (0 - 59)The following named entries can be used:
- Day of Week: sun, mon, tue, wed, thu, fri, sat.
- Month: jan, feb, mar, apr, may, jun, jul, aug, sep, oct, nov, dec.
A single space is required between each field. The values for each field can be composed of:
| Field Value | Example | Example Description |
|---|---|---|
| A single value, within the limits displayed above for each field. | ||
A wildcard '*' to indicate no restriction based on the field. | '0 0 1 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) on the first day of each month. |
A range '2-5', indicating the range of accepted values for the field. | '0 0 1-10 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) on the first 10 days of each month. |
A list of comma-separated values '2,3,4,5', indicating the list of accepted values for the field. | 0 0 1,11,21 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) every 1st, 11th, and 21st day of each month. |
A periodicity indicator '*/5' to express how often based on the field's valid range of values a schedule is allowed to run. | '30 */2 1 * *' | Configures the schedule to run on the 1st of every month, every 2 hours starting at 00:30. '0 0 */5 * *' configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) every 5 days starting on the 5th of each month. |
A comma-separated list of any of the above except the '*' wildcard is also supported '2,*/5,8-10'. | '0 0 5,*/10,25 * *' | Configures the schedule to run at midnight (00:00) every 5th, 10th, 20th, and 25th day of each month. |
- (Optional) You can delay the start time of a query by enabling the Delay execution.
Save the query with a name and run, or just run the query. Upon successful completion of the query, the query result is automatically exported to the specified destination.
Scheduled jobs that continuously fail due to configuration errors may be disabled on the system side after several notifications.
(Optional) You can delay the start time of a query by enabling the Delay execution.
You can also send segment data to the target platform by creating an activation in the Audience Studio.
- Navigate to Audience Studio.
- Select a parent segment.
- Open the target segment, right-mouse click, and then select Create Activation.
- In the Details panel, enter an Activation name and configure the activation according to the previous section on Configuration Parameters.
- Customize the activation output in the Output Mapping panel.
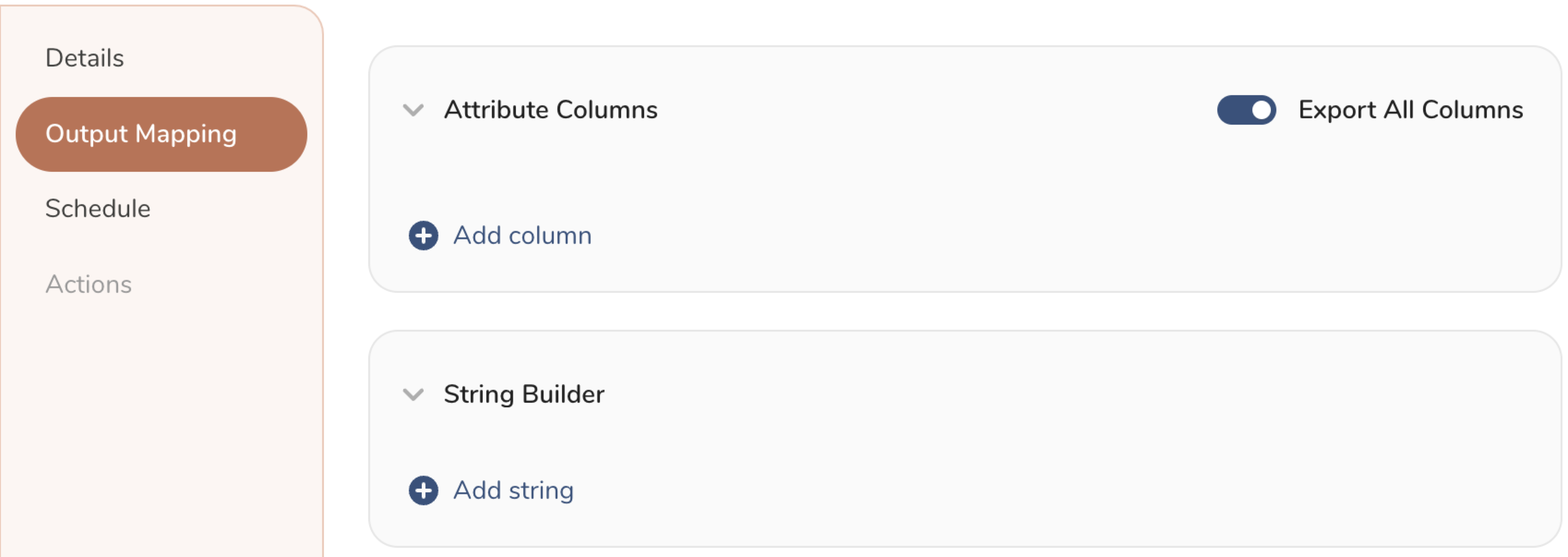
- Attribute Columns
- Select Export All Columns to export all columns without making any changes.
