Learn more about Installing td-agent on AWS Linux.
You can write job results to your existing Amazon Redshift cluster. For sample workflows on Amazon Redshift for Export, view Treasure Boxes.
- Basic knowledge of Treasure Data, including the TD Toolbelt
- An Amazon Redshift cluster setup and running – either a single or multi-node cluster
- At least ‘Query only’ privileges to the Treasure Data table to be queried
- When exporting results to Redshift, Redshift tries to convert the column type if the destination table already exists. If a column becomes NULL during conversion, and all records are rejected if the column on Redshift is a NOT NULL field. This may be the case even when the job for exporting results to Redshift was successful, but your Redshift doesn’t get any data.
- This connector does not support timestamp/date type data. You need to convert that type of data to string column or Unix timestamp.
Result Output to Redshift can export data to several regions. The following are the supported regions:
- us-east-1 (US Standard)
- us-west-2 (Oregon)
- eu-west-1 (Ireland)
- ap-northeast-1 (Tokyo)
- us-west-1 (N. California)
- ap-southeast-1 (Singapore)
- ap-southeast-2 (Sydney)
- sa-east-1 (São Paulo)
The following regions are not supported:
- us-east-2 (Ohio)
- ap-south-1 (Mumbai)
- ap-northeast-2 (Seoul)
- ca-central-1 (Central)
- eu-central-1 (Frankfurt)
- eu-west-2 (London)
If you have other regions that you want to support, contact Treasure Data support.
A front-end application streams data to be collected in Treasure Data via Treasure Agent (td-agent). Treasure Data periodically runs jobs on the data, then writes the job results to your Redshift cluster.
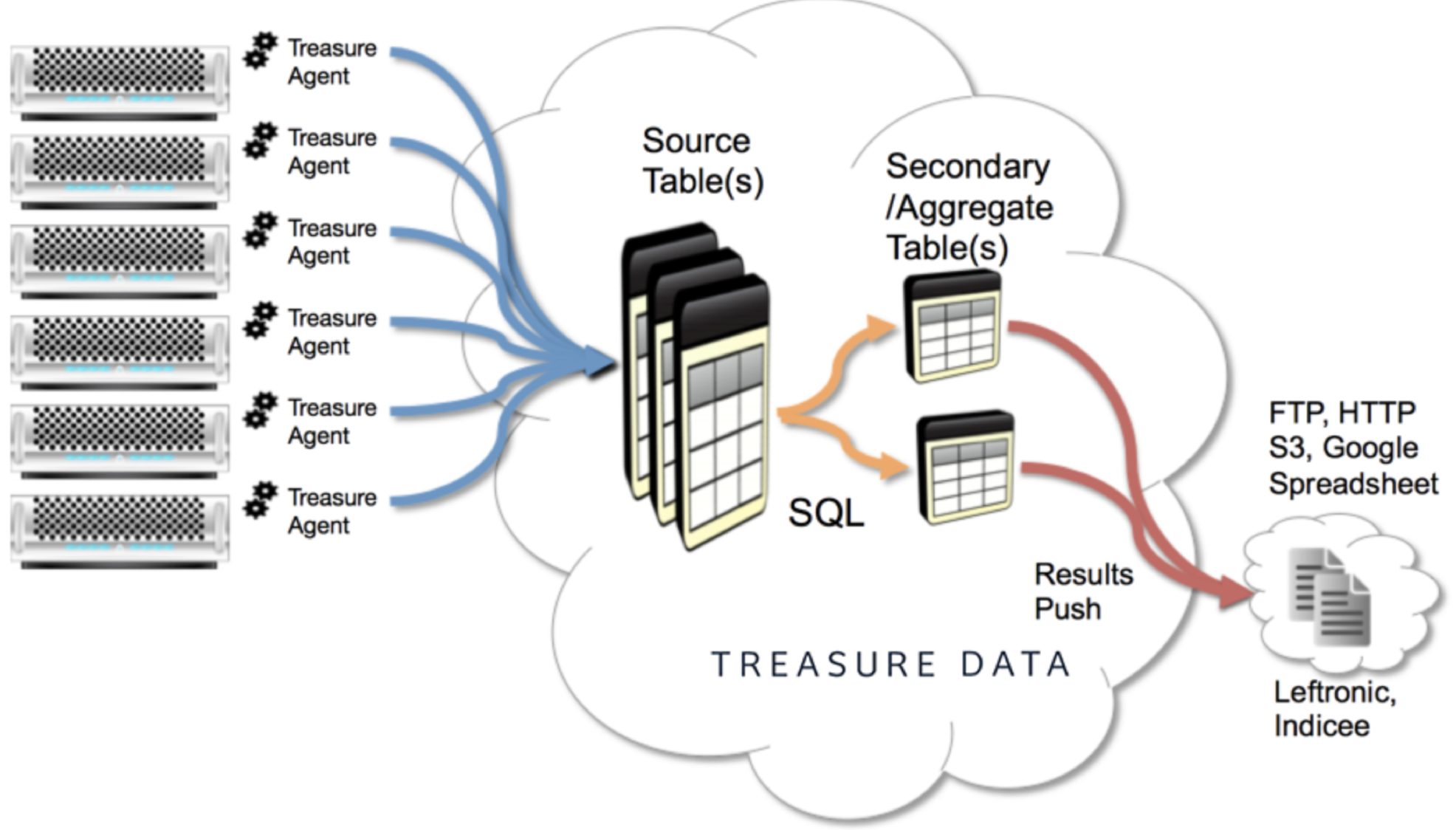
The image shows a fairly common architecture that enables data analysts, well versed in using Redshift, to focus on queries and visualizations rather than how to get the data uploaded.
If your security policy requires IP whitelisting, you must add Treasure Data's IP addresses to your allowlist to ensure a successful connection.
Please find the complete list of static IP addresses, organized by region, at the following document
Amazon Redshift can be configured in single-node mode or multi-node/cluster mode. The multi-node configuration provides more query computation power by means of parallelization of the query execution on the available nodes.
In Treasure Data, you must create and configure the data connection prior to running your query. As part of the data connection, you provide authentication to access the integration.
Open TD Console.
Navigate to Integrations Hub > Catalog.
Click the search icon on the far-right of the Catalog screen, and enter Amazon Redshift.
Hover over the Amazon Redshift connector and select Create Authentication.

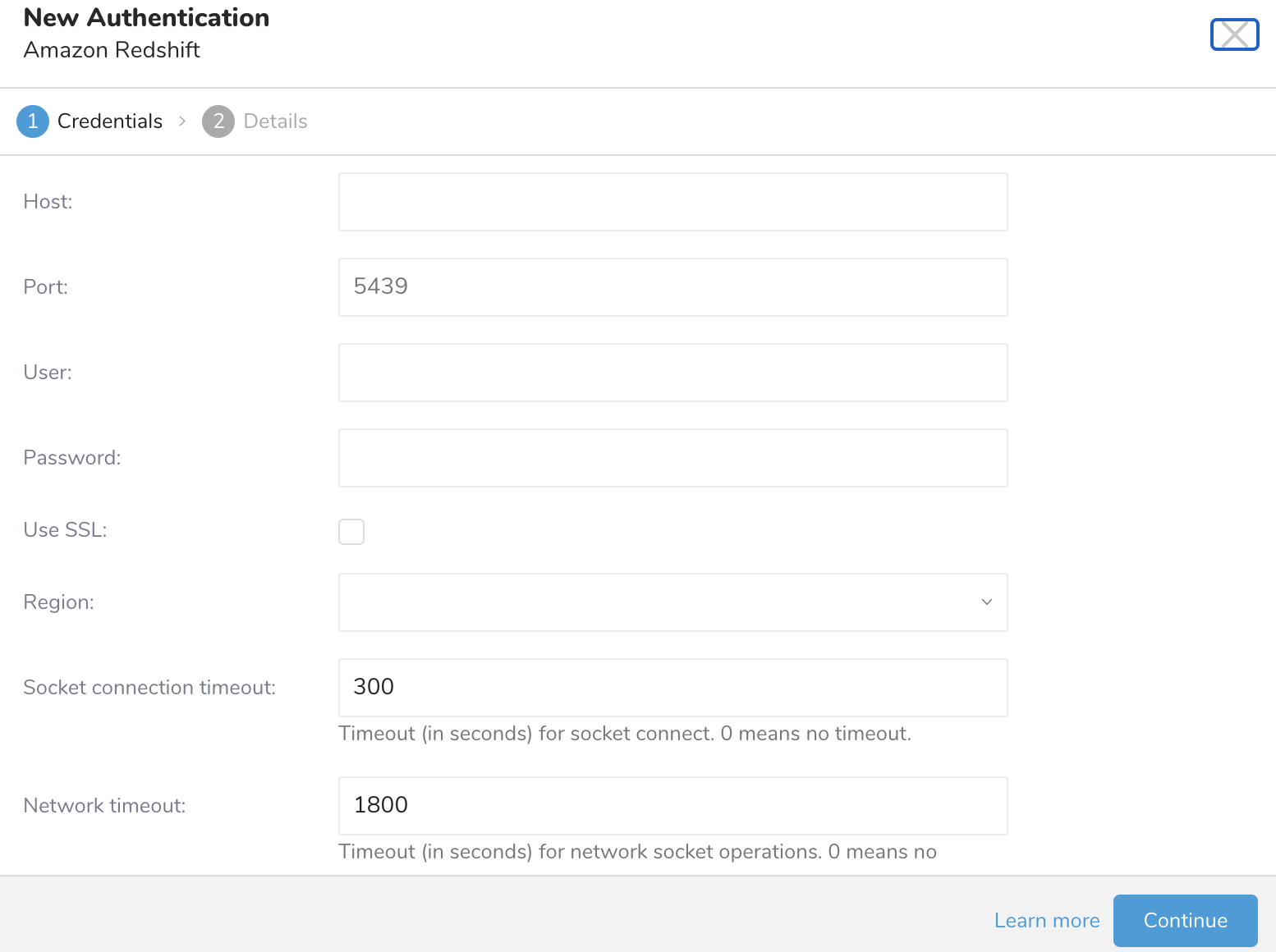
Type the credentials to authenticate.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Host | The host information of the source database, such as an IP address. can be retrieved from the Redshift configuration page. Typically, the format is: name.<instance_id>.region.redshift.amazonaws.com. The name is the one provided for the cluster, the instance id is auto-generated by Amazon Redshift upon creation of the cluster, the region is the Amazon availability zone of choice. If you are using an IP address instead of hostname, you must set region option explicitly. |
| Port | The connection port on the source instance. The PostgreSQL default is 5432. The port number through which the Redshift server is accessible. ":" is optional and assumed to be 5439 by default. It may vary for multi-node cluster configurations. The actual value can be retrieved from the Redshift cluster detail page. |