- Select + Add Columns to add specific columns for the export. The Output Column Name pre-populates with the same Source column name. You can update the Output Column Name. Continue to select + Add Columnsto add new columns for your activation output.
- String Builder
- + Add string to create strings for export. Select from the following values:
- String: Choose any value; use text to create a custom value.
- Timestamp: The date and time of the export.
- Segment Id: The segment ID number.
- Segment Name: The segment name.
- Audience Id: The parent segment number.
- + Add string to create strings for export. Select from the following values:
- Set a Schedule.
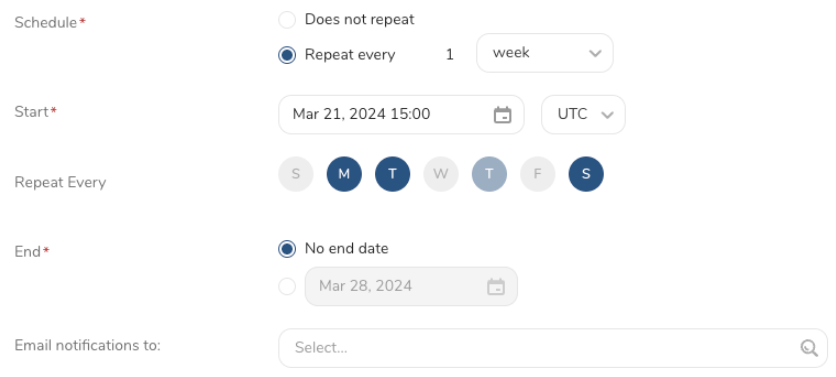
- Select the values to define your schedule and optionally include email notifications.
- Select Create.
If you need to create an activation for a batch journey, review Creating a Batch Journey Activation.
You can also use CLI (Toolbelt) to export results to BigQuery.
You need to specify the information for export to your Snapchat server using the *--result option of*the td query command. For more information about the *td query*command, refer to this article.
The format of the option is JSON, and the general structure is as follows.
APPEND mode:
type: 'bigquery_v2'
json_keyfile: |
{
"type": "service_account",
"private_key_id": "xxx",
"private_key": "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----xxx-----END PRIVATE KEY-----\n",
"client_email": "account@xxx.iam.gserviceaccount.com",
"client_id": "xxx",
"auth_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth",
"token_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/token",
"auth_provider_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/certs",
"client_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/robot/v1/metadata/x509/account%40xxx.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
}
mode: APPEND
project: gcp project id
dataset: bigquery dataset
table: bigquery table
location: gcp location
auto_create_table: true
add_missing_columns: true
schema_file: |
[
{"name": "c1", "type": "STRING", "mode": "NULLABLE"},
{"name": "c2", "type": "INTEGER", "mode": "REQUIRED"}
]
skip_invalid_records: trueREPLACE mode:
type: 'bigquery_v2'
json_keyfile: |
{
"type": "service_account",
"private_key_id": "xxx",
"private_key": "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----xxx-----END PRIVATE KEY-----\n",
"client_email": "account@xxx.iam.gserviceaccount.com",
"client_id": "xxx",
"auth_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth",
"token_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/token",
"auth_provider_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/certs",
"client_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/robot/v1/metadata/x509/account%40xxx.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
}
mode: REPLACE
project: gcp project id
dataset: bigquery dataset
table: bigquery table
location: gcp location
auto_create_table: true
add_missing_columns: true
schema_file: |
[
{"name": "c1", "type": "STRING", "mode": "NULLABLE"},
{"name": "c2", "type": "INTEGER", "mode": "REQUIRED"}
]
skip_invalid_records: trueREPLACE_BACKUP mode:
type: 'bigquery_v2'
json_keyfile: |
{
"type": "service_account",
"private_key_id": "xxx",
"private_key": "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----xxx-----END PRIVATE KEY-----\n",
"client_email": "account@xxx.iam.gserviceaccount.com",
"client_id": "xxx",
"auth_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth",
"token_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/token",
"auth_provider_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/certs",
"client_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/robot/v1/metadata/x509/account%40xxx.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
}
mode: REPLACE_BACKUP
backup_mode: TABLE_RENAME
project: gcp project id
dataset: bigquery dataset
table: bigquery table
location: gcp location
auto_create_table: true
add_missing_columns: true
schema_file: |
[
{"name": "c1", "type": "STRING", "mode": "NULLABLE"},
{"name": "c2", "type": "INTEGER", "mode": "REQUIRED"}
]
skip_invalid_records: trueTRUNCATE mode:
type: 'bigquery_v2'
json_keyfile: |
{
"type": "service_account",
"private_key_id": "xxx",
"private_key": "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----xxx-----END PRIVATE KEY-----\n",
"client_email": "account@xxx.iam.gserviceaccount.com",
"client_id": "xxx",
"auth_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth",
"token_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/token",
"auth_provider_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/certs",
"client_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/robot/v1/metadata/x509/account%40xxx.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
}
mode: TRUNCATE
project: gcp project id
dataset: bigquery dataset
table: bigquery table
location: gcp location
auto_create_table: true
add_missing_columns: true
schema_file: |
[
{"name": "c1", "type": "STRING", "mode": "NULLABLE"},
{"name": "c2", "type": "INTEGER", "mode": "REQUIRED"}
]
skip_invalid_records: true| Name | Description | Value | Default Value | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| type | connector type | bigquery_v2 | N/A | Yes |
| json_keyfile | GCP json keyfile | Format as json | N/A | Yes |
| mode | Export mode | Supported modes: - APPEND - REPLACE - REPLACE_BACKUP - TRUNCATE | APPEND | Yes |
| backup_mode | Backup table in BigQuery | Supported values: - TABLE_RENAME - TABLE_SNAPSHOT | TABLE_RENAME | Yes if mode is REAPLCE_BACKUP |
| project | GCP project id | N/A | N/A | Yes |
| dataset | BigQuery dataset | N/A | N/A | Yes |
| table | BigQuery table | N/A | N/A | Yes |
| location | BigQuery data location | N/A | N/A | No |
| auto_create_table | Allow to auto create table in BigQuery when it does not exist. This option does not support for TRUNCATE mode | true/false | false | No |
| add_missing_columns | Allow addition columns that does not existed in BigQuery table. | true/false | false | No |
| skip_invalid_records | The flag to continue or stop the job when handling the invalid record. | true/false | true | No |
APPEND mode
$ td query --result '{"type": "bigquery_v2", "td_authentication_id": 123456, "mode": "APPEND", "project": "gcp_project_id", "dataset": "bg_dataset", "table": "bg_table", "location": "US", "auto_create_table": true, "add_missing_columns": true, "schema_file": "[{\"name\": \"c1\", \"type\": \"INTEGER\"}, {\"name\": \"c2\", \"type\": \"STRING\"}]", "skip_invalid_records":true}' -d sample_datasets "select ........ from ........" -T prestoREPLACE mode
$ td query --result '{"type": "bigquery_v2", "td_authentication_id": 123456, "mode": "REPLACE", "project": "gcp_project_id", "dataset": "bg_dataset", "table": "bg_table", "location": "US", "auto_create_table": true, "add_missing_columns": true, "schema_file": "[{\"name\": \"c1\", \"type\": \"INTEGER\"}, {\"name\": \"c2\", \"type\": \"STRING\"}]", "skip_invalid_records":true}' -d sample_datasets "select ........ from ........" -T prestoREPLACE_BACKUP mode
$ td query --result '{"type": "bigquery_v2", "td_authentication_id": 123456, "mode": "REPLACE_BACKUP", "backup_mode": "TABLE_RENAME", "project": "gcp_project_id", "dataset": "bg_dataset", "table": "bg_table", "location": "US", "auto_create_table": true, "add_missing_columns": true, "schema_file": "[{\"name\": \"c1\", \"type\": \"INTEGER\"}, {\"name\": \"c2\", \"type\": \"STRING\"}]", "skip_invalid_records":true}' -d sample_datasets "select ........ from ........" -T prestoTRUNCATE mode
$ td query --result '{"type": "bigquery_v2", "td_authentication_id": 123456, "mode": "TRUNCATE", "project": "gcp_project_id", "dataset": "bg_dataset", "table": "bg_table", "location": "US", "auto_create_table": true, "add_missing_columns": true, "schema_file": "[{\"name\": \"c1\", \"type\": \"INTEGER\"}, {\"name\": \"c2\", \"type\": \"STRING\"}]", "skip_invalid_records":true}' -d sample_datasets "select ........ from ........" -T presto- The Result Export can be scheduled to periodically upload data to a target destination.
- All import and export integrations can be added to a TD Workflow. The td data operator can export a query result to a specified integration. For more information, see Reference for Treasure Data Operators.