| User | Username to connect to the source database. The credentials to the Amazon Redshift instance. These credentials are specified when first creating the Redshift cluster and they are different from the S3 public/private access keys. |
| Password | The password to connect to the source database. |
| Use SSL | Check this box to connect using SSL |
| JDBC Connection options | Any special JDBC connections required by the source database (optional). |
| Region | The AWS regions in which your Redshift instance is hosted. Specify the region where your Redshift instance is located. This option is required if your hostname does not contain the region name. redshift://user:password@host/database/table?region=us-east-1 |
| Socket connection timeout | Timeout (in seconds) for socket connection (default is 300). |
| Network timeout | Timeout (in seconds) for network socket operations. 0 means no timeout. |
| Rows per batch | Number of rows to fetch one time. |
| Options | Options that you want to give to the JDBC driver. See Installing Redshift JDBC Driver. For example, you can use these parameterand value fields to define various URL options such as LogLevel or LogPath. jdbc:redshift://company.us-west1.redshift.amazonaws.com:9000/Default;LogLevel=3;LogPath =C: empResult output to Redshift supports various options that can be specified as optional URL parameters. The options are compatible with each other and can be combined. Where applicable, the default behavior is indicated. SSL Option ssl option determines whether to use SSL or not for connecting to Redshift. ssl=true Use SSL from Treasure Data to Redshift connection. redshift://user:password@host/database/table?ssl=true ssl=false (default) Do not use SSL from Treasure Data to Redshift. redshift://user:password@host/database/table?ssl=false |
Select Continue after entering the required connection details.
Name the connection so you can find it later should you need to modify any of the connection details.
Optionally, select Share with others, if you would like to share this connection with other users in your organization.
Select Done.
- Complete the instructions in Creating a Destination Integration.
- Navigate to Data Workbench > Queries.
- Select a query for which you would like to export data.
- Run the query to validate the result set.
- Select Export Results.
- Select an existing integration authentication.

- Define any additional Export Results details. In your export integration content review the integration parameters. For example, your Export Results screen might be different, or you might not have additional details to fill out:
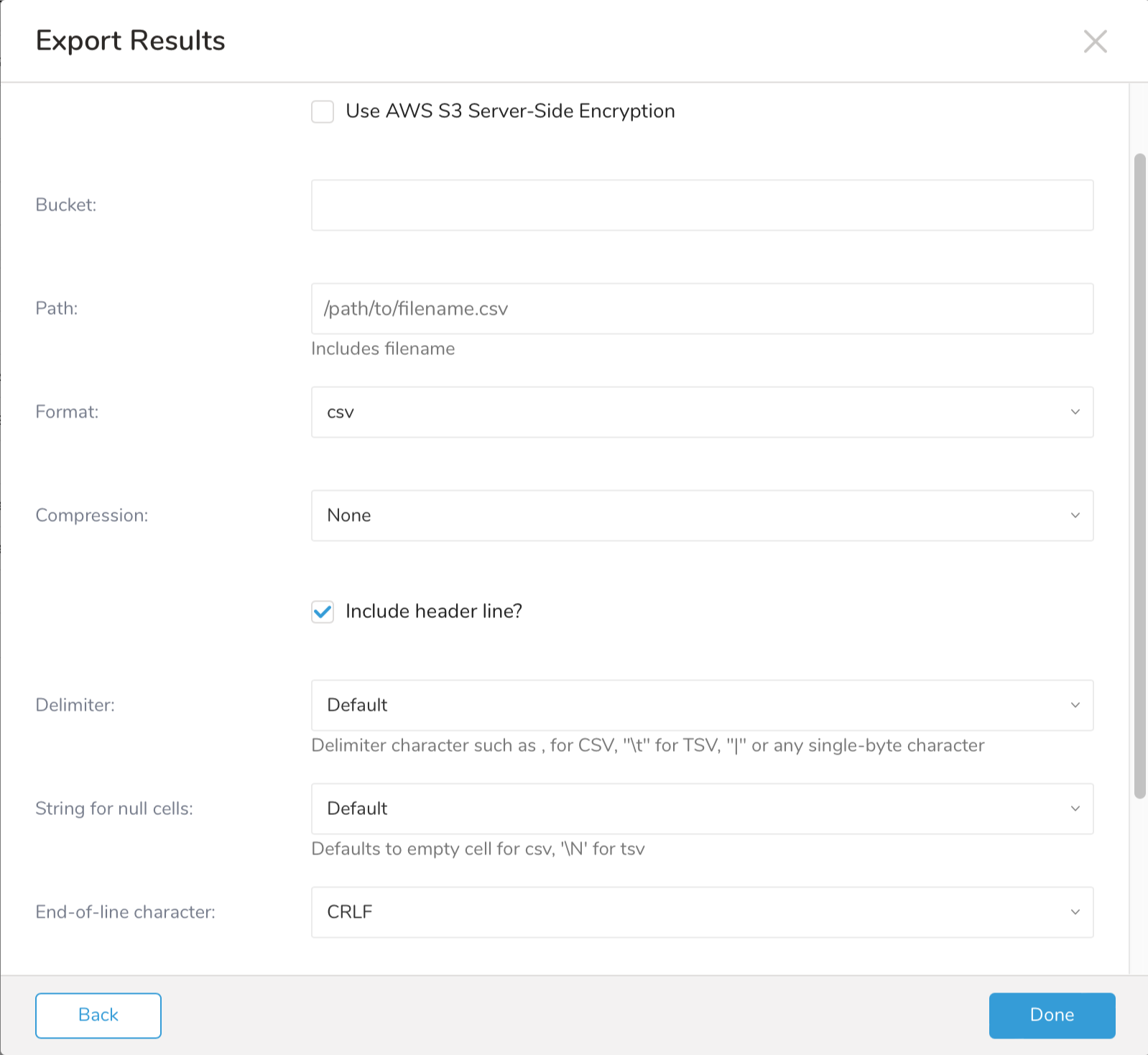
- Select Done.
- Run your query.
- Validate that your data moved to the destination you specified.
| Parameter | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|
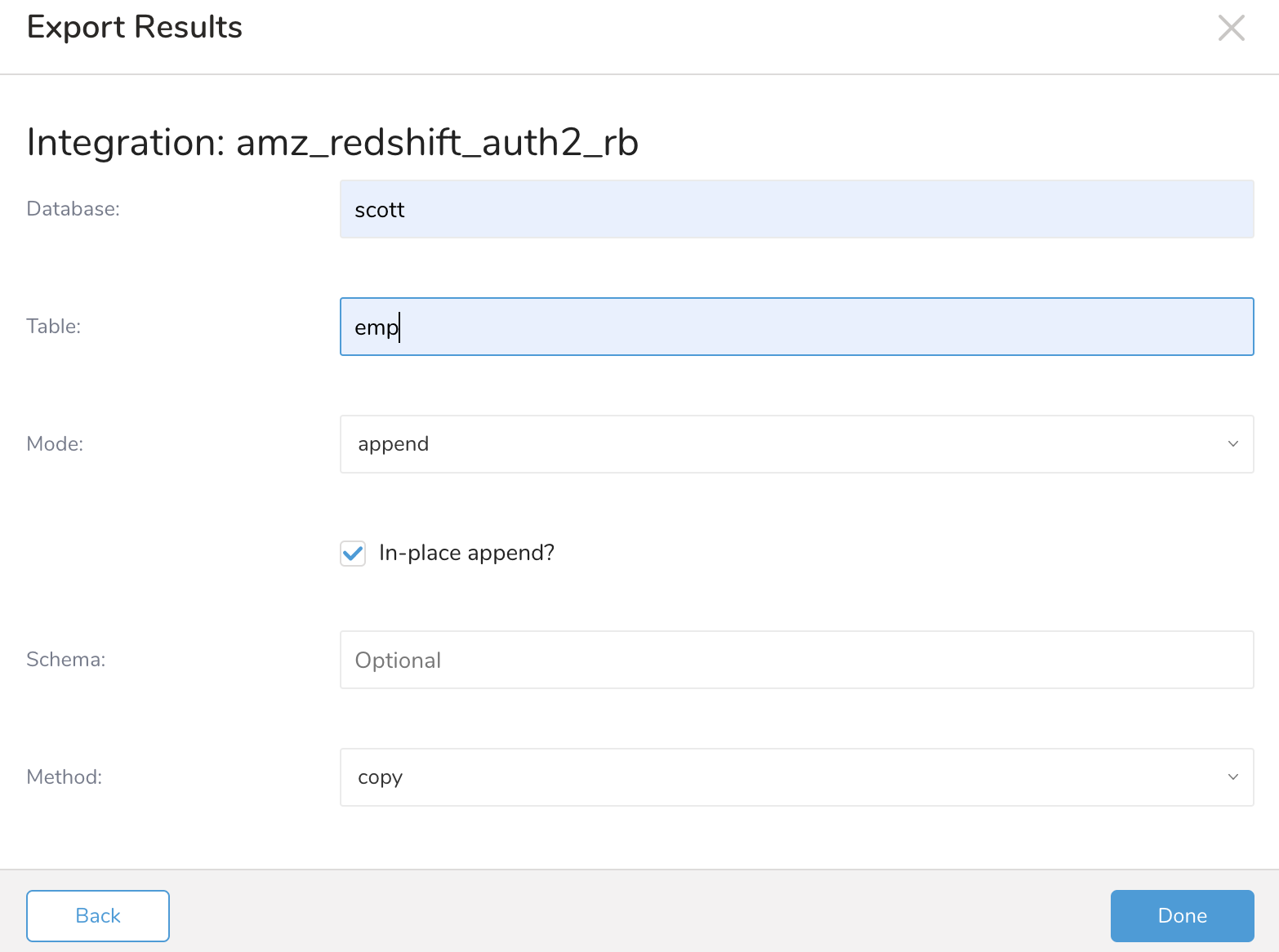
| Database | Name of the database to export the data to. The name of the database specified at the creation of the Redshift cluster. It can be retrieved from the Redshift cluster detail page. | |
| Table | Name of the table within the database to export the data to. The name of a table within the database. It may not exist when the query output is executed. If the table does not exist, a table with the specified name is created. | |
| Mode | Controls the various ways of modifying the database data.
| |
| In-place append | select clear | Select to modify the existing data rather than copying it. This can be a big performance gain. When mode=append, the inplace minor option can control the atomicity of the action. When it is true, no temporary table is used and the operation is not guaranteed to be atomic. When the option is false, a temporary table is used. The default value is true. |
| Schema | Controls the schema the target table is located. If not specified, a default schema is used. The default schema depends on the user's "search_path" setting but it is usually "public". | |
| Method | copy bulk copy | copy (default) This option allows you to use the COPY Redshift SQL command to export data in different flows. bulk_copy This option uses the copy command but with a different flow. You can use SSL from Treasure Data to instantiate the Redshift connection. For example: redshift://user:password@host/database/table?method=bulk_copy. |
| Serial Copy | select clear | The serial_copy option determines whether to upload all the files in order one by one, to avoid some deadlocks that could happen when uploading files parallel. serial_copy=true serial_copy=false(default) |
select * from an_redshift_data limit 800000000You can also send segment data to the target platform by creating an activation in the Audience Studio.
- Navigate to Audience Studio.
- Select a parent segment.
- Open the target segment, right-mouse click, and then select Create Activation.
- In the Details panel, enter an Activation name and configure the activation according to the previous section on Configuration Parameters.
- Customize the activation output in the Output Mapping panel.
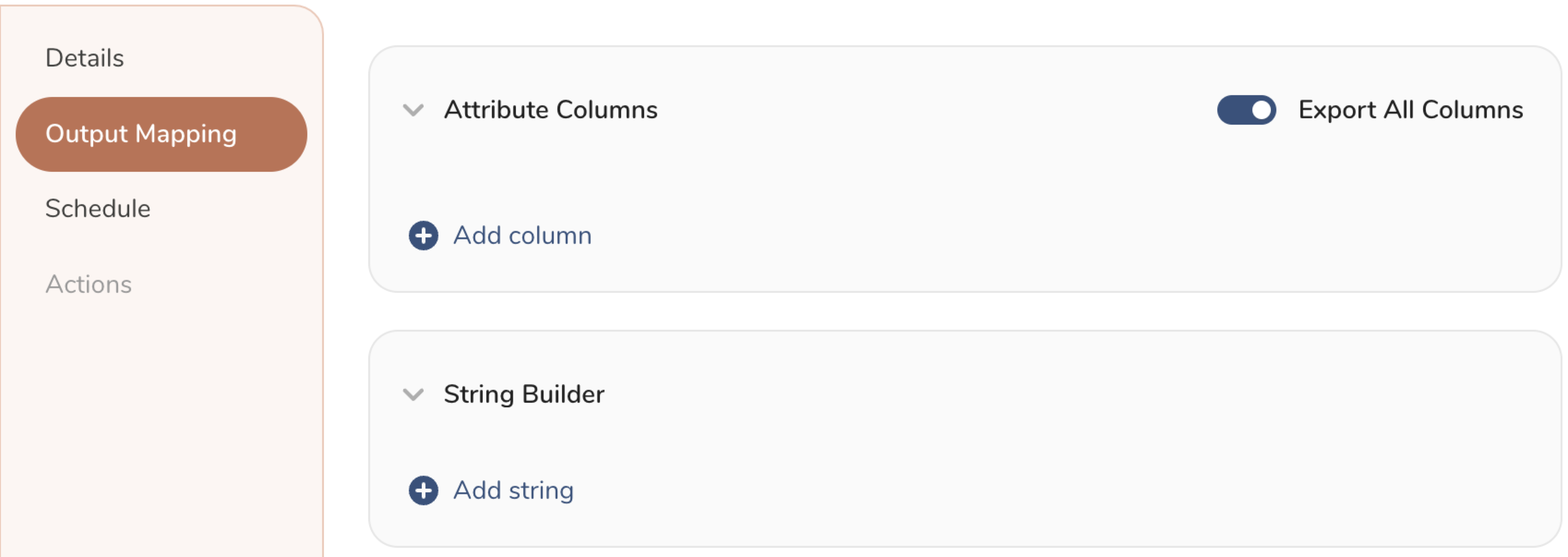
- Attribute Columns
- Select Export All Columns to export all columns without making any changes.
- Select + Add Columns to add specific columns for the export. The Output Column Name pre-populates with the same Source column name. You can update the Output Column Name. Continue to select + Add Columnsto add new columns for your activation output.
- String Builder
- + Add string to create strings for export. Select from the following values:
- String: Choose any value; use text to create a custom value.
- Timestamp: The date and time of the export.
- Segment Id: The segment ID number.
- Segment Name: The segment name.
- Audience Id: The parent segment number.
- + Add string to create strings for export. Select from the following values:
- Set a Schedule.
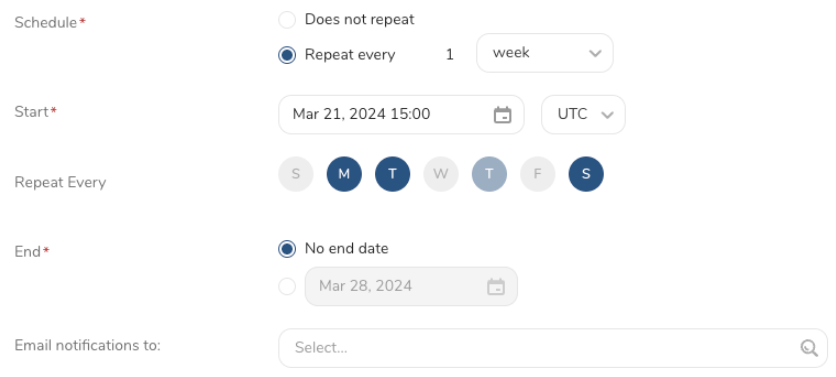
- Select the values to define your schedule and optionally include email notifications.
- Select Create.
If you need to create an activation for a batch journey, review Creating a Batch Journey Activation.
If you use the TD Toolbelt to run the query that returns the data that you want to have exported to Amazon Redshift:
td query -w -d testdb \
--result 'redshift://username:password@host.redshift.amazonaws.com/database/table?mode=replace' \
"SELECT code, COUNT(1) FROM www_access GROUP BY code"td sched:create hourly_count_example "0 * * * *" -d testdb \
--result 'redshift://username:password@host.redshift.amazonaws.com/database/table?mode=replace' \
"SELECT COUNT(*) FROM www_access"Result Output to Redshift tries to convert column type if the destination table already exists. If the conversion fails, the column becomes NULL and all records are rejected if the column on Redshift is NOT NULL field